Immune Netw.
2011 Dec;11(6):420-423. 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.420.
CKD-712, (S)-1-(alpha-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, Inhibits the NF-kappaB Activation and Augments Akt Activation during TLR4 Signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Institute for Immunology and Immunological Diseases, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. inhong@yuhs.ac
- 2CKD Research Institute, Jung-dong, Gheung-gu, Yongin 446-916, Korea.
- KMID: 2150730
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.6.420
Abstract
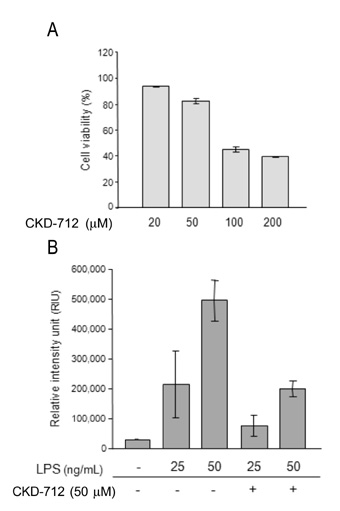
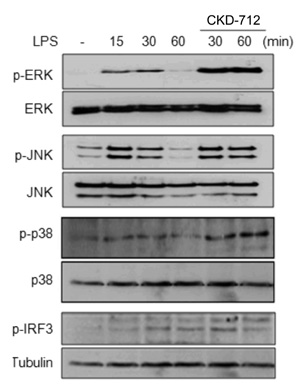
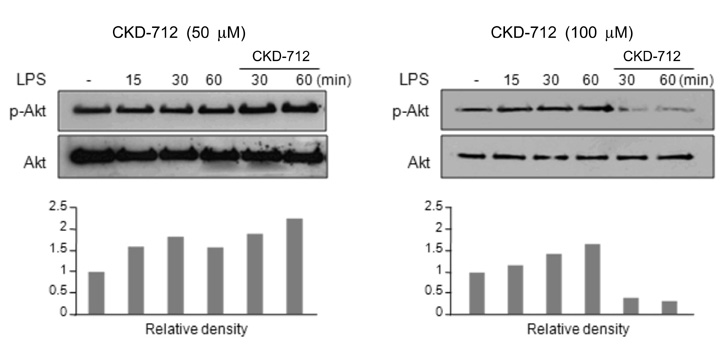
- Since CKD-712 has been developed as an anti-inflammatory agent, we examined the effect of CKD-712 during TLR4 signaling. Using HEK293 cells expressing TLR4, CKD-712 was pre-treated 1 hr before LPS stimulation. Activation of NF-kappaB was assessed by promoter assay. The activation of ERK, JNK, p38, IRF3 and Akt was measured by western blotting. CKD-712 inhibited the NF-kappaB signaling triggered by LPS. The activation of ERK, JNK, p38 or IRF3 was not inhibited by CKD-712. On the contrary the activation of these molecules was augmented slightly. The activation of Akt with stimulation of LPS was also enhanced with CKD-712 pre-treatment at lower concentration, but was inhibited at higher concentration. We suggest that during TLR4 signaling CKD-712 inhibits NF-kappaB activation. However, CKD-712 augmented the activation of Akt as well as Map kinases. Therefore, we suggest that CKD-712 might have a role as an immunomodulator.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Clermont G, Angus DC, Kalassian KG, Linde-Zwirble WT, Ramakrishnan N, Linden PK, Pinsky MR. Reassessing the value of short-term mortality in sepsis: comparing conventional approaches to modeling. Crit Care Med. 2003. 31:2627–2633.
Article2. Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998. 282:2085–2088.
Article3. Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe M, Kirschning CJ. Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:17406–17409.
Article4. Flo TH, Halaas O, Lien E, Ryan L, Teti G, Golenbock DT, Sundan A, Espevik T. Human toll-like receptor 2 mediates monocyte activation by Listeria monocytogenes, but not by group B streptococci or lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 2000. 164:2064–2069.
