J Vet Sci.
2015 Dec;16(4):475-481. 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.4.475.
Helicobacter apodemus sp. nov., a new Helicobacter species identified from the gastrointestinal tract of striped field mice in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Developmental Biology and Genomics, College of Veterinary Medicine, BIO-MAX Institute, Program for Cancer Biology, and Interdisciplinary Program for Bioinformatics, BK21Plus Program for Creative Veterinary Science Research, Research Institut
- 2Incheon International Airport Imported Food Inspection Center, Gyeongin Regional Food and Drug Administration, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Incheon 22382, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Veterinary Public Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, BIO-MAX Institute, Program for Cancer Biology, and Interdisciplinary Program for Bioinformatics, BK21Plus Program for Creative Veterinary Science Research, Research Institute for Vete
- 4College of Pharmacy, Gachon University, Incheon 21936, Korea.
- 5College of Veterinary Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju 63241, Korea.
- 6College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 05029, Korea.
- 7Department of Medical Genetics, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon 24252, Korea.
- 8Biomedical Mouse Resource Center, Korea Research Institute for Bioscience and Biotechnology, Ochang 34141, Korea.
- KMID: 2133630
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2015.16.4.475
Abstract
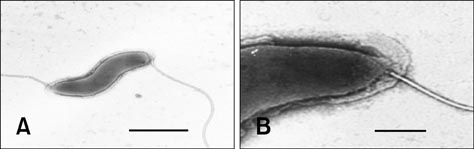
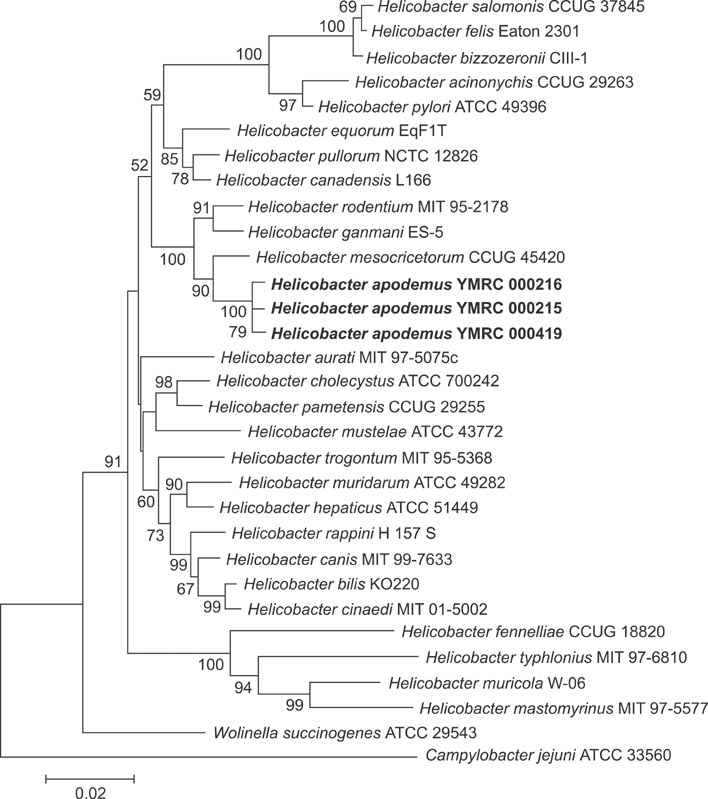
- A novel Helicobacter species was identified from the gastrointestinal tract of the Korean striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius). Biochemical testing, ultrastructure characterization, and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis suggested that this bacterium represents a distinct taxon. The bacterium was positive for urease activity, susceptible to cephalothin and nalidixic acid, and weakly positive for oxidase and catalase activity. Electron microscopy revealed that the bacterium has spirally curved rod morphology with singular bipolar nonsheathed flagella. Genotypically, the isolated bacterial strains (YMRC 000215, YMRC 000216, and YMRC 000419) were most closely related to a reference strain of Helicobacter mesocricetorum (97.25%, 97.32%, and 97.03% 16S rRNA sequence similarities, respectively). The 16S rRNA sequences of these strains were deposited into GenBank under accession numbers AF284754, AY009129, and AY009130, respectively. We propose the name Helicobacter apodemus for this novel species.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Andersen LP, Wadström T. Basic bacteriology and culture. In : Mobley HLT, Mendz GL, Hazell SL, editors. Helicobacter pylori: Physiology and Genetics. Chapt. 4. Washington, D.C.: ASM press;2001.2. Baele M, Decostere A, Vandamme P, Ceelen L, Hellemans A, Mast J, Chiers K, Ducatelle R, Haesebrouck F. Isolation and characterization of Helicobacter suis sp. nov. from pig stomachs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008; 58:1350–1358.
Article3. Bezdekova B, Futas J. Helicobacter species and gastric ulceration in horses: a clinical study. Vet Med (Praha). 2009; 54:577–582.
Article4. Chai JY, Park JH, Jung BK, Guk SM, Kim JL, Shin EH, Klein TA, Kim HC, Chong ST, Baek LJ, Song JW. Echinostome infections in the striped-field mouse, Apodemus agrarius, and the Ussuri white-toothed shrew, Crocidura lasiura, caught near the demilitarized zone, Gyeonggi-do (Province), Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2009; 47:311–314.
Article5. De Groote D, van Doorn LJ, Ducatelle R, Verschuuren A, Tilmant K, Quint WGV, Haesebrouck F, Vandamme P. Phylogenetic characterization of 'Candidatus Helicobacter bovis', a new gastric Helicobacter in cattle. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999; 49:1707–1715.
Article6. Dewhirst FE, Seymour C, Fraser GJ, Paster BJ, Fox JG. Phylogeny of Helicobacter isolates from bird and swine feces and description of Helicobacter pametensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1994; 44:553–560.
Article7. Finegold SM, Martin WJ, Scott EG. Baily and Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;1982. p. 663–673.8. Fox JG, Dewhirst FE, Tully JG, Paster BJ, Yan L, Taylor NS, Collins MJ Jr, Gorelick PL, Ward JM. Helicobacter hepaticus sp. nov., a microaerophilic bacterium isolated from livers and intestinal mucosal scrapings from mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1994; 32:1238–1245.
Article9. Fox JG, Ge Z, Whary MT, Erdman SE, Horwitz BH. Helicobacter hepaticus infection in mice: models for understanding lower bowel inflammation and cancer. Mucosal Immunol. 2011; 4:22–30.
Article10. Fox JG, Yan LL, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Shames B, Murphy JC, Hayward A, Belcher JC, Mendes EN. Helicobacter bilis sp. nov., a novel Helicobacter species isolated from bile, livers, and intestines of aged, inbred mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1995; 33:445–454.
Article11. Franklin CL, Gorelick PL, Riley LK, Dewhirst FE, Livingston RS, Ward JM, Beckwith CS, Fox JG. Helicobacter typhlonius sp. nov., a novel murine urease-negative Helicobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 39:3920–3926.
Article12. Goto K, Jiang W, Zheng Q, Oku Y, Kamiya H, Itoh T, Ito M. Epidemiology of Helicobacter infection in wild rodents in the Xinjiang-Uygur autonomous region of China. Curr Microbiol. 2004; 49:221–223.13. Harris AG, Hinds FE, Beckhouse AG, Kolesnikow T, Hazell SL. Resistance to hydrogen peroxide in Helicobacter pylori: role of catalase (KatA) and Fur, and functional analysis of a novel gene product designated 'KatA-associated protein', KapA (HP0874). Microbiology. 2002; 148:3813–3825.
Article14. Iten A, Graf S, Egger M, Täuber M, Graf J. Helicobacter sp. flexispira bacteremia in an immunocompetent young adult. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 39:1716–1720.
Article15. Johansson SK, Feinstein RE, Johansson KE, Lindberg AV. Occurrence of Helicobacter species other than H. hepaticus in laboratory mice and rats in Sweden. Comp Med. 2006; 56:110–113.16. Jukes TH, Cantor CR. Evolution of protein molecules. In : Munro HN, Allison JB, editors. Mammalian Protein Metabolism. New York: Academic Press;1969. p. 22–132.17. Marshall B, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984; 323:1311–1315.
Article18. O'Rourke JL, Grehan M, Lee A. Non-pylori Helicobacter species in humans. Gut. 2001; 49:601–606.19. Patterson MM, Schrenzel MD, Feng Y, Fox JG. Gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in Syrian hamsters infected with Helicobacter aurati and two other microaerobes. Vet Pathol. 2000; 37:589–596.
Article20. Peters CJ, Simpson GL, Levy H. Spectrum of hantavirus infection: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Annu Rev Med. 1999; 50:531–545.
Article21. Queiroz DM, Contigli C, Coimbra RS, Nogueira AM, Mendes EN, Rocha GA, Moura SB. Spiral bacterium associated with gastric, ileal and caecal mucosa of mice. Lab Anim. 1992; 26:288–294.
Article22. Riley LK, Franklin CL, Hook RR Jr, Besch-Williford C. Identification of murine helicobacters by PCR and restriction enzyme analyses. J Clin Microbiol. 1996; 34:942–946.
Article23. Robertson BR, O'Rourke JL, Vandamme P, On S, Lee A. Helicobacter ganmani sp. nov., a urease-negative anaerobe isolated from the intestines of laboratory mice. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001; 51:1881–1889.
Article24. Robić M, Artuković B, Beck A, Turk R, Belić M, Svetina A, Grabarević Ž. Histopathological changes in the stomachs of wild rodents in Croatia and the first finding of the Helicobacter species. Vet Arh. 2011; 81:415–421.25. Sabbaghian MS, Ranaudo J, Zeng L, Alongi AP, Perez-Perez G, Shamamian P. Identification of Helicobacter spp. in bile and gallbladder tissue of patients with symptomatic gallbladder disease. HPB (Oxford). 2010; 12:129–133.
Article26. Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987; 4:406–425.27. Shen Z, Fox JG, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Foltz CJ, Yan L, Shames B, Perry L. Helicobacter rodentium sp. nov., a urease-negative Helicobacter species isolated from laboratory mice. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997; 47:627–634.
Article28. Shen Z, Xu S, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Pena JA, Modlin IM, Kidd M, Fox JG. A novel enterohepatic Helicobacter species 'Helicobacter mastomyrinus' isolated from the liver and intestine of rodents. Helicobacter. 2005; 10:59–70.
Article29. Simmons JH, Riley LK, Besch-Williford CL, Franklin CL. Helicobacter mesocricetorum sp. nov., a novel Helicobacter isolated from the feces of Syrian hamsters. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:1811–1817.
Article30. Solnick JV. Clinical significance of Helicobacter species other than Helicobacter pylori. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:349–354.
Article31. Strugatsky D, McNulty R, Munson K, Chen CK, Soltis SM, Sachs G, Luecke H. Structure of the proton-gated urea channel from the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 2013; 493:255–258.
Article32. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013; 30:2725–2729.
Article33. Tee W, Leder K, Karroum E, Dyall-Smith M. "Flexispira rappini" bacteremia in a child with pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:1679–1682.
Article34. Ward JM, Anver MR, Haines DC, Melhorn JM, Gorelick P, Yan L, Fox JG. Inflammatory large bowel disease in immunodeficient mice naturally infected with Helicobacter hepaticus. Lab Anim Sci. 1996; 46:15–20.35. Whary MT, Fox JG. Natural and experimental Helicobacter infections. Comp Med. 2004; 54:128–158.36. Won YS, Yoon JH, Lee CH, Kim BH, Hyun BH, Choi YK. Helicobacter muricola sp. nov., a novel Helicobacter species isolated from the ceca and feces of Korean wild mouse (Mus musculus molossinus). FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002; 209:45–51.
Article37. Yoon MH, Jung SJ, Oh HS. Population structure and reproductive pattern of the Korean striped field mouse, apodemus agrarius. Korean J Biol Sci. 1997; 1:53–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intestinal Helminthic Infections in Striped Field Mice, Apodemus agrarius, from Two Southern Regions of Korea
- Helicobacter pylori Eradication Restores the Diversity of Gastric Microbiota
- Do We Have to Treat Helicobacter pylori for Elderly Patients to Prevent Gastric Cancer?
- A New Effective Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication Using a Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker
- Can Helicobacter pylori Eradication Regress Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps?