J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Feb;84(2):88-93. 10.4174/jkss.2013.84.2.88.
Resolution of type 2 diabetes after gastrectomy for gastric cancer with long limb Roux-en Y reconstruction: a prospective pilot study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. choish@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Endocrinology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2144995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.84.2.88
Abstract
- PURPOSE
It is unclear whether metabolic surgery is effective in non obese type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and the result after gastrectomy and conventional reconstruction for gastric cancer with non obese T2DM are not satisfactory for improvement of T2DM. Prospective single-arm pilot study with long limb Roux-en Y reconstruction after gastrectomy was evaluated on its safety and efficacy as a potential cure for T2DM in patients with non obese gastric cancer.
METHODS
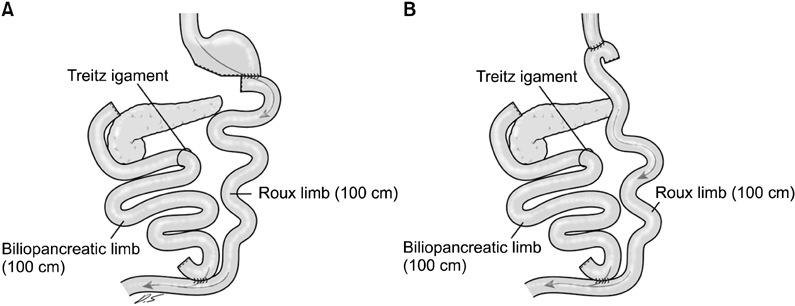
Fifteen patients with non obese T2DM and gastric cancer were enrolled. After gastrectomy, the gastrointestinal tract was reconstructed by Roux-en Y gastrojejunostomy or esophagojejunostomy. The biliopancreatic and Roux limb were 100 to 120 cm long each.
RESULTS
There was no surgery-related mortality, but four cases experienced complications (26.7%). Before surgery, the mean body mass index was 25.2 +/- 3.4 kg/m2 and mean glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was 7.7 +/- 1.4% with antidiabetic medications. The mean BMI decreased to 21.7 +/- 3.1 kg/m2 (P < 0.05) and the mean HbA1c decreased to 6.3 +/- 0.8% (P < 0.05) 6 months after surgery. At the end of the study (follow-up duration, 12.5 +/- 5.5 months), HbA1c decreased to <6% in 11 patients (78.6%) without any antidiabetic medications. There were no patients who had anemia, and/or malnutrition after surgery except one patient who died due to recurrence four months after surgery.
CONCLUSION
Long limb Roux-en Y reconstruction after gastrectomy is feasible and has the potential to cure T2DM in non obese gastric cancer patients. A randomized controlled trial is needed to confirm this result.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. Lancet. 2011. 378:31–40.2. Abdulla S, Schellenberg JR, Mukasa O, Lengeler C. Usefulness of a dispensary-based case-control study for assessing morbidity impact of a treated net programme. Int J Epidemiol. 2002. 31:175–180.3. American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. In 2007. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:596–615.4. Williams R, Van Gaal L, Lucioni C. CODE-2 Advisory Board. Assessing the impact of complications on the costs of Type II diabetes. Diabetologia. 2002. 45:S13–S17.5. Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D, Jensen MD, Pories WJ, et al. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009. 122:248–256.e5.6. Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, Brown BM, et al. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 1995. 222:339–350.7. Sjostrom L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M, Torgerson J, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:2683–2693.8. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006. 368:1681–1688.9. Mu YM, Misra A, Adam JM, Chan SP, Chow FC, Cunanan EC, et al. Managing diabetes in Asia: overcoming obstacles and the role of DPP-IV inhibitors. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012. 95:179–188.10. Friedman MN, Sancetta AJ, Magovern GJ. The amelioration of diabetes mellitus following subtotal gastrectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1955. 100:201–204.11. Angervall L, Dotevall G, Tillander H. Amelioration of diabetes mellitus following gastric resection. Acta Med Scand. 1961. 169:743–748.12. Yang J, Li C, Liu H, Gu H, Chen P, Liu B. Effects of subtotal gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy on the clinical outcome of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Surg Res. 2010. 164:e67–e71.13. Kim JW, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, Choi SH, Noh SH. Outcome after gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. 18:49–54.14. DeFronzo RA, Matsuda M. Reduced time points to calculate the composite index. Diabetes Care. 2010. 33:e93.15. Emoto M, Nishizawa Y, Maekawa K, Hiura Y, Kanda H, Kawagishi T, et al. Homeostasis model assessment as a clinical index of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients treated with sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:818–822.16. Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G, et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:2402–2410.17. Levy JC, Matthews DR, Hermans MP. Correct homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) evaluation uses the computer program. Diabetes Care. 1998. 21:2191–2192.18. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2010 (ver. 3). Gastric Cancer. 2011. 14:113–123.19. Thaler JP, Cummings DE. Minireview: Hormonal and metabolic mechanisms of diabetes remission after gastrointestinal surgery. Endocrinology. 2009. 150:2518–2525.20. Frenken M, Cho EY, Karcz WK, Grueneberger J, Kuesters S. Improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese and non-obese patients after the duodenal switch operation. J Obes. 2011. 2011:860169.21. Navarrete SA, Leyba JL, Llopis SN. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy with duodenojejunal bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in non-obese patients: technique and preliminary results. Obes Surg. 2011. 21:663–667.22. Cohen R, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Schiavon CA. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for BMI < 35 kg/m2: a tailored approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2006. 2:401–404.23. Lee WJ, Wang W, Lee YC, Huang MT, Ser KH, Chen JC. Effect of laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass for type 2 diabetes mellitus: comparison of BMI>35 and <35 kg/m2. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008. 12:945–952.24. DePaula AL, Macedo AL, Mota BR, Schraibman V. Laparoscopic ileal interposition associated to a diverted sleeve gastrectomy is an effective operation for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with BMI 21-29. Surg Endosc. 2009. 23:1313–1320.25. Cohen RV, Schiavon CA, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Rubino F. Duodenal-jejunal bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with body mass index of 22-34 kg/m2: a report of 2 cases. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2007. 3:195–197.26. Salameh BS, Khoukaz MT, Bell RL. Metabolic and nutritional changes after bariatric surgery. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 4:217–223.27. Orci L, Chilcott M, Huber O. Short versus long Roux-limb length in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for the treatment of morbid and super obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Surg. 2011. 21:797–804.28. Ahn SM, Pomp A, Rubino F. Metabolic surgery for type 2 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. 1212:E37–E45.29. Rubino F, Forgione A, Cummings DE, Vix M, Gnuli D, Mingrone G, et al. The mechanism of diabetes control after gastrointestinal bypass surgery reveals a role of the proximal small intestine in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Ann Surg. 2006. 244:741–749.30. Wang TT, Hu SY, Gao HD, Zhang GY, Liu CZ, Feng JB, et al. Ileal transposition controls diabetes as well as modified duodenal jejunal bypass with better lipid lowering in a nonobese rat model of type II diabetes by increasing GLP-1. Ann Surg. 2008. 247:968–975.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Clinical Study of the Uncut Roux-en-Y Gastrojejunostomy Using a Short Roux Limb after Subtotal Gastrectomy
- Long-limb Roux-en-Y Reconstruction after Subtotal Gastrectomy to Treat Severe Diabetic Gastroparesis
- A Peterson's hernia and subsequent small bowel volvulus: surgical reconstruction utilizing transverse colon as a new Roux-en-Y limb - 1 case
- Efficacy of Roux-en-Y Reconstruction Using Two Circular Staplers after Subtotal Gastrectomy: Results from a Pilot Study Comparing with Billroth-I Reconstruction
- Pancreatoduodenectomy with uncut-Roux-en-Y reconstruction in patients with previous radical gastrectomy