Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
2016 Jan;5(1):75-82. 10.7774/cevr.2016.5.1.75.
In silico analysis of Brucella abortus Omp2b and in vitro expression of SOmp2b
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Molecular Biology, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran. saeidbouzari@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Biotechemistry, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran.
- KMID: 2152700
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2016.5.1.75
Abstract
- PURPOSE
At present, there is no vaccine available for the prevention of human brucellosis. Brucella outer membrane protein 2b (Omp2b) is a 36 kD porin existed in common Brucella pathogens and it is considered as priority antigen for designing a new subunit vaccine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
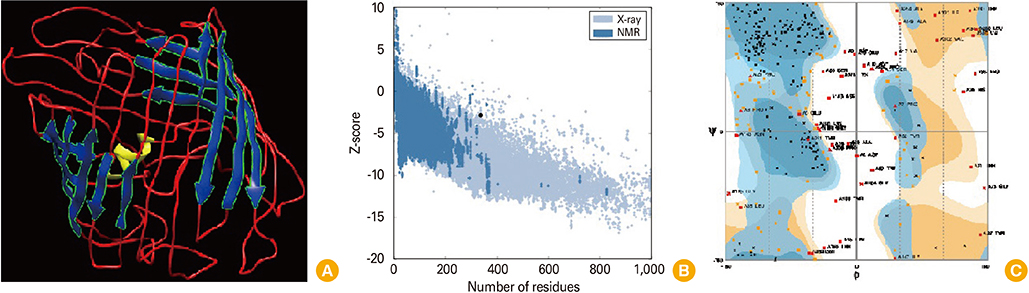
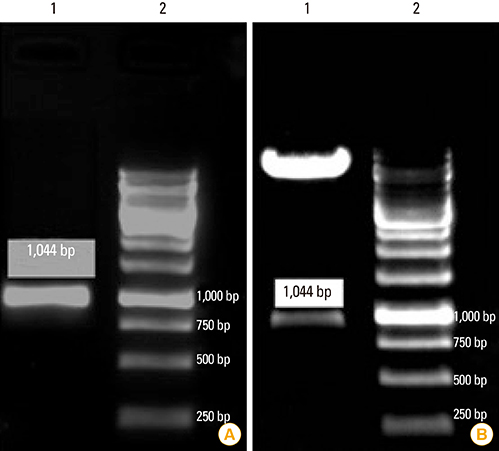
In the current study, we aimed to predict and analyze the secondary and tertiary structures of the Brucella abortus Omp2b protein, and to predict T-cell and B-cell epitopes with the help of bioinformatics tools. Subsequently, cloning and expression of the short form of Omp2b (SOmp2b) was performed using pET28a expression vector and Escherichia coli BL21 host, respectively. The recombinant SOmp2b (rSOmp2b) was purified with Ni-NTA column.
RESULTS
The recombinant protein was successfully expressed in E. coli host and purified under denaturation conditions. The yield of the purified rSOmp2b was estimated by Bradford method and found to be 220 microg/mL of the culture.
CONCLUSION
Our results indicate that Omp2b protein has a potential to induce both B-cell- and T-cell-mediated immune responses and it can be evaluated as a new subunit vaccine candidate against brucellosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jain S, Kumar S, Dohre S, Afley P, Sengupta N, Alam SI. Identification of a protective protein from stationary-phase exoproteome of Brucella abortus. Pathog Dis. 2014; 70:75–83.
Article2. von Bargen K, Gorvel JP, Salcedo SP. Internal affairs: investigating the Brucella intracellular lifestyle. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012; 36:533–562.
Article3. Sung KY, Jung M, Shin MK, et al. Induction of immune responses by two recombinant proteins of brucella abortus, outer membrane proteins 2b porin and Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase, in mouse model. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014; 24:854–861.
Article4. Gwida M, Al Dahouk S, Melzer F, Rosler U, Neubauer H, Tomaso H. Brucellosis: regionally emerging zoonotic disease? Croat Med J. 2010; 51:289–295.5. Lopes LB, Nicolino R, Haddad JP. Brucellosis: risk factors and prevalence: a review. Open Vet Sci J. 2010; 4:72–84.6. Avila-Calderon ED, Lopez-Merino A, Sriranganathan N, Boyle SM, Contreras-Rodriguez A. A history of the development of Brucella vaccines. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:743509.7. Perkins SD, Smither SJ, Atkins HS. Towards a Brucella vaccine for humans. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010; 34:379–394.8. Salhi I, Boigegrain RA, Machold J, Weise C, Cloeckaert A, Rouot B. Characterization of new members of the group 3 outer membrane protein family of Brucella spp. Infect Immun. 2003; 71:4326–4332.
Article9. Cloeckaert A, Vizcaino N, Paquet JY, Bowden RA, Elzer PH. Major outer membrane proteins of Brucella spp.: past, present and future. Vet Microbiol. 2002; 90:229–247.
Article10. Paquet JY, Diaz MA, Genevrois S, et al. Molecular, antigenic, and functional analyses of Omp2b porin size variants of Brucella spp. J Bacteriol. 2001; 183:4839–4847.
Article11. He Y, Xiang Z. Bioinformatics analysis of Brucella vaccines and vaccine targets using VIOLIN. Immunome Res. 2010; 6:Suppl 1. S5.
Article12. Laloux G, Deghelt M, de Barsy M, Letesson JJ, De Bolle X. Identification of the essential Brucella melitensis porin Omp2b as a suppressor of Bax-induced cell death in yeast in a genome-wide screening. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e13274.
Article13. Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992; 8:189–191.
Article14. Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods. 2011; 8:785–786.
Article15. Persson B, Argos P. Topology prediction of membrane proteins. Protein Sci. 1996; 5:363–371.
Article16. Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy Server. In : Walker JM, editor. The proteomics protocols handbook. Totowa: Humana Press Inc.;2005. p. 571–607.17. Sen TZ, Jernigan RL, Garnier J, Kloczkowski A. GOR V server for protein secondary structure prediction. Bioinformatics. 2005; 21:2787–2788.
Article18. Zhang Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008; 9:40.
Article19. Wiederstein M, Sippl MJ. ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:W407–W410.
Article20. Lovell SC, Davis IW, Arendall WB 3rd, et al. Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi,psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins. 2003; 50:437–450.
Article21. Wang P, Sidney J, Kim Y, et al. Peptide binding predictions for HLA DR, DP and DQ molecules. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010; 11:568.
Article22. El-Manzalawy Y, Dobbs D, Honavar V. Predicting linear B-cell epitopes using string kernels. J Mol Recognit. 2008; 21:243–255.
Article23. Ponomarenko J, Bui HH, Li W, et al. ElliPro: a new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008; 9:514.
Article24. Golshani M, Rafati S, Jahanian-Najafabadi A, et al. In silico design, cloning and high level expression of L7/L12-TOmp31 fusion protein of Brucella antigens. Res Pharm Sci. 2015; 10:436–445.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diversity of Humoral Immune Responses to Recombinant Proteins of Brucella abortus Among Residents in Cheju Province
- Different invasion efficiencies of Brucella abortus wild-type and mutantsin RAW 264.7 and THP-1 phagocytic cells and HeLa non-phagocytic cells
- Successful Medical Treatment of Prosthetic Mitral Valve Endocarditis Caused by Brucella abortus
- Analysis of protein expression in Brucella abortus mutants with different growth rates by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and LC-MS/MS peptide analysis
- Identification of Brucella abortus using the sequencing of omp gene