J Bacteriol Virol.
2015 Jun;45(2):155-158. 10.4167/jbv.2015.45.2.155.
The First Case of Non-retrospective Clinical Identification of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Patient in 2013 in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Disease, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. ksko@skku.edu
- KMID: 2149216
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2015.45.2.155
Abstract
- In this study, we report the first clinically identified case of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in a 73-year old man from Jeju Island, South Korea. Although his initial manifestation suggested tsutsugamushi disease with cutaneous lesion, later the patient presented with symptoms characteristic of SFTS. Despite intensive medical therapies upon the clinical diagnosis of SFTS, patient's condition rapidly deteriorated. SFTS is a fatal disease that requires early diagnosis and appropriate supportive treatment.
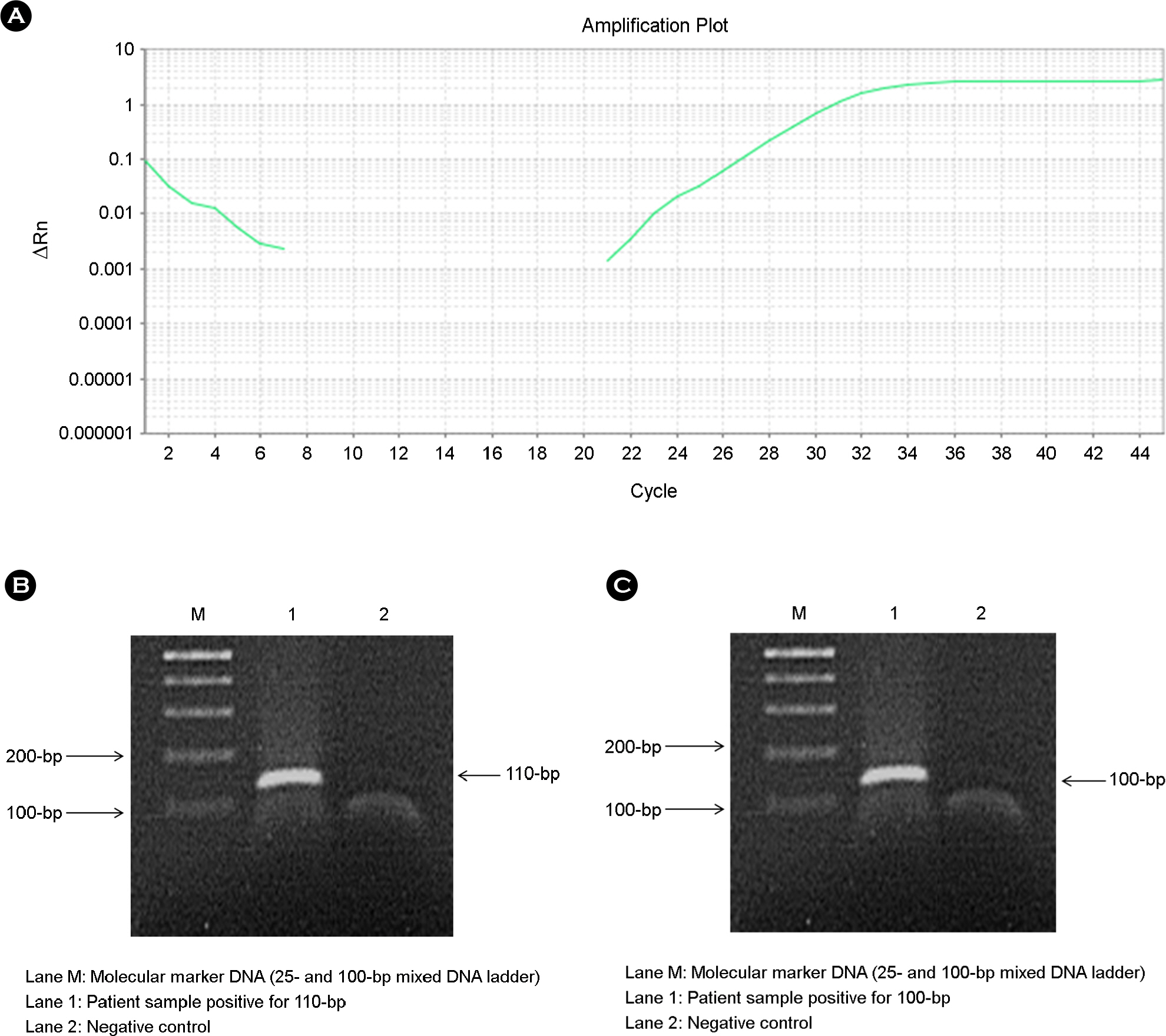
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Status and Infection Control of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Korea
Hyunjoo Oh, Jeong Rae Yoo, Misun Kim, Sang Taek Heo
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2022;27(1):18-27. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.18.
Reference
-
1). Li S, Xue C, Fu Y, Wang J, Ding X, Liu R, et al. Sporadic case infected by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus in a non-epidemic region of China. Biosci Trends. 2011; 5:273–6.
Article2). Lee KH, Medlock JM, Heo ST. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome virus, Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever virus, and migratory birds. J Bacteriol Virol. 2013; 43:235–43.
Article3). Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1523–32.4). Gai ZT, Zhang Y, Liang MF, Jin C, Zhang S, Zhu CB, et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J Infect Dis. 2012; 206:1095–102.
Article5). Zhao L, Zhai S, Wen H, Cui F, Chi Y, Wang L, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, Shandong Province, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:963–5.
Article6). Bao CJ, Guo XL, Qi X, Hu JL, Zhou MH, Varma JK, et al. A family cluster of infections by a newly recognized bunyavirus in eastern China, 2007: further evidence of person-to-person transmission. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 53:1208–14.
Article7). Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, Choi SJ, Jun KI, Kim NH, et al. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:1892–4.
Article8). Zhang YZ, He YW, Dai YA, Xiong Y, Zheng H, Zhou DJ, et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel Bunyavirus in China: pathogenesis and correlates of fatal outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54:527–33.9). Ha NY, Choi MS, Choi NH. Molecular characterization of sca genes found in Orientia tsutsugamushi Genome. J Bacteriol Virol. 2013; 43:155–8.10). Tang X, Wu W, Wang H, Du Y, Liu L, Kang K, et al. Human-to-human transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus through contact with infectious blood. J Infect Dis. 2013; 207:736–9.
Article11). Lam TT, Liu W, Bowden TA, Cui N, Zhuang L, Liu K, et al. Evolutionary and molecular analysis of the emergent severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Epidemics. 2013; 5:1–10.
Article12). Sun Y, Liang M, Qu J, Jin C, Zhang Q, Li J, et al. Early diagnosis of novel SFTS bunyavirus infection by quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay. J Clin Virol. 2012; 53:48–53.
Article13). Erduran E, Bahadir A, Palanci N, Gedik Y. The treatment of crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever with high-dose methylprednisolone, intravenous immunoglobulin, and fresh frozen plasma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2013; 35:e19–24.
Article14). Fisher-Hoch SP, Khan JA, Rehman S, Mirza S, Khurshid M, McCormick JB. Crimean Congo-haemorrhagic fever treated with oral ribavirin. Lancet. 1995; 346:472–5.15). Oh WS, Heo ST, Kim SH, Choi WJ, Han MG, Kim JY. Plasma exchange and ribavirin for rapidly progressive severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Int J Infect Dis. 2014; 18:84–6.
Article16). Ding F, Zhang W, Wang L, Hu W, Soares Magalhaes RJ, Sun H, et al. Epidemiologic features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–2012. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56:1682–3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome
- Differences of clinical manifestation of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome between Korean and Chinese patients
- Strategies Against Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Increasing in Korea
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Patients with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Retrospectively Identified in Korea, 2008–2013
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome