Restor Dent Endod.
2015 May;40(2):149-154. 10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.149.
Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College and Hospital, Meenakshi Academy of Higher Education and Research (MAHER), Tamil Nadu, India. vadhansekar@gmail.com
- KMID: 2148865
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.149
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
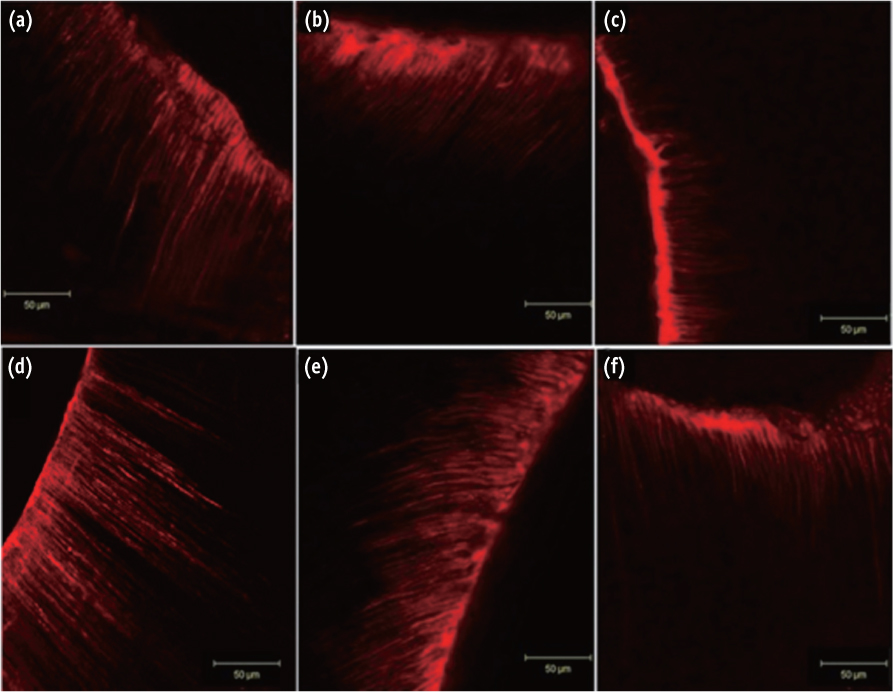
This study evaluated the penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) into root dentinal tubules and the influence of passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty freshly extracted anterior teeth were decoronated and instrumented using Mtwo rotary files up to size 40, 4% taper. The samples were randomly divided into two groups (n = 10), that is, conventional syringe irrigation (CSI) and PUI. CHX was mixed with Rhodamine B dye and was used as the final irrigant. The teeth were sectioned at coronal, middle and apical levels and viewed under CLSM to record the penetration depth of CHX. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests.
RESULTS
The mean penetration depths of 2% CHX in coronal, middle and apical thirds were 138 microm, 80 microm and 44 microm in CSI group, respectively, whereas the mean penetration depths were 209 microm, 138 microm and 72 microm respectively in PUI group. Statistically significant difference was present between CSI group and PUI group at all three levels (p < 0.01 for coronal third and p < 0.001 for middle and apical thirds. On intragroup analysis, both groups showed statistically significant difference among three levels (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Penetration depth of 2% CHX into root dentinal tubules is deeper in coronal third when compared to middle and apical third. PUI aided in deeper penetration of 2% CHX into dentinal tubules when compared to conventional syringe irrigation at all three levels.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Push-out bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of different root canal sealers used with coated core materials
Derya Deniz Sungur, Nuhan Purali, Erdal Coşgun, Semra Calt
Restor Dent Endod. 2016;41(2):114-120. doi: 10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.114.Dentinal tubule penetration of sodium hypochlorite in root canals with and without mechanical preparation and different irrigant activation methods
Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Matheus Albino Souza, Rodrigo Gonçalves Ribeiro, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Restor Dent Endod. 2022;48(1):e1. doi: 10.5395/rde.2023.48.e1.
Reference
-
1. Hülsmann M, Peters OA, Dummer PMH. Mechanical preparation of root canals: shaping goals, techniques and means. Endod Topics. 2005; 10:30–76.
Article2. Peters OA, Schönenberger K, Laib A. Effects of four Ni-Ti preparation techniques on root canal geometry assessed by micro computed tomography. Int Endod J. 2001; 34:221–230.
Article3. Zehnder M. Root canal irrigants. J Endod. 2006; 32:389–398.
Article4. Souza M, Cecchin D, Farina AP, Leite CE, Cruz FF, Pereira Cda C, Ferraz CC, Figueiredo JA. Evaluation of chlorhexidine substantivity on human dentin: a chemical analysis. J Endod. 2012; 38:1249–1252.
Article5. Haapasalo M, Orstavik D. In vitro infection and disinfection of dentinal tubules. J Dent Res. 1987; 66:1375–1379.6. Al-Nazhan S, Al-Sulaiman A, Al-Rasheed F, Alnajjar F, Al-Abdulwahab B, Al-Badah A. Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls. In vitro SEM study. Restor Dent Endod. 2014; 39:258–264.
Article7. Zou L, Shen Y, Li W, Haapasalo M. Penetration of sodium hypochlorite into dentin. J Endod. 2010; 36:793–796.
Article8. Krithikadatta J, Indira R, Dorothykalyani AL. Disinfection of dentinal tubules with 2% chlorhexidine, 2% metronidazole, bioactive glass when compared with calcium hydroxide as intracanal medicaments. J Endod. 2007; 33:1473–1476.
Article9. de Gregorio C, Estevez R, Cisneros R, Paranjpe A, Cohenca N. Efficacy of different irrigation and activation systems on the penetration of sodium hypochlorite into simulated lateral canals and up to working length: an in vitro study. J Endod. 2010; 36:1216–1221.
Article10. Spoorthy E, Velmurugan N, Ballal S, Nandini S. Comparison of irrigant penetration up to working length and into simulated lateral canals using various irrigating techniques. Int Endod J. 2013; 46:815–822.
Article11. van der Sluis LW, Versluis M, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. Passive ultrasonic irrigation of the root canal: a review of literature. Int Endod J. 2007; 40:415–426.
Article12. Brunson M, Heilborn C, Johnson DJ, Cohenca N. Effect of apical preparation size and preparation taper on irrigant volume delivered by using negative pressure irrigation system. J Endod. 2010; 36:721–724.
Article13. van der Sluis LW, Shemesh H, Wu MK, Wesselink PR. An evaluation of the influence of passive ultrasonic irrigation on the seal of root canal fillings. Int Endod J. 2007; 40:356–361.
Article14. Ahmad M, Pitt Ford TJ, Crum LA. Ultrasonic debridement of root canals: acoustic streaming and its possible role. J Endod. 1987; 13:490–499.
Article15. Mamootil K, Messer HH. Penetration of dentinal tubules by endodontic sealer cements in extracted teeth and in vivo. Int Endod J. 2007; 40:873–881.
Article16. Chandra SS, Shankar P, Indira R. Depth of penetration of four resin sealers into radicular dentinal tubules: a confocal microscopic study. J Endod. 2012; 38:1412–1416.
Article17. Berkhoff JA, Chen PB, Teixeira FB, Diogenes A. Evaluation of triple antibiotic paste removal by different irrigation procedures. J Endod. 2014; 40:1172–1177.
Article18. Kara Tuncer A, Tuncer S. Effect of different final irrigation solutions on dentinal tubule penetration depth and percentage of root canal sealer. J Endod. 2012; 38:860–863.
Article19. Ma J, Wang Z, Shen Y, Haapasalo M. A new noninvasive model to study the effectiveness of dentin disinfection by using confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Endod. 2011; 37:1380–1385.
Article20. Giardino L, Ambu E, Becce C, Rimondini L, Morra M. Surface tension comparison of four common root canal irrigants and two new irrigants containing antibiotic. J Endod. 2006; 32:1091–1093.
Article21. Bukiet F, Soler T, Guivarch M, Camps J, Tassery H, Cuisinier F, Candoni N. Factors affecting the viscosity of sodium hypochlorite and their effect on irrigant flow. Int Endod J. 2013; 46:954–961.
Article22. Taşman F, Cehreli ZC, Oğan C, Etikan I. Surface tension of root canal irrigants. J Endod. 2000; 26:586–587.
Article23. Violich DR, Chandler NP. The smear layer in endodontics - a review. Int Endod J. 2010; 43:2–15.
Article24. Crumpton BJ, Goodell GG, McClanahan SB. Effects on smear layer and debris removal with varying volumes of 17% REDTA after rotary instrumentation. J Endod. 2005; 31:536–538.
Article25. Boutsioukis C, Lambrianidis T, Verhaagen B, Versluis M, Kastrinakis E, Wesselink PR, van der Sluis LW. The effect of needle-insertion depth on the irrigant flow in the root canal: evaluation using an unsteady computational fluid dynamics model. J Endod. 2010; 36:1664–1668.
Article26. Carrigan PJ, Morse DR, Furst ML, Sinai IH. A scanning electron microscopic evaluation of human dentinal tubules according to age and location. J Endod. 1984; 10:359–363.
Article27. Mjör IA, Smith MR, Ferrari M, Mannocci F. The structure of dentine in the apical region of human teeth. Int Endod J. 2001; 34:346–353.
Article28. Ribeiro RG, Marchesan MA, Silva RG, Sousa-Neto MD, Pécora JD. Dentin permeability of the apical third in different groups of teeth. Braz Dent J. 2010; 21:216–219.
Article29. Vinhorte MC, Suzuki EH, de Carvalho MS, Marques AA, Sponchiado Júnior EC, Garcia LFR. Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation. Restor Dent Endod. 2014; 39:104–108.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
- Effect of dentinal tubules orientation on penetration pattern of dentin adhesives using confocal laser scanning microscopy
- Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls. In vitro SEM study
- Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
- A Scanning electron microscopic study of the dentinal tubule obliteration effect by the different irradiations of a pulsed Nd:YAG laser