Article5. Tamandl D, Bahrami M, Wessner B, Weigel G, Ploder M, Fürst W, Roth E, Boltz-Nitulescu G, Spittler A. Modulation of toll-like receptor 4 expression on human monocytes by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6: tumor necrosis factor evokes lipopolysaccharide hyporesponsiveness, whereas interleukin-6 enhances lipopolysaccharide activity. Shock. 2003. 20:224–229.
Article6. Kang YJ, Koo EB, Lee YS, Yun-Choi HS, Chang KC. Prevention of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by a novel positive inotropic agent, YS 49, in rat vascular smooth muscle and RAW 264.7 macrophages. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. 128:357–364.
Article7. Kang YJ, Seo SJ, Yun-Choi HS, Lee DH, Kim YM, Chang KC. A synthetic isoquinoline alkaloid, 1-(beta-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (YS 51), reduces inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and improves survival in a rodent model of endotoxic shock. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. 301:561–567.
Article8. Tsoyi K, Kim HJ, Shin JS, Kim DH, Cho HJ, Lee SS, Ahn SK, Yun-Choi HS, Lee JH, Seo HG, Chang KC. HO-1 and JAK-2/STAT-1 signals are involved in preferential inhibition of iNOS over COX-2 gene expression by newly synthesized tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, CKD712, in cells activated with lipopolysacchride. Cell Signal. 2008. 20:1839–1847.
Article9. Oh YJ, Youn JH, Min HJ, Kim DH, Lee SS, Choi IH, Shin JS. CKD712, (S)-1-(α-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated secretion of HMGB1 by inhibiting PI3K and classical protein kinase C. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. 11:1160–1165.
Article10. Ojaniemi M, Glumoff V, Harju K, Liljeroos M, Vuori K, Hallman M. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is involved in Toll-like receptor 4-mediated cytokine expression in mouse macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 2003. 33:597–605.
Article11. Lee SH, Park DW, Park SC, Park YK, Hong SY, Kim JR, Lee CH, Baek SH. Calcium-independent phospholipase A2beta-Akt signaling is involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced NADPH oxidase 1 expression and foam cell formation. J Immunol. 2009. 183:7497–7504.
Article12. Yang J, Chen L, Yang J, Ding J, Rong H, Dong W, Li X. High mobility group box-1 induces migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via TLR4-dependent PI3K/Akt pathway activation. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. [Epub ahead of print].
Article13. Lu C, Liu L, Chen Y, Ha T, Kelley J, Schweitzer J, Kalbfleisch JH, Kao RL, Williams DL, Li C. TLR2 ligand induces protection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling. J Immunol. 2011. 187:1458–1466.
Article14. Joung SM, Park ZY, Rani S, Takeuchi O, Akira S, Lee JY. Akt contributes to activation of the TRIF-dependent signaling pathways of TLRs by interacting with TANK-binding kinase 1. J Immunol. 2011. 186:499–507.
Article15. Tsoyi K, Kim WS, Kim YM, Kim HJ, Seo HG, Lee JH, Yun-Choi HS, Chang KC. Upregulation of PTEN by CKD712, a synthetic tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, selectively inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced VCAM-1 but not ICAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2009. 207:412–419.
Article16. Jin YC, Lee YS, Kim YM, Seo HG, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Yun-Choi HS, Chang KC. (S)-1-(alpha-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (CKD712) reduces rat myocardial apoptosis against ischemia and reperfusion injury by activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling and anti-inflammatory action in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. 330:440–448.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- NF-kappaB Activation in T Helper 17 Cell Differentiation
- Role of PI3K/Akt Pathway in the Activation of IkappaB/NF-kappaB Pathway in Lung Epithelial Cells
- Rutin inhibits osteoclast formation by decreasing reactive oxygen species and TNF-alpha by inhibiting activation of NF-kappaB
- Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Inhibits Nuclear Factor kappaB and Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Rats with Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis
- Role of protein kinases on NF- kappaB activation and cell death in bovine cerebral endothelial cells