J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2015 Dec;41(6):327-331. 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.6.327.
Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in a patient with osteoporosis following treatment of testicular cancer: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. yongdae.kwon@gmail.com
- KMID: 2133180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.6.327
Abstract
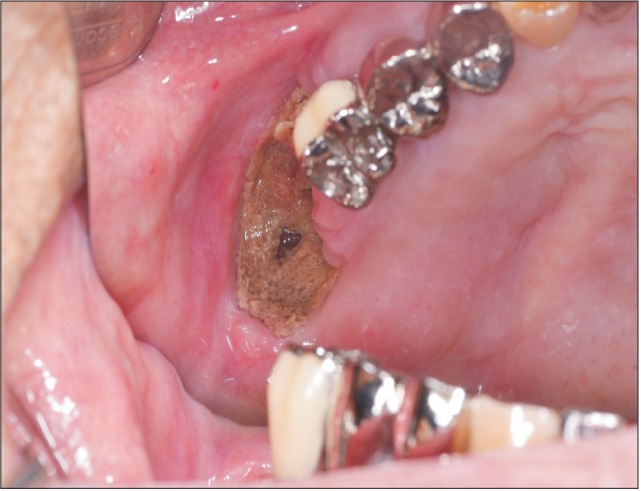
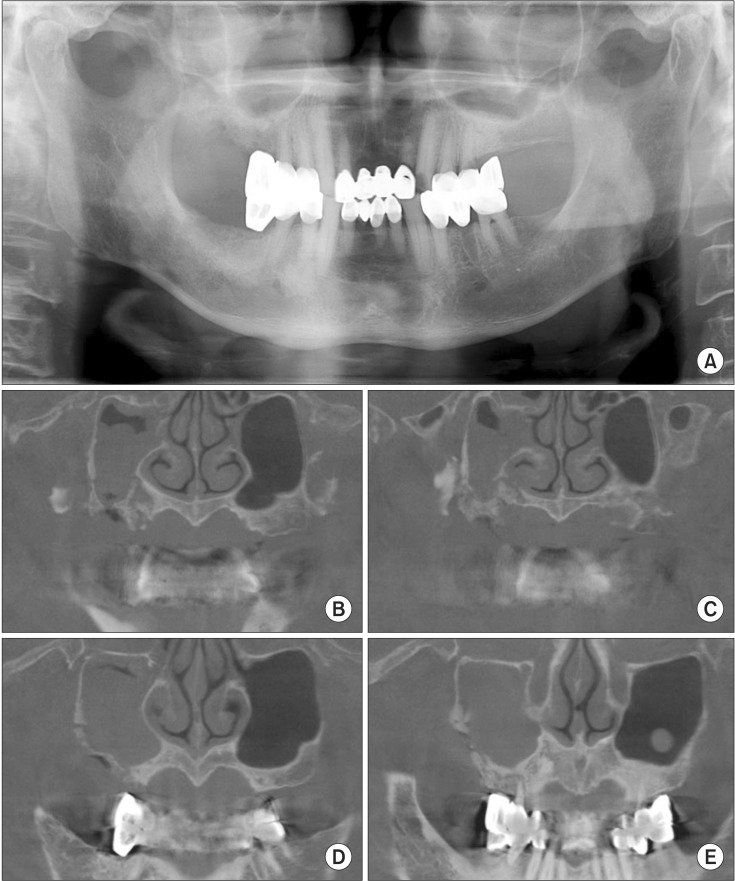
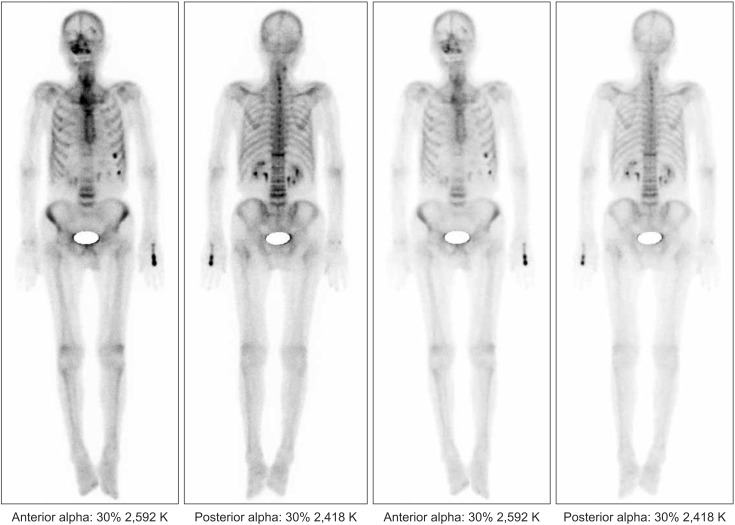
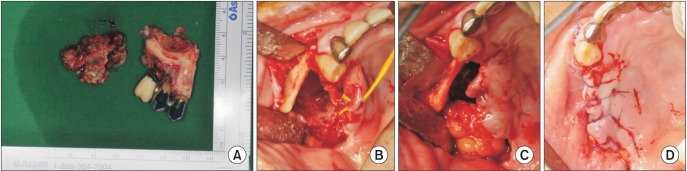
- Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) occurs mainly in female patients. In males the occurrence rate is low, which seems to be related to the low incidence of osteoporosis in men. Unfortunately, BRONJ tends to be ignored in general dental clinics in male patients with a history of osteoporosis treatment. BRONJ occurred in a male patient due to the clinician's lack of interest in the patient's history. In this case, the male patient was on bisphosphonate therapy because of a orchiectomy, and a dental treatment was performed without consideration of his medical history, resulting in BRONJ. We performed careful examinations and treatment with antibiotics and surgical operations. The postoperative healing was successful. In light of this particular case, we concluded that careful listening to the patient's history is very important.
MeSH Terms
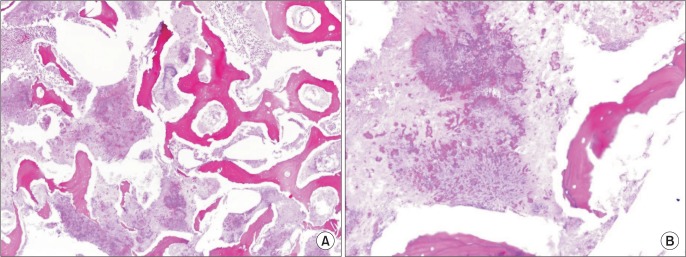
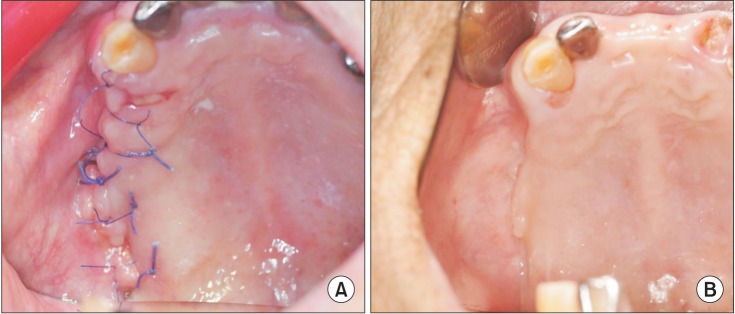
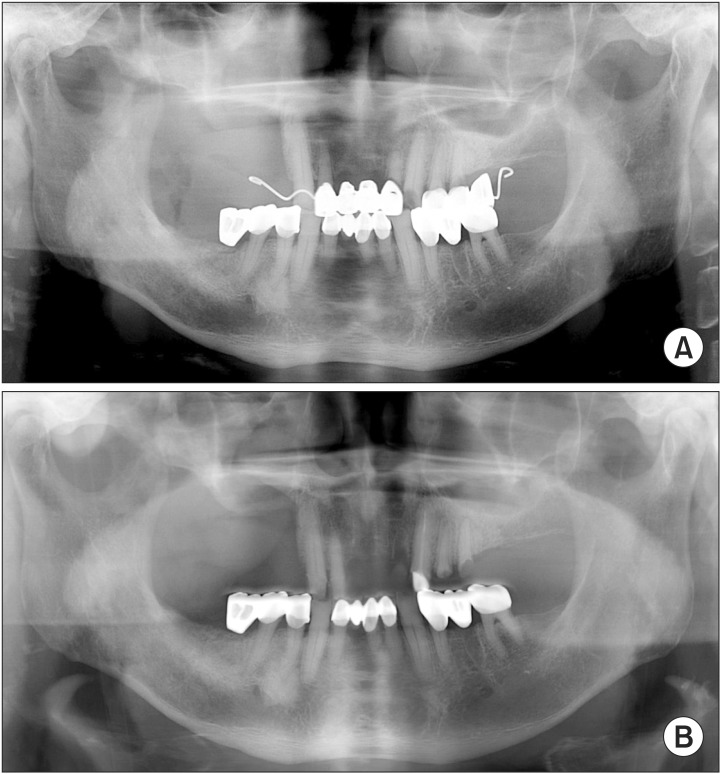
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park YD, Kim YR, Kim DY, Chung YS, Lee JK, Kim YG, et al. Awareness of Korean dentists on bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaws: preliminary report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 35:153–157.2. Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, Goodday R, Aghaloo T, Mehrotra B, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: 2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72:1938–1956. PMID: 25234529.3. Ikebe T. Pathophysiology of BRONJ: drug-related osteoclastic disease of the jaw. Oral Science International. 2013; 10:1–8.
Article4. Ohe JY, Kwon YD, Kim YG, Lee BS, Yoon BW, Choi BJ. Features of histopathologic and radiographic findings in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of jaw: clinical review. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 34:550–554.5. Assaf AT, Smeets R, Riecke B, Weise E, Gröbe A, Blessmann M, et al. Incidence of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in consideration of primary diseases and concomitant therapies. Anticancer Res. 2013; 33:3917–3924. PMID: 24023329.6. Tsao C, Darby I, Ebeling PR, Walsh K, O'Brien-Simpson N, Reynolds E, et al. Oral health risk factors for bisphosphonate-associated jaw osteonecrosis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 71:1360–1366. PMID: 23582590.
Article7. Gielen E, Vanderschueren D, Callewaert F, Boonen S. Osteoporosis in men. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 25:321–335. PMID: 21397201.
Article8. Kaufman JM, Reginster JY, Boonen S, Brandi ML, Cooper C, Dere W, et al. Treatment of osteoporosis in men. Bone. 2013; 53:134–144. PMID: 23201268.
Article9. Maurer P, Sandulescu T, Kriwalsky MS, Rashad A, Hollstein S, Stricker I, et al. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the maxilla and sinusitis maxillaris. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 40:285–291. PMID: 21163624.
Article10. Choi BJ, Kwon YD, Lee BS, Walter C, Nawas BA. Maxillary sinusitis as a complication of oral bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaw: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 35:39–40.11. Khan AM, Sindwani R. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the skull base. Laryngoscope. 2009; 119:449–452. PMID: 19235747.
Article12. Rotaru H, Kim MK, Kim SG, Park YW. Pedicled buccal fat pad flap as a reliable surgical strategy for the treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 73:437–442. PMID: 25544302.
Article13. Farré-Guasch E, Martí-Pagè C, Hernádez-Alfaro F, Klein-Nulend J, Casals N. Buccal fat pad, an oral access source of human adipose stem cells with potential for osteochondral tissue engineering: an in vitro study. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010; 16:1083–1094. PMID: 20078198.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis in a Patient with Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia
- A Case of Sinusitis due to Bisphosphonate Related Osteonecrosis of Jaw
- Clinical feature and treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of jaw about oral bisphosphonate administrated patients: