Ann Dermatol.
2011 May;23(2):239-241. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.2.239.
Interferon-alpha Induced Sarcoidosis with Cutaneous Involvement along the Lines of Venous Drainage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ostksy@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2156673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.2.239
Abstract
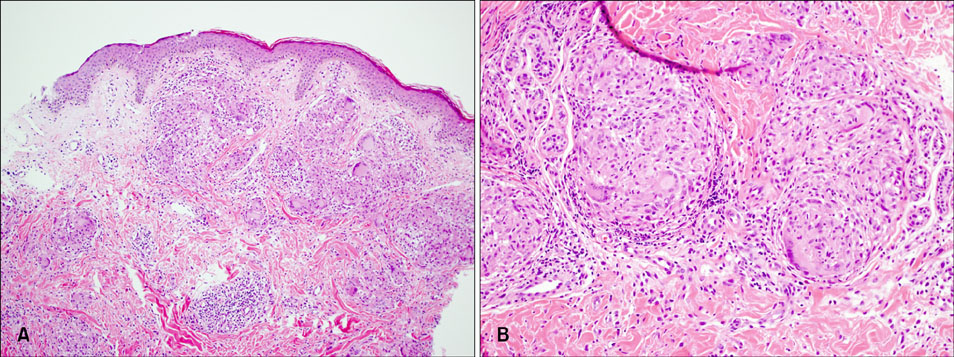
- Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease of an unknown origin and it is characterized by the presence of noncaseating epitheloid cell granulomas in multiple organs. Herein we report on a case of cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis that was associated with interferon alpha treatment for hepatitis C. A 39-year-old man, a former intravenous drug user, presented with several erythematous papules on both antecubital areas. The histopathologic finding of a skin biopsy showed noncaseating granuloma. The mediastinal and axillary lymph nodes were enlarged on chest X-ray and computed tomography. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis that was associated with interferon treatment in the Korean dermatologic literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA, Teirstein AS. Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:2153–2165.
Article2. Statement on sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 160:736–755.3. Hurst EA, Mauro T. Sarcoidosis associated with pegylated interferon alfa and ribavirin treatment for chronic hepatitis C: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2005. 141:865–868.4. Faurie P, Broussolle C, Zoulim F, Trepo C, Sève P. Sarcoidosis and hepatitis C: clinical description of 11 cases. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 22:967–972.
Article5. Leclerc S, Myers RP, Moussalli J, Herson S, Poynard T, Benveniste O. Sarcoidosis and interferon therapy: report of five cases and review of the literature. Eur J Intern Med. 2003. 14:237–243.
Article6. Akahoshi M, Ishihara M, Remus N, Uno K, Miyake K, Hirota T, et al. Association between IFNA genotype and the risk of sarcoidosis. Hum Genet. 2004. 114:503–509.
Article7. Ramos-Casals M, Mañá J, Nardi N, Brito-Zerón P, Xaubet A, Sánchez-Tapias JM, et al. Sarcoidosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: analysis of 68 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005. 84:69–80.8. Doyle MK, Berggren R, Magnus JH. Interferon-induced sarcoidosis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006. 12:241–248.
Article9. Goldberg HJ, Fiedler D, Webb A, Jagirdar J, Hoyumpa AM, Peters J. Sarcoidosis after treatment with interferon-alpha: a case series and review of the literature. Respir Med. 2006. 100:2063–2068.
Article10. Shuja F, Kavoussi SC, Mir MR, Jogi RP, Rosen T. Interferon induced sarcoidosis with cutaneous involvement along lines of venous drainage in a former intravenous drug user. Dermatol Online J. 2009. 15:4.
Article11. Zampino MR, Corazza M, Borghi A, Marzola A, Virgili A. HLA typing in an IFN-alpha-induced scar sarcoidosis: possible pathogenetic and clinical implications. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009. 89:661–662.
Article12. Ramos-Casals M, Font J. Extrahepatic manifestations in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005. 17:447–455.
Article13. Fantini F, Padalino C, Gualdi G, Monari P, Giannetti A. Cutaneous lesions as initial signs of interferon alpha-induced sarcoidosis: report of three new cases and review of the literature. Dermatol Ther. 2009. 22:Suppl. 1. S1–S7.14. Pietinalho A, Ohmichi M, Hirasawa M, Hiraga Y, Lofroos AB, Selroos O. Familial sarcoidosis in Finland and Hokkaido, Japan--a comparative study. Respir Med. 1999. 93:408–412.
Article15. Rybicki BA, Major M, Popovich J Jr, Maliarik MJ, Iannuzzi MC. Racial differences in sarcoidosis incidence: a 5-year study in a health maintenance organization. Am J Epidemiol. 1997. 145:234–241.
Article16. Martinetti M, Luisetti M, Cuccia M. HLA and sarcoidosis: new pathogenetic insights. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2002. 19:83–95.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Associated with Pegylated Interferon Alpha-2a and Ribavirin Therapy
- Cutaneous Ulceration after Injection of Interferon Alpha in a Melanoma Patient
- A Case of Capecitabine-Induced Sarcoidosis
- Exacerbation of Sarcoidosis Following Interferon-alpha Therapy for Chronic Active Hepatitis C
- A Case of Coexistent Cutaneous Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Tuberculous Pleurisy