Korean J Neurotrauma.
2013 Oct;9(2):150-153. 10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.150.
Traumatic Delayed Subdural Hematoma Accompanied Acute Cerebral Infarction during Anticoagulant Therapy in an Old Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kyung-Hee University Hospital, Kyung-Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. coolguy_ho@naver.com
- KMID: 2156119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.150
Abstract
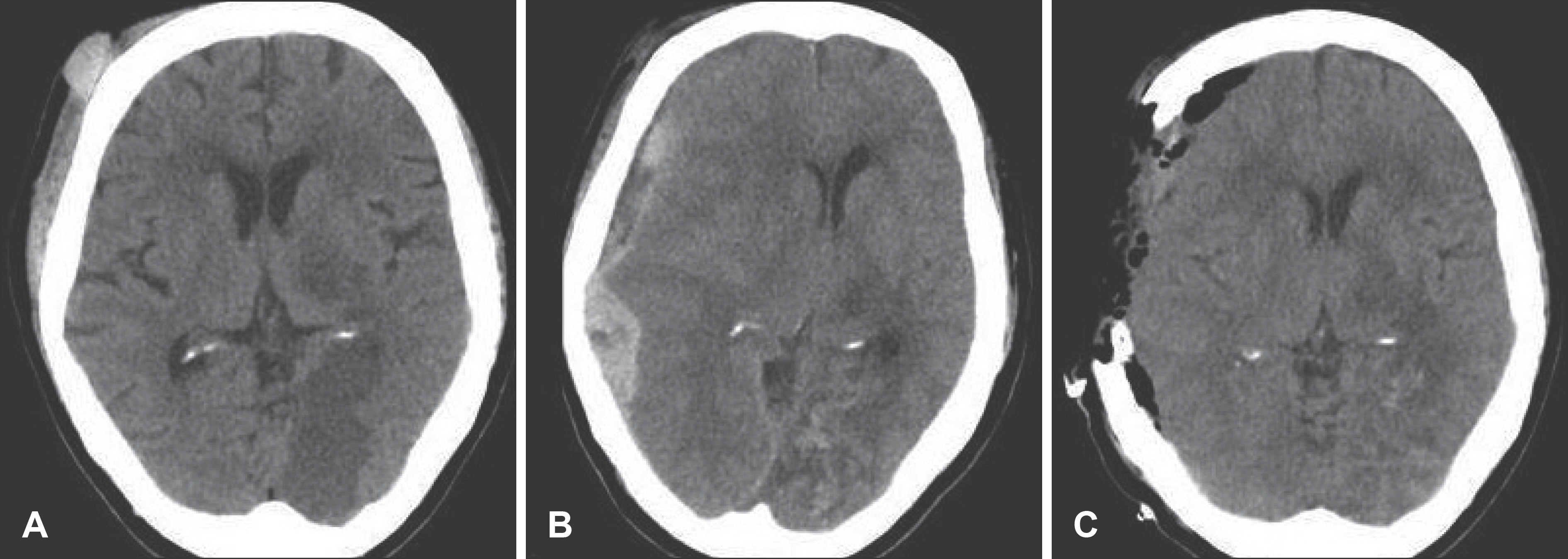
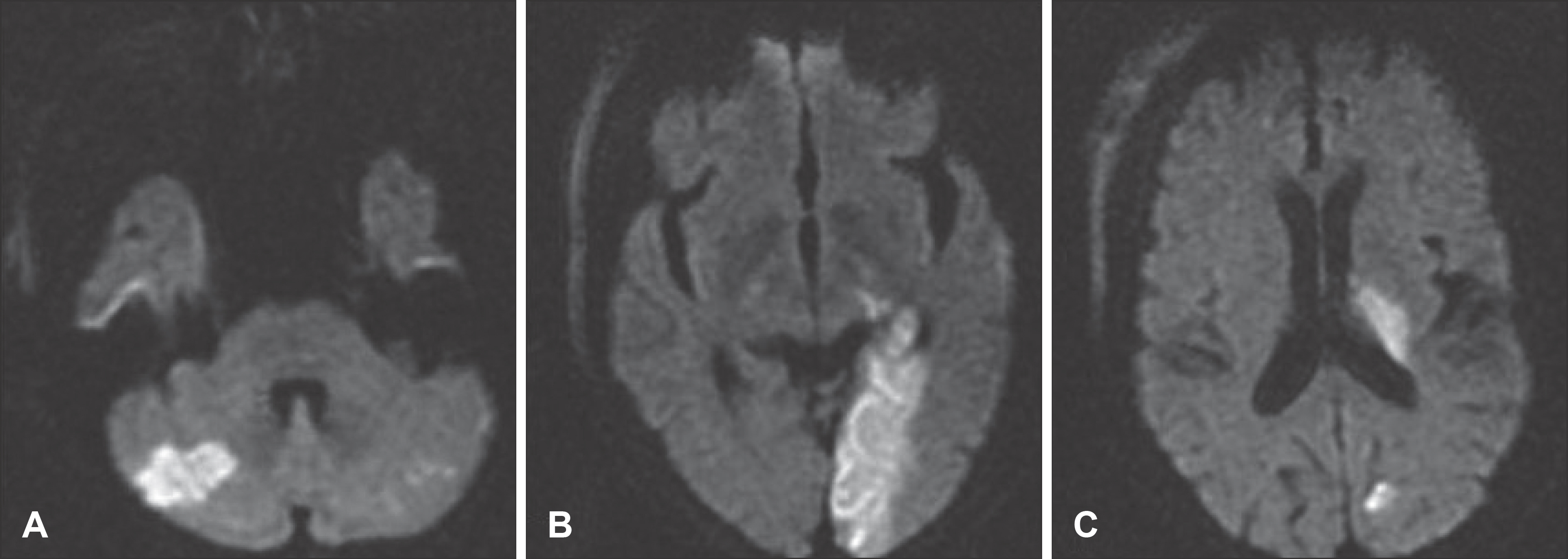
- Oral anticoagulant therapy is generally being used in patient with a high thromboembolic risk such as cerebrovascular or cardiovascular accident, in spite of increased bleeding tendencies and most of them are old-age patients. A stroke frequently leads to a fall, which in turn causes a minor trauma, and it is often reported that anticoagulant therapy for treatment of stroke may aggravate traumatic brain injury. The authors report a case that required surgical treatments for subacute subdural hematoma which was found during antiplatelets and anticoagulant therapy for acute ischemic stroke. The hematoma had not been found at the time of head injury accompanied by a cerebral infarction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Baraniskin A, Steffens C, Harders A, Schmiegel W, Schroers R, Spangenberg P. Impact of Pre-Hospital Antithrombotic Medication on the Outcome of Chronic and Acute Subdural Hematoma. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg, 2013 Feb 20 [Epub ahead of print].2. Cannegieter SC, Rosendaal FR, Briët E. Thromboembolic and bleeding complications in patients with mechanical heart valve prostheses. Circulation. 89:635–641. 1994.
Article3. Crawley F, Bevan D, Wren D. Management of intracranial bleeding associated with anticoagulation: balancing the risk of further bleeding against thromboembolism from prosthetic heart valves. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 69:396–398. 2000.
Article4. Ezekowitz MD, Levine JA. Preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA. 281:1830–1835. 1999.
Article5. Ferrera PC, Bartfield JM. Outcomes of anticoagulated trauma patients. Am J Emerg Med. 17:154–156. 1999.
Article6. Forster MT, Mathé AK, Senft C, Scharrer I, Seifert V, Gerlach R. The influence of preoperative anticoagulation on outcome and quality of life after surgical treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 17:975–979. 2010.
Article7. Franko J, Kish KJ, O'Connell BG, Subramanian S, Yuschak JV. Advanced age and preinjury warfarin anticoagulation increase the risk of mortality after head trauma. J Trauma. 61:107–110. 2006.
Article8. Furness N, Da Costa TM, Bishay M. Anterior hip dislocation in conjunction with a stroke: a diagnosis not to miss. BMJ Case Rep 2013. 2013.
Article9. Gonugunta V, Buxton N. Warfarin and chronic subdural haematomas. Br J Neurosurg. 15:514–517. 2001.
Article10. Jeffree RL, Gordon DH, Sivasubramaniam R, Chapman A. Warfarin related intracranial haemorrhage: a case-controlled study of anticoagulation monitoring prior to spontaneous subdural or intracerebral haemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci. 16:882–885. 2009.
Article11. Kawamata T, Takeshita M, Kubo O, Izawa M, Kagawa M, Takakura K. Management of intracranial hemorrhage associated with anticoagulant therapy. Surg Neurol. 44:438–442. ; discussion 443,. 1995.
Article12. Majeed A, Kim YK, Roberts RS, Holmström M, Schulman S. Optimal timing of resumption of warfarin after intracranial hemorrhage. Stroke. 41:2860–2866. 2010.
Article13. Mattle H, Kohler S, Huber P, Rohner M, Steinsiepe KF. Anticoagulation-related intracranial extracerebral haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 52:829–837. 1989.
Article14. Moreland CJ, Kravitz RL, Paterniti DA, Li CS, Lin TC, White RH. Anticoagulation education: do patients understand potential medication-related emergencies? Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 39:22–31. 2013.
Article15. Rust T, Kiemer N, Erasmus A. Chronic subdural haematomas and anticoagulation or antithrombotic therapy. J Clin Neurosci. 13:823–827. 2006.
Article16. Schulman S. Resumption of oral anticoagulation after warfarin-associated intracerebral hemorrhage: no. Stroke. 42:3663–3664. 2011.17. Yeon JY, Kong DS, Hong SC. Safety of early warfarin resumption following burr hole drainage for warfarin-associated subacute or chronic subdural hemorrhage. J Neurotrauma. 29:1334–1341. 2012.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Subdural Hematoma Developed During Anticoagulant or Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Cerebral Infarction
- Intraoperative Development of Contralateral Subdural Hematoma during Evacuation of Acute Subdural Hematoma: Case Report
- Paradoxical Herniation after Decompressive Craniectomy for Acute Subdural Hematoma
- Spinal Subdural Hematoma Associated with Anticoagulant Treatment for Acute Cerebral Infarct: A case report
- Intramural Hematoma of the Intestine during Anticoagulant Therapy in a Patient with Cerebral Infarction