Electrolyte Blood Press.
2007 Jun;5(1):28-33. 10.5049/EBP.2007.5.1.28.
Regulation of Urea Transporters by Tonicity-responsive Enhancer Binding Protein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. jyjung@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Medicine, University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, USA.
- 3Department of Anatomy, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2134802
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2007.5.1.28
Abstract
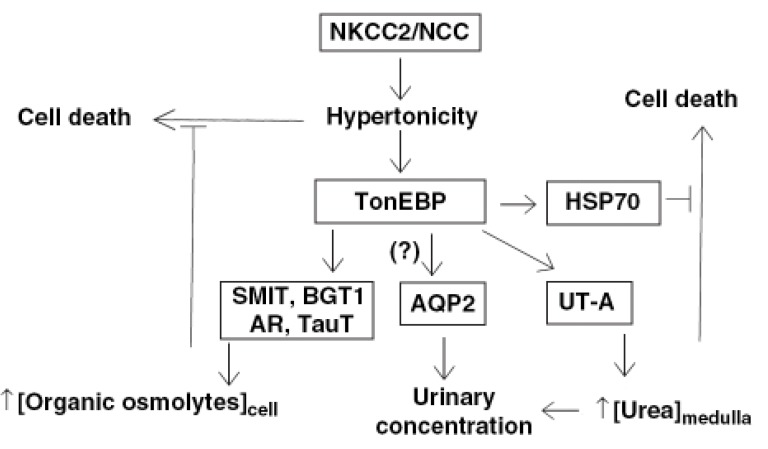
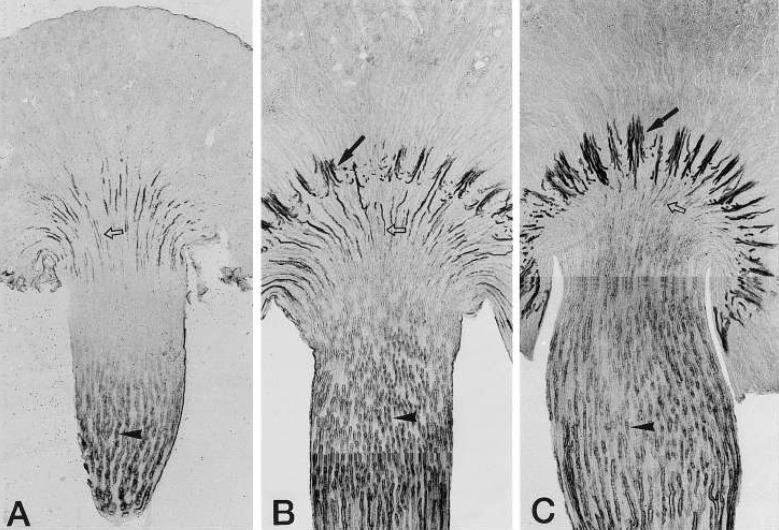
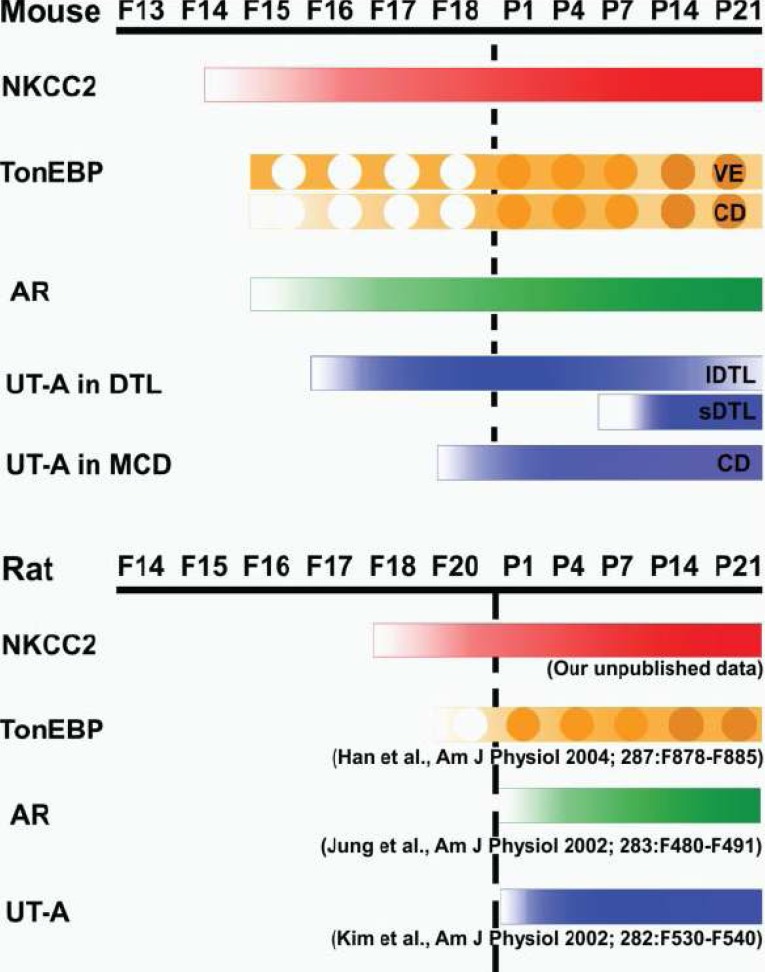
- Urea accumulation in the renal inner medulla plays a key role in the maintenance of maximal urinary concentrating ability. Urea transport in the kidney is mediated by transporter proteins that include renal urea transporter (UT-A) and erythrocyte urea transporter (UT-B). UT-A1 and UT-A2 are produced from the same gene. There is an active tonicity-responsive enhancer (TonE) in the promoter of UT-A1, and the UT-A1 promoter is stimulated by hypertonicity via tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein (TonEBP). The downregulation of UT-A2 raises the possibility that TonEBP also regulates its promoter. There is some evidence that TonEBP regulates expression of UT-A in vivo; (1) during the renal development of the urinary concentrating ability, expression of TonEBP precedes that of UT-A1; (2) in transgenic mice expressing a dominant negative form of TonEBP, expression of UT-A1 and UT-A2 is severely impaired; (3) in treatment with cyclosporine A, TonEBP was significantly downregulated after 28 days. This downregulation involves mRNA levels of UT-A2; (4) in hypokalemic animals, downregulation of TonEBP contributed to the down regulation of UT-A in the inner medulla. These data support that TonEBP directly contributes to the urinary concentration and renal urea recycling by the regulation of urea transporters.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sands JM. Molecular approaches to urea transporters. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:2795–2806. PMID: 12397052.
Article2. Nakayama Y, Peng T, Sands JM, Bagnasco SM. The TonE/TonEBP pathway mediates tonicity-responsive regulation of UT-A urea transporter expression. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:38275–38280. PMID: 10995747.
Article3. Cha JH, Woo SK, Han KH, Kim YH, Handler JS, Kim J, Kwon HM. Hydration status affects nuclear distribution of transcription factor tonicity responsive enhancer binding protein in rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:2221–2230. PMID: 11675398.
Article4. Kim YH, Kim DU, Han KH, Jung JY, Sands JM, Knepper MA, Madsen KM, Kim J. Expression of urea transporters in the developing rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002; 282:F530–F540. PMID: 11832436.5. Han KH, Woo SK, Kim WY, Park SH, Cha JH, Kim J, Kwon HM. Maturation of TonEBP expression in developing rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004; 287:F878–F885. PMID: 15226152.
Article6. Lim SW, Ahn KO, Sheen MR, Jeon US, Kim J, Yang CW, Kwon HM. Downregulation of renal sodium transporters and tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein by long-term treatment with cyclosporin A. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:421–429. PMID: 17202415.
Article7. Lee HW, Kim WY, Song HK, Yang CW, Han KH, Kwon HM, Kim J. Sequential expression of NKCC2, TonEBP, aldose reductase, and urea transporter-A in developing mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007; 292:F269–F277. PMID: 16926446.
Article8. Lam AK, Ko BC, Tam S, Morris R, Yang JY, Chung SK, Chung SS. Osmotic response element-binding protein (OREBP) is an essential regulator of the urine concentrating mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:48048–48054. PMID: 15347663.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-Term Regulation of Renal Urea Transporters during Antidiuresis
- The Abundance and Nuclear Distribution of TonEBP in Response to Changes of Tonicity in Hyperglycemic Cells
- Expression of Tonicity-Responsive Enhancer Binding Protein (TonEBP) in the Rat Cochlea: An Immunohistochemical Study
- The role of tonicity responsive enhancer sites in the transcriptional regulation of human hsp70-2 in response to hypertonic stress
- Nuclear protein binding patterns in the 5'-upstream regulatory elements of HLA class I genes