J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2011 Dec;37(6):550-555. 10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.6.550.
Analysis of copy number abnormality (CNA) and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in the whole genome using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping arrays in tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Tokyo Dental College, Japan. tkuroiwa@m7.gyao.ne.jp
- KMID: 2136997
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2011.37.6.550
Abstract
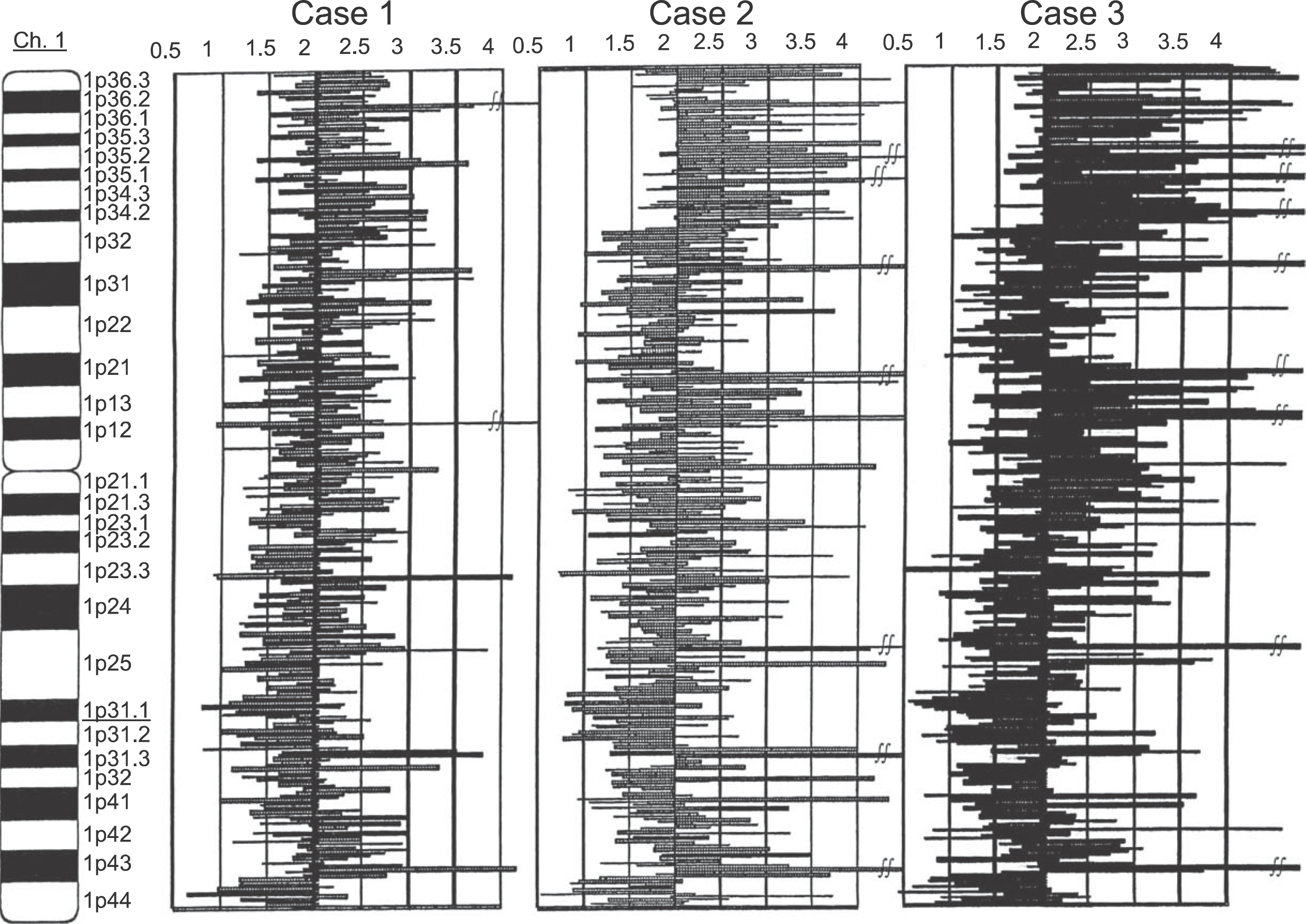
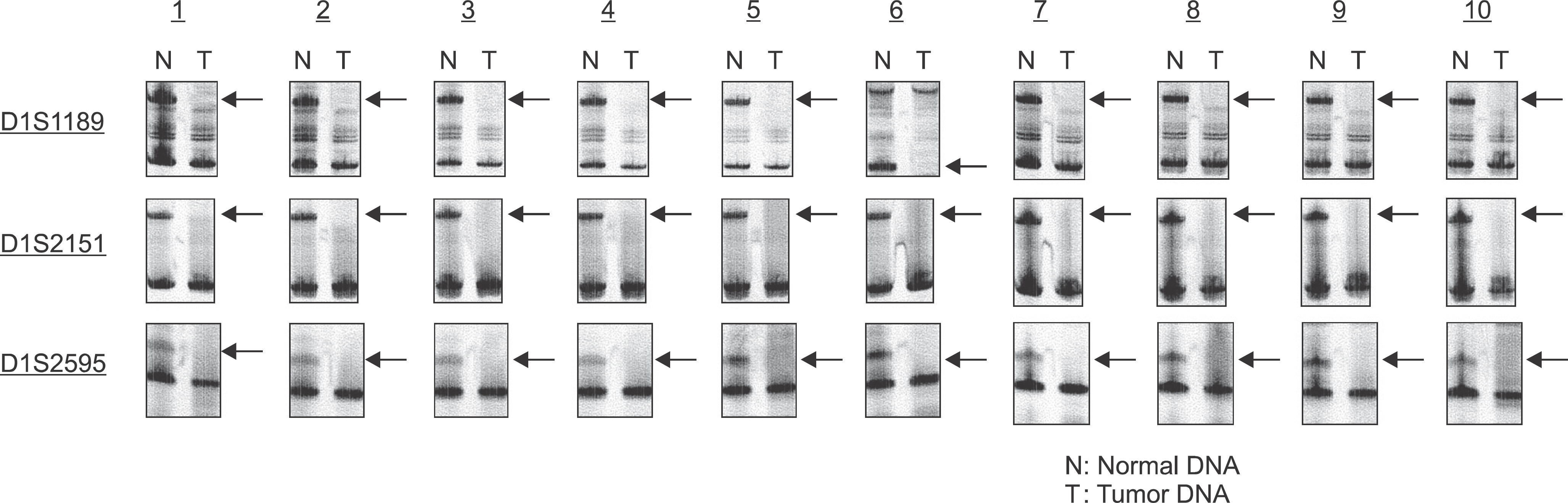
- Chromosomal loss of heterozygosity (LOH) is a common mechanism for the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in human epithelial cancers. LOH patterns can be generated through allelotyping using polymorphic microsatellite markers; however, owing to the limited number of available microsatellite markers and the requirement for large amounts of DNA, only a modest number of microsatellite markers can be screened. Hybridization to single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays using Affymetarix GeneChip Mapping 10 K 2.0 Array is an efficient method to detect genome-wide cancer LOH. We determined the presence of LOH in oral SCCs using these arrays. DNA was extracted from tissue samples obtained from 10 patients with tongue SCCs who presented at the Hospital of Tokyo Dental College. We examined the presence of LOH in 3 of the 10 patients using these arrays. At the locus that had LOH, we examined the presence of LOH using microsatellite markers. LOH analysis using Affymetarix GeneChip Mapping 10K Array showed LOH in all patients at the 1q31.1. The LOH regions were detected and demarcated by the copy number 1 with the series of three SNP probes. LOH analysis of 1q31.1 using microsatellite markers (D1S1189, D1S2151, D1S2595) showed LOH in all 10 patients (100). Our data may suggest that a putative tumor suppressor gene is located at the 1q31.1 region. Inactivation of such a gene may play a role in tongue tumorigenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ogawa S. Analysis of DNA copy number. Blood Frontier. 2006; 16:35–42.2. Yamamoto N, Mizoe JE, Numasawa H, Yokoe H, Uzawa K, Shibahara T, et al. Allelic loss of chromosome 2 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma: correlation with lymph node metastasis. Oral Oncol. 2003; 39:64–8.
Article3. Numasawa H, Yamamoto N, Katakura A, Shibahara T. Loss of heterozygosity and microsatellite instability on chromosome 2q in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2005; 46:17–25.
Article4. Kakimoto Y, Numasawa H, Yamamoto N, Takeda E, Yamauchi T, Shibahara T. Loss of heterozygosity and microsatellite instability on the long arm of chromosome 2 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Jap J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 51:374–81.
Article5. Arai K, Shibahara T, Yamamoto N, Yakushiji T, Tanaka C, Noma H. Frequent allelic loss/imbalance on the short arm of chromosome 3 in tongue cancer. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2001; 42:151–7.
Article6. Arai K, Shibahara T, Yamamoto N, Noma H. The presence of candidate tumor suppressor gene loci at chromosome 3p for oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2002; 38:763–71.
Article7. Yamamoto N, Uzawa K, Miya T, Watanabe T, Yokoe H, Shibahara T, et al. Frequent allelic loss/imbalance on the long arm of chromosome 21 in oral cancer: evidence for three discrete tumor suppressor gene loci. Oncol Rep. 1999; 6:1223–7.
Article8. Yamamoto N, Noma H, Shibahara T. Allelic imbalance on the long arm of chromosome 21 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma: relationship between allelic imbalances (LOH and MSI) and clinicopathologic features. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2001; 42:211–23.
Article9. Huang J, Wei W, Zhang J, Liu G, Bignell GR, Stratton MR, et al. Whole genome DNA copy number changes identified by high density oligonucleotide arrays. Hum Genomics. 2004; 1:287–99.
Article10. Zhao X, Li C, Paez JG, Chin K, Jänne PA, Chen TH, et al. An integrated view of copy number and allelic alterations in the cancer genome using single nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:3060–71.
Article11. Schubert EL, Hsu L, Cousens LA, Glogovac J, Self S, Reid BJ, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis of flow-sorted epithelial cells from frozen versus fixed tissues for whole genome analysis of allelic loss in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 2002; 160:73–9.
Article12. Wang ZC, Lin M, Wei LJ, Li C, Miron A, Lodeiro G, et al. oss of heterozygosity and its correlation with expression profiles in subclasses of invasive breast cancers. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:64–71.13. Paez JG, Lin M, Beroukhim R, Lee JC, Zhao X, Richter DJ, et al. Genome coverage and sequence fidelity of phi29 polymerase-based multiple strand displacement whole genome amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32:e71.14. Primdahl H, Wikman FP, von der Maase H, Zhou XG, Wolf H, Orntoft TF. Allelic imbalances in human bladder cancer: genome-wide detection with high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002; 94:216–23.
Article15. Hoque MO, Lee CC, Cairns P, Schoenberg M, Sidransky D. Genome-wide genetic characterization of bladder cancer: a comparison of high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays and PCR-based microsatellite analysis. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:221622.16. Lieberfarb ME, Lin M, Lechpammer M, Li C, Tanenbaum DM, Febbo PG, et al. Genome-wide loss of heterozygosity analysis from laser capture microdissected prostate cancer using single nucleotide polymorphic allele (SNP) arrays and a novel bioinformatics platform dChipSNP. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:4781–5.17. Dumur CI, Dechsukhum C, Ware JL, Cofield SS, Best AM, Wilkinson DS, et al. Genome-wide detection of LOH in prostate cancer using human SNP microarray technology. Genomics. 2003; 81:260–9.
Article18. Wong KK, Tsang YT, Shen J, Cheng RS, Chang YM, Man TK, et al. Allelic imbalance analysis by high-density single-nucleotide polymorphic allele (SNP) array with whole genome amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32:e69.
Article19. Lindblad-Toh K, Tanenbaum DM, Daly MJ, Winchester E, Lui WO, Villapakkam A, et al. Loss-of-heterozygosity analysis of small-cell lung carcinomas using single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Nat Biotechnol. 2000; 18:1001–5.
Article20. Jänne PA, Li C, Zhao X, Girard L, Chen TH, Minna J, et al. High-resolution single-nucleotide polymorphism array and clustering analysis of loss of heterozygosity in human lung cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 2004; 23:2716–26.
Article21. World Health Organization. International Histological Classification of Tumours. No. 4. Histological Typing of Oral and Oropharyngeal Tumours. Geneva: WHO;1971. p. 9–28.22. UICC: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 4th ed.Berlin: Springer;1987. p. 16–18.23. Zhou X, Mok SC, Chen Z, Li Y, Wong DT. Concurrent analysis of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) and copy number abnormality (CNA) for oral premalignancy progression using the Affymetrix 10K SNP mapping array. Hum Genet. 2004; 115:327–30.
Article24. Wang J, Meza-Zepeda LA, Kresse SH, Myklebost O. M-CGH: analysing microarray-based CGH experiments. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004; 5:74.25. Lin M, Wei LJ, Sellers WR, Lieberfarb M, Wong WH, Li C. dChipSNP: significance curve and clustering of SNP-array-based loss-of-heterozygosity data. Bioinformatics. 2004; 20:1233–40.
Article26. Yamamoto N, Mizoe J, Numasawa H, Tsujii H, Shibahara T, Noma H. Allelic loss on chromosomes 2q, 3p and 21q: possibly a poor prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2003; 39:796–805.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Significance of Previously Cryptic Copy Number Alterations and Loss of Heterozygosity in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Determined Using Combined Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization plus Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Microarray Analyses
- Comparison of the copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity identified from whole-exome sequencing data using three different tools
- Effect of Combining Multiple CNV Defining Algorithms on the Reliability of CNV Calls from SNP Genotyping Data
- Additional Genomic Aberrations Identified by Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Array-Based Karyotyping in an Acute Myeloid Leukemia Case with Isolated del(20q) Abnormality
- Comparison of the Affymetrix SNP Array 5.0 and Oligoarray Platforms for Defining CNV