Immune Netw.
2011 Dec;11(6):412-415. 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.412.
Immunomodulatory Effects of Hypocrellin A on MHC-restricted Antigen Processing
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea. cklee@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2150728
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.6.412
Abstract
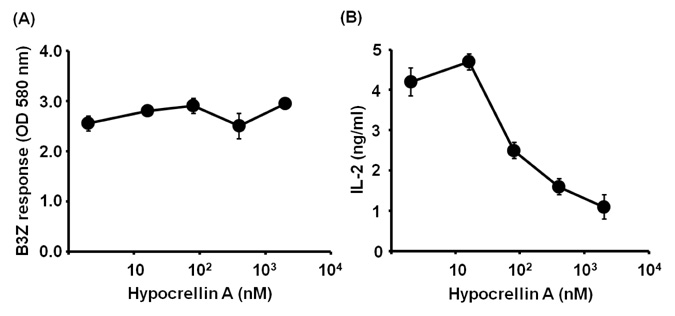
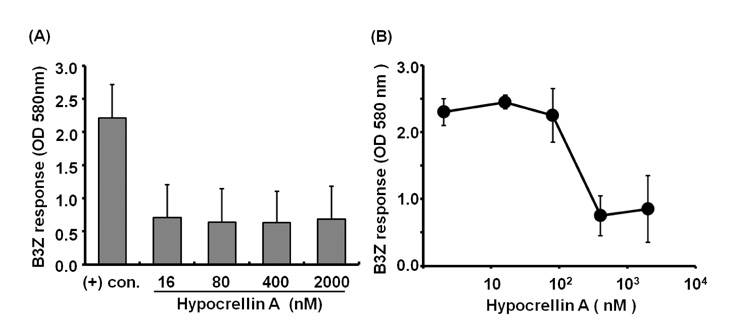
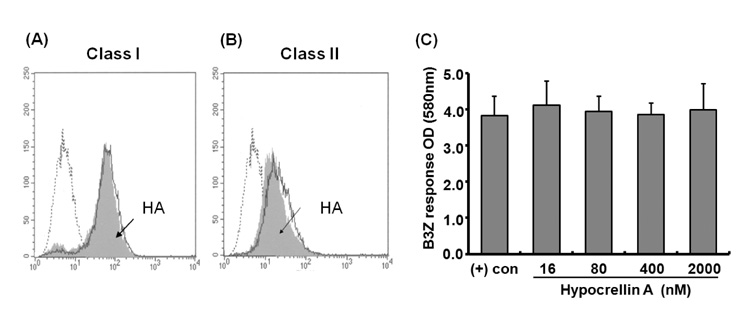
- Hypocrellin A has gained much attention in recent years due to its light-induced antitumor, antifungal and antiviral activities. Here we report that hypocrellin A exerts immunomodulatory effects on MHC-restricted presentation of antigen. Hypocrellin A inhibited class II-MHC restricted presentation of exogenous antigen, but not class I MHC-restricted presentation of exogenous antigen, in dendritic cells. Hypocrellin A also inhibited the cytosolic pathway of endogenous antigen presentation. However, hypocrellin A did not inhibit the expression of class I and class II MHC molecules on dendritic cells (DCs), the phagocytic activity of DCs, or the H-2K(b)-restricted presentation of a synthetic peptide, SIINFEKL. These results show that hypocrellin A differentially modulates the MHC-restricted antigen presentation pathways.
Figure
Reference
-
1. He YY, Jiang LJ. Synthesis and EPR investigations of new aminated hypocrellin derivatives. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000. 28:1642–1651.
Article2. Wan XY, Chen YT. Hypocrellin A, a new drug for photochemotherapy. Chinese Sci Bull. 1981. 26:1040–1041.3. Ma JS, Yan F, Wang CQ, An JY. Hypocrellin-A sensitized photooxidation of bilirubin. Photochem Photobiol. 1989. 50:827–830.
Article4. Schinazi RF, Chu CK, Babu JR, Oswald BJ, Saalmann V, Cannon DL, Eriksson BF, Nasr M. Anthraquinones as a new class of antiviral agents against human immunodeficiency virus. Antiviral Res. 1990. 13:265–272.
Article5. Daub ME, Ehrenshaft M. The photoactivated cercospora toxin cercosporin: Contributions to Plant Disease and Fundamental Biology. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2000. 38:461–490.
Article6. Ma L, Tai H, Li C, Zhang Y, Wang ZH, Ji WZ. Photodynamic inhibitory effects of three perylenequinones on human colorectal carcinoma cell line and primate embryonic stem cell line. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. 9:485–490.
Article7. Liang XH, Cai YJ, Liao XR, Wu K, Wang L, Zhang DB, Meng Q. Isolation and identification of a new hypocrellin A-producing strain Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168. Microbiol Res. 2009. 164:9–17.
Article8. Ali SM, Chee SK, Yuen GY, Olivo M. Hypocrellins and hypericin induced apoptosis in human tumor cells: a possible role of hydrogen peroxide. Int J Mol Med. 2002. 9:461–472.
Article9. Diwu Z, Zimmermann J, Meyer T, Lown JW. Design, synthesis and investigation of mechanisms of action of novel protein kinase C inhibitors: perylenequinonoid pigments. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994. 47:373–385.
Article10. Park J, English DS, Wannemuehler Y, Carpenter S, Petrich JW. The role of oxygen in the antiviral activity of hypericin and hypocrellin. Photochem Photobiol. 1998. 68:593–597.
Article11. Ma G, Khan SI, Jacob MR, Tekwani BL, Li Z, Pasco DS, Walker LA, Khan IA. Antimicrobial and antileishmanial activities of hypocrellins A and B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. 48:4450–4452.
Article12. Gerelchuluun T, Lee YH, Lee YR, Im SA, Song S, Park JS, Han K, Kim K, Lee CK. Dendritic cells process antigens encapsulated in a biodegradable polymer, poly(D,L-lactideco-glycolide), via an alternate class I MHC processing pathway. Arch Pharm Res. 2007. 30:1440–1446.
Article13. Lee YR, Yang IH, Lee YH, Im SA, Song S, Li H, Han K, Kim K, Eo SK, Lee CK. Cyclosporin A and tacrolimus, but not rapamycin, inhibit MHC-restricted antigen presentation pathways in dendritic cells. Blood. 2005. 105:3951–3955.
Article14. Lee YH, Lee YR, Kim KH, Im SA, Song S, Lee MK, Kim Y, Hong JT, Kim K, Lee CK. Baccatin III, a synthetic precursor of taxol, enhances MHC-restricted antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. 11:985–991.
Article15. Harding CV. Phagocytic processing of antigens for presentation by MHC molecules. Trends Cell Biol. 1995. 5:105–109.
Article16. Heath WR, Carbone FR. Cross-presentation, dendritic cells, tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. 19:47–64.
Article17. Carbone FR, Kurts C, Bennett SR, Miller JF, Heath WR. Cross-presentation: a general mechanism for CTL immunity and tolerance. Immunol Today. 1998. 19:368–373.
Article18. Ackerman AL, Cresswell P. Cellular mechanisms governing cross-presentation of exogenous antigens. Nat Immunol. 2004. 5:678–684.
Article19. Groothuis TA, Neefjes J. The many roads to crosspresentation. J Exp Med. 2005. 202:1313–1318.
Article20. Kovacsovics-Bankowski M, Rock KL. A phagosome-to-cytosol pathway for exogenous antigens presented on MHC class I molecules. Science. 1995. 267:243–246.
Article21. Ojcius DM, Gapin L, Kourilsky P. Dissociation of the peptide/MHC class I complex: pH dependence and effect of endogenous peptides on the activation energy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993. 197:1216–1222.
Article22. Diwu Z. Novel therapeutic and diagnostic applications of hypocrellins and hypericins. Photochem Photobiol. 1995. 61:529–539.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evidence for Direct Inhibition of MHC-Restricted Antigen Processing by Dexamethasone
- Metformin Suppresses MHC-Restricted Antigen Presentation by Inhibiting Co-Stimulatory Factors and MHC Molecules in APCs
- Lectins Isolated from Mushroom Fomitella fraxinea Enhance MHC-restricted Exogenous Antigen Presentation
- Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors, Aspirin and Ibuprofen, Inhibit MHC-restricted Antigen Presentation in Dendritic Cells
- Cordyceps militaris Enhances MHC-restricted Antigen Presentation via the Induced Expression of MHC Molecules and Production of Cytokines