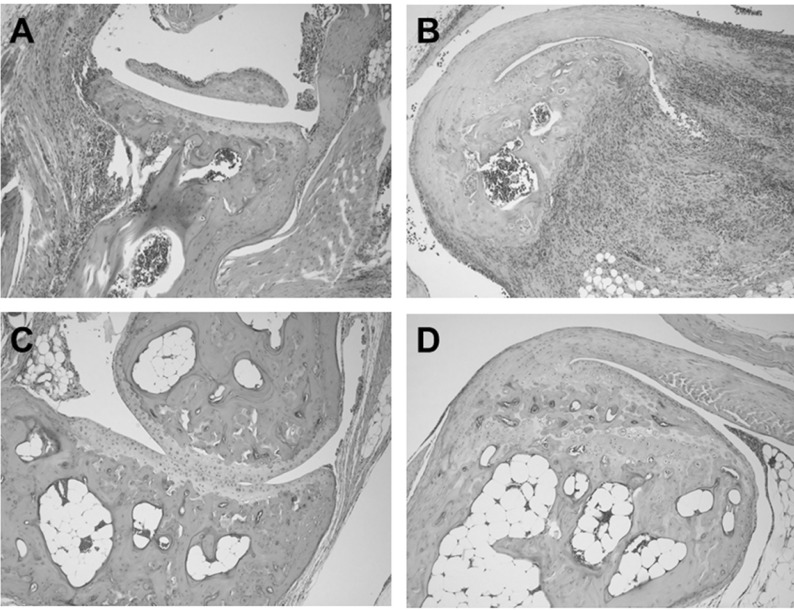
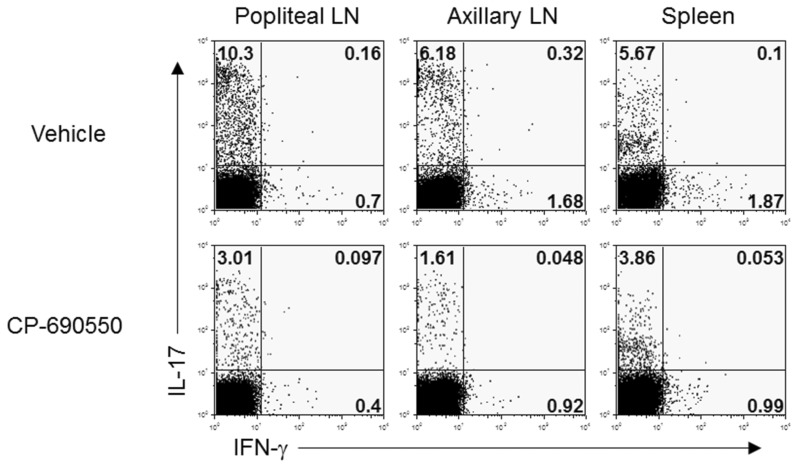
Immune Netw.
2013 Dec;13(6):257-263. 10.4110/in.2013.13.6.257.
CP-690550 Treatment Ameliorates Established Disease and Provides Long-Term Therapeutic Effects in an SKG Arthritis Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Immunology, Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea. dlee5522@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea.
- 3Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea.
- 4Department of Chemistry, KAIST, Daejeon 305-701, Korea.
- KMID: 2150786
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2013.13.6.257
Abstract
- Although pathogenesis of human rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains unclear, arthritogenic T cells and downstream signaling mediators have been shown to play critical roles. An increasing numbers of therapeutic options have been added for the effective control of RA. Nevertheless, there is still a category of patients that fails treatment and suffers from progressive disease. The recently developed immunosuppressant CP-690550, a small molecule JAK kinase inhibitor, has been implicated as an important candidate treatment modality for autoimmune arthritis. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic effect of CP-690550 on established arthritis using an SKG arthritis model, a pathophysiologically relevant animal model for human RA. CP-690550 treatment revealed remarkable long-term suppressive effects on SKG arthritis when administered to the well-advanced disease (clinical score 3.5~4.0). The treatment effect lasted at least 3 more weeks after cessation of drug infusion, and suppression of disease was correlated with the reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17, IFN-gamma, and IL-6 and increased level of immunoregulatory IL-10.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Firestein GS. Immunologic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2005; 11:S39–S44. PMID: 16357749.
Article2. VanderBorght A, Geusens P, Raus J, Stinissen P. The autoimmune pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: role of autoreactive T cells and new immunotherapies. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 31:160–175. PMID: 11740797.
Article3. McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007; 7:429–442. PMID: 17525752.
Article4. Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003; 423:356–361. PMID: 12748655.
Article5. Fournier C. Where do T cells stand in rheumatoid arthritis? Joint Bone Spine. 2005; 72:527–532. PMID: 16087382.
Article6. Brand DD, Kang AH, Rosloniec EF. Immunopathogenesis of collagen arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003; 25:3–18. PMID: 12904888.
Article7. Klareskog L, McDevitt H. Rheumatoid arthritis and its animal models: the role of TNF-alpha and the possible absence of specific immune reactions. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999; 11:657–662. PMID: 10631551.8. Horai R, Nakajima A, Habiro K, Kotani M, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Saijo S, Kotaki H, Sudo K, Okahara A, Tanioka H, Ikuse T, Ishii N, Schwartzberg PL, Abe R, Iwakura Y. TNF-alpha is crucial for the development of autoimmune arthritis in IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:1603–1611. PMID: 15578092.9. Hata H, Sakaguchi N, Yoshitomi H, Iwakura Y, Sekikawa K, Azuma Y, Kanai C, Moriizumi E, Nomura T, Nakamura T, Sakaguchi S. Distinct contribution of IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-10 to T cell-mediated spontaneous autoimmune arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:582–588. PMID: 15314695.10. Ferrari-Lacraz S, Zanelli E, Neuberg M, Donskoy E, Kim YS, Zheng XX, Hancock WW, Maslinski W, Li XC, Strom TB, Moll T. Targeting IL-15 receptor-bearing cells with an antagonist mutant IL-15/Fc protein prevents disease development and progression in murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2004; 173:5818–5826. PMID: 15494535.
Article11. Gracie JA, Forsey RJ, Chan WL, Gilmour A, Leung BP, Greer MR, Kennedy K, Carter R, Wei XQ, Xu D, Field M, Foulis A, Liew FY, McInnes IB. A proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1999; 104:1393–1401. PMID: 10562301.
Article12. Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2003; 171:6173–6177. PMID: 14634133.
Article13. Lubberts E, Koenders MI, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Joosten LA, van den Berg WB. Treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine interleukin-17 antibody after the onset of collagen-induced arthritis reduces joint inflammation, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:650–659. PMID: 14872510.
Article14. Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Sedgwick JD, Cua DJ. Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2003; 198:1951–1957. PMID: 14662908.
Article15. Hirota K, Hashimoto M, Yoshitomi H, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Yamaguchi T, Iwakura Y, Sakaguchi N, Sakaguchi S. T cell self-reactivity forms a cytokine milieu for spontaneous development of IL-17+ Th cells that cause autoimmune arthritis. J Exp Med. 2007; 204:41–47. PMID: 17227914.16. Lubberts E, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB. The role of T-cell interleukin-17 in conduction destructive arthritis: lessons from animal models. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7:29–37. PMID: 15642151.17. Changelian PS, Flanagan ME, Ball DJ, Kent CR, Magnuson KS, Martin WH, Rizzuti BJ, Sawyer PS, Perry BD, Brissette WH, McCurdy SP, Kudlacz EM, Conklyn MJ, Elliott EA, Koslov ER, Fisher MB, Strelevitz TJ, Yoon K, Whipple DA, Sun J, Munchhof MJ, Doty JL, Casavant JM, Blumenkopf TA, Hines M, Brown MF, Lillie BM, Subramanyam C, Shang-Poa C, Milici AJ, Beckius GE, Moyer JD, Su C, Woodworth TG, Gaweco AS, Beals CR, Littman BH, Fisher DA, Smith JF, Zagouras P, Magna HA, Saltarelli MJ, Johnson KS, Nelms LF, Des Etages SG, Hayes LS, Kawabata TT, Finco-Kent D, Baker DL, Larson M, Si MS, Paniagua R, Higgins J, Holm B, Reitz B, Zhou YJ, Morris RE, O'Shea JJ, Borie DC. Prevention of organ allograft rejection by a specific Janus kinase 3 inhibitor. Science. 2003; 302:875–878. PMID: 14593182.
Article18. Kudlacz E, Perry B, Sawyer P, Conklyn M, McCurdy S, Brissette W, Flanagan M, Changelian P. The novel JAK-3 inhibitor CP-690550 is a potent immunosuppressive agent in various murine models. Am J Transplant. 2004; 4:51–57. PMID: 14678034.
Article19. Borie DC, Changelian PS, Larson MJ, Si MS, Paniagua R, Higgins JP, Holm B, Campbell A, Lau M, Zhang S, Flores MG, Rousvoal G, Hawkins J, Ball DA, Kudlacz EM, Brissette WH, Elliott EA, Reitz BA, Morris RE. Immunosuppression by the JAK3 inhibitor CP-690,550 delays rejection and significantly prolongs kidney allograft survival in Nonhuman Primates. Transplantation. 2005; 79:791–801. PMID: 15818321.
Article20. Paniagua R, Si MS, Flores MG, Rousvoal G, Zhang S, Aalami O, Campbell A, Changelian PS, Reitz BA, Borie DC. Effects of JAK3 inhibition with CP-690,550 on immune cell populations and their functions in Nonhuman Primate recipients of kidney allografts. Transplantation. 2005; 80:1283–1292. PMID: 16314797.
Article21. Park HB, Oh K, Garmaa N, Seo MW, Byoun OJ, Lee HY, Lee DS. CP-690550, a Jak inhibitor, suppresses CD4+ T cell-mediated acute graft-versus-host disease by inhibiting the IFN-g pathway. Transplantation. 2010; 90:825–835. PMID: 20697326.22. Ghoreschi K, Jesson MI, Li X, Lee JL, Ghosh S, Alsup JW, Warner JD, Tanaka M, Steward-Tharp SM, Gadina M, Thomas CJ, Minnerly JC, Storer CE, LaBranche TP, Radi ZA, Dowty ME, Head RD, Meyer DM, Kishore N, O'Shea JJ. Modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by tofacitinib (CP-690,550). J Immunol. 2011; 186:4234–4243. PMID: 21383241.
Article23. Tak PP, Kalden JR. Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13(Suppl 1):S5. PMID: 21624184.
Article24. Flanagan ME, Blumenkopf TA, Brissette WH, Brown MF, Casavant JM, Shang-Poa C, Doty JL, Elliott EA, Fisher MB, Hines M, Kent C, Kudlacz EM, Lillie BM, Magnuson KS, McCurdy SP, Munchhof MJ, Perry BD, Sawyer PS, Strelevitz TJ, Subramanyam C, Sun J, Whipple DA, Changelian PS. Discovery of CP-690,550: a potent and selective Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and organ transplant rejection. J Med Chem. 2010; 53:8468–8484. PMID: 21105711.
Article25. West K. CP-690550, a JAK3 inhibitor as an immunosuppressant for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, transplant rejection, psoriasis and other immune-mediated disorders. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009; 10:491–504.26. Milici AJ, Kudlacz EM, Audoly L, Zwillich S, Changelian P. Cartilage preservation by inhibition of Janus kinase 3 in two rodent models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10:R14. PMID: 18234077.
Article27. Sakaguchi N, Takahashi T, Hata H, Nomura T, Tagami T, Yamazaki S, Sakihama T, Matsutani T, Negishi I, Nakatsuru S, Sakaguchi S. Altered thymic T-cell selection due to a mutation of the ZAP-70 gene causes autoimmune arthritis in mice. Nature. 2003; 426:454–460. PMID: 14647385.
Article28. Yoshitomi H, Sakaguchi N, Kobayashi K, Brown GD, Tagami T, Sakihama T, Hirota K, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Miki I, Gordon S, Akira S, Nakamura T, Sakaguchi S. A role for fungal {beta}-glucans and their receptor Dectin-1 in the induction of autoimmune arthritis in genetically susceptible mice. J Exp Med. 2005; 201:949–960. PMID: 15781585.29. Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Yoshitomi H, Hata H, Takahashi T, Nomura T. Spontaneous development of autoimmune arthritis due to genetic anomaly of T cell signal transduction: Part 1. Semin Immunol. 2006; 18:199–206. PMID: 16713715.
Article30. Oh K, Joo KM, Jung YS, Lee J, Kang H, Lee HY, Lee DS. A receptor-independent, cell-based JAK activation assay for screening for JAK3-specific inhibitors. J Immunol Methods. 2010; 354:45–52. PMID: 20138049.
Article31. Asadullah K, Sabat R, Friedrich M, Volk HD, Sterry W. Interleukin-10: an important immunoregulatory cytokine with major impact on psoriasis. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004; 3:185–192. PMID: 15180472.
Article32. You S, Alyanakian MA, Segovia B, Damotte D, Bluestone J, Bach JF, Chatenoud L. Immunoregulatory pathways controlling progression of autoimmunity in NOD mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008; 1150:300–310. PMID: 19120317.
Article33. Cope AP, Schulze-Koops H, Aringer M. The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007; 25:S4–S11. PMID: 17977483.34. Podojil JR, Miller SD. Molecular mechanisms of T-cell receptor and costimulatory molecule ligation/blockade in autoimmune disease therapy. Immunol Rev. 2009; 229:337–355. PMID: 19426232.
Article35. Appel S, Brossart P. Development of novel compounds to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases and graft versus host reactions. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2007; 7:93–97. PMID: 17584149.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Autoantibody-Mediated Dysfunction of Salivary Glands Leads to Xerostomia in SKG Mice
- Chronic Arthritis in Childhood
- Long-term treatment of allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells in a dog with rheumatoid arthritis
- Long-term follow-up study and long-term care of childhood cancer survivors
- Experimental Animal Models for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Methods and Applications