Nutr Res Pract.
2008 Dec;2(4):240-246. 10.4162/nrp.2008.2.4.240.
Effect of butanol fraction from Cassia tora L. seeds on glycemic control and insulin secretion in diabetic rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Center of Smart Foods and Drugs, Inje University, 607 Obang-dong, Gimhae, Kyeongnam 621-749, Korea. chj@inje.ac.kr
- KMID: 2139198
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2008.2.4.240
Abstract
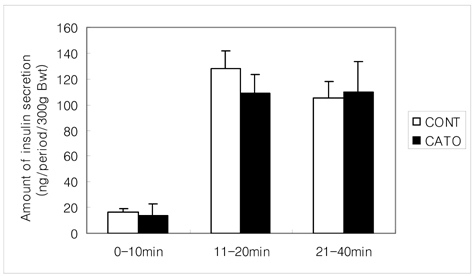
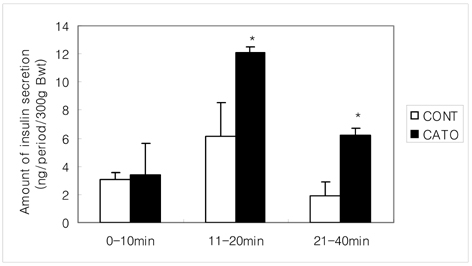
- Cassia tora L. seeds have previously been reported to reduce blood glucose level in human and animals with diabetes. In the present study, the effects of Cassia tora L. seed butanol fraction (CATO) were studied on postprandial glucose control and insulin secretion from the pancreas of the normal and diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced by an i.p. injection of Streptozotocin (55 mg/kg BW) into the male Sprague-Dawley rats. The postprandial glucose control was monitored during a 240 min-period using a maltose loading test. In normal rats, rats fed CATO (20 mg/100 g BW/d) showed lower postprandial glucose levels in all the levels from 30 min up to 180 min than those in the control rats without CATO (p<0.05). In diabetic rats, those levels in the CATO group seemed to be lower during the 30~180 min, but only glucose level at 30 min showed significant difference compared to that in the control group. Moreover, CATO delayed the peak time of the glucose rise in both normal and diabetic rats in the glucose curves. On the other hand, when CATO was administered orally to the diabetic rats for 5 days, 12 hr fasting serum glucose level was decreased in the diabetic rats (p<0.05). Degree of a decrease in 12 hr fasting serum insulin levels was significantly less in the diabetic CATO rats as compared to diabetic control rats. On the last day of feeding, beta cells of the pancreas were stimulated by 200 mg/dL glucose through a 40 min-pancreas perfusion. Amounts of the insulin secreted from the pancreas during the first phase (11~20 min) and the second phase (21~40 min) in the CATO fed diabetic rats were significantly greater than those in the diabetic control group (p<0.05). These findings indicated that constituents of Cassia tora L. seeds have beneficial effect on postprandial blood glucose control which may be partially mediated by stimulated insulin secretion from the pancreas of the diabetic rats.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adisakwattana S, Moonsan P, Yibchok-anun S. Insulin-releasing properties of a series of cinnamic acid derivatives in vitro and in vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 2008. 56:7838–7844.
Article2. Ahn DK. Illustrated book of Korean medicinal herbs. 1998. Seoul, Republic of Korea: Kyo-Hak Publishing Co., Ltd;636.3. Ahren B, Taborsky GJ Jr. The mechanism of vagal nerve stimulation of glucagon and insulin secretion in the dog. Endocrinology. 1986. 118:1551–1556.
Article4. Ahren B, Veith RC, Taborshy GJ Jr. Sympathetic nerve stimulation versus pancreatic norepinephrine infusion in the dog: effects on basal release of insulin and glucagon. Endocrinology. 1987. 121:323–331.
Article5. Baly DL, Curry DL, Keen CL, Hurley LS. Effect of manganese deficiency on insulin secretion and carbohydrate homeostasis in rats. J Nutr. 1984. 114:1438–1446.
Article6. Brockman RP. Insulin and glucagon responses in plasma to intraportal infusions of propionate and butyrate in sheep (Ovia aries). Comp Biochem Physiol. 1982. 73:237–238.
Article7. Choi HJ. Calcium modulation of insulin secretion in perfused pancreata of obese Zucker rats. J Food Sci Nutr. 1997. 2:144–148.8. Choi JS, Lee HJ, Ha JO, Park KY, Kang SS. In vitro antimutagenic effects of anthraquinone alycones and naphthopyrone glycodises from Cassia tora. Planta Med. 1997. 63:11–14.
Article9. Choi JS, Lee HJ, Lang SS. Alaternin, cassiaside and rubrofusarin-gentibiodise, radical scavenging principles from the seeds of Cassia tora on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. Arch Pharm Res. 1994. 17:462–466.
Article10. Choi HJ. Effects of cephalic glucopenia on insulin and glucagons secretion in central nervous system-intact pancreas perfused rats. Korean Journal of Biomedical Laboratory. 2000. 6:229–235.11. Curry DL. Direct tonic inhibition of insulin secretion by central nervous system. Am J Physiol. 1983. 244:E425–E429.
Article12. Curry DL. Reflex inhibition of insulin secretion: vagus nerve involvement via CNS. Am J Phsiol. 1984. 247:E827–E832.
Article13. Curry DL. Insulin content and insulinogenesis by the perfused rat pancreas: effects of long term glucose stimulation. Endocrinology. 1986. 118:170–175.
Article14. Curry DL, Joy RM, Bennett LL. Magnesium modulation of glucose-induced insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1977. 101:203–208.
Article15. Curry DL, Maclachlan SA. Synthesis-secretion coupling of insulin: effect of aging. Endocrinology. 1987. 121:241–247.16. Curry DL, Morris JG, Rogers QR. Dynamics of insulin and glucagon secretion by the isolated perfused cat pancreas. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1982. 72:333–338.
Article17. Gorsuch AN, Spencer KM, Lister JM, McNally JM, Dean BM, Bottazzo GF, Cudworth AG. Evidence for a long prediabetic period in type I (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1981. 2:1363–1365.18. Hennige AM, Burks DJ, Ozcan U, Kulkarni RN, Ye J, Park S, Schubert M, Fisher TL, Dow MA, Leshan R, Zakaria M, Mossa-Basha M, White MF. Upregulation of insulin receptor substrate-2 in pancreatic β cells prevents diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2003. 112:1521–1532.
Article19. Hsu JH, Wu YC, Liu IM, Cheng JT. Release of acetylcholine to raise insulin secretion in Wistar rats by oleanolic acid, one of the active principles contained in Cornus offcinalis. Neurosci Lett. 2006. 404:112–116.
Article20. Jang DS, Lee GY, Kim YS, Lee YM, Kim CS, Yoo JL, Kim JS. Anthraquinones from the seeds of Cassia tora with inhibitory activity on protein glycation and aldose reductase. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. 30:2207–2210.
Article21. Kim JM, Kim HT, Hwang SM. Instant tea preparation from Cassia tora Seeds. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology. 1990. 22:241–247.22. Kim SH, Choi JS, Moon YH. Antioxidative activity and anticlastogenicity of Cassia tora L. seeds extract and its major component, nor-rubrofusarin-6-β-D-glucoside. Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety. 1998. 13:394–399.23. Kim SH, Ryu DS, Lee MY, Kim KH, Kim YH, Lee DS. Anti-diabetic activity of polysaccharide from Salicornia herbacea. Korean Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2008. 36:43–48.24. Kim SJ, Baek SH, Heo JW, Kim US, Lee JD, Kang GW, Park SH, Han JH, Jeong SY, Lee SH. Effect of Cassia tora L. powder aged-diets on the accumulation of cadmium in rat. Journal of East Asian Society of Dietary Life. 2002. 12:554–565.25. Kim YS, Chun JH, Park JH, Kang CI. Status and associating factors of complementary and alternative medicine among Korean diabetic patients. The Journal of Korean Diabetes Association. 2000. 24:7–89.26. Lee HC, Curry DL, Stern JS. Direct effect of CNS on insulin hypersecretion in obese Zucker rats: involvement of vagus nerve. Am J Physiol. 1989. 256:E439–E444.
Article27. Lee HC, Curry DL, Stern JS. Tonic sympathetic nervous system inhibition of insulin is diminished in obese Zucker rats. Obes Res. 1993. 1:371–376.
Article28. Lee JR. Inquiry into the insulin injection. Korean Clinical Diabetes. 2008. 9:117–122.
Article29. Lim SJ, Han HK. Hypoglycemic effect of fractions of Cassia tora extract in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic Rats. Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition. 1997. 13:23–29.30. Lim SJ, Kim SY, Lee JW. The effects of Korean wild vegetables on blood glucose levels and liver muscle metabolism of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The Korean Journal of Nutrition. 1995. 28:585–594.31. Na GM, Han HS, Ye SH, Kim HK. Extraction characteristics and antioxidative activity of Cassia tora L. extracts. Korean Journal of Food Culture. 2004. 19:499–505.32. Nolan CJ, Madiraju MSR, Delghingaro-Augusto V, Peyot M, Prentki M. Fatty Acid Signaling in the β-cell and Insulin Secretion. Diabetes. 2006. 55:S16–S23.
Article33. Park KJ, Oh YJ, Lee SY, Kim HS, Ha HC. Anti-diabetic effect of crude polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa in KK-Ay diabetic mouse and 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology. 2007. 39:330–335.34. Park S, Dong X, Fisher TL, Dunn S, Omer AK, Weir G, White MF. Exendin-4 Uses Irs2 Signaling to Mediate Pancreatic β-Cell Growth and Function. J Biol Chem. 2006. 281:1159–1168.
Article35. Park SH, Wang SG. A research on anti-diabetic functional food intake of the subjects with type 2 diabetic mellitus in Daejeon. Korean Journal of Human Ecology. 2008. 17:797–805.
Article36. Pørksen N, Hollingdal M, Juhl C, Butler P, Veldhuis JD, Schmitz O. Pulsatile insulin secretion: detection, regulation, and role in diabetes. Diabetes. 2002. 51:S245–S254.
Article37. Rossetti L, Giaccari A, DeFronzo RA. Glucose toxicity. Diabetes Care. 1990. 13:610–630.
Article38. Steele C, Hagopian WA, Gitelman S, Masharani U, Cavaghan M, Rother KI, Donaldson D, Harlan DM, Bluestone J, Herold KC. Insulin secretion in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004. 53:426–433.
Article39. Strandgaard C, Curry DL. Differential insulin secretory responses to cationic and branched-chain amino acids. Pancreas. 1998. 17:65–71.
Article40. Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S. Five Stages of Evolving β-Cell Dysfunction During Progression to Diabetes. Diabetes. 2004. 53:S16–S21.41. Yen GC, Chen HW, Duh PD. Extraction and identification of an antioxidative component from Jue Ming Zi (Cassia tora L.). J Agric Food Chem. 1998. 46:820–824.
Article42. Yibchok-anun S, Adisakwattana A, Moonsan P, Hsu WH. Insulin - secretagogue activity of p-Methoxycinnamic acid in rats, perfused rat pancreas and pancreatic β-Cell line. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008. 102:476–482.
Article43. Yki-Jarvinen H. Glucose toxicity. Endocr Rev. 1992. 13:415–431.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Occurrence of Alternaria cassiae in Seeds of Sickle Senna in Korea
- Effects of insulin and metformin on fetal kidney development of streptozotocin-induced gestational diabetic albino rats
- The Effects of Alisma canaliculatum Butanol Fraction with Selenium on Glycogen Level, Lipid Metabolism and Lipid Peroxidation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Analysis of the Relative Importance of Insulin Resistance and Insulin Secretion Defect by Homeostasis Model Assessment in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Effects of Benincasa hispida Seeds Intake on Blood Glucose and Lipid Levels in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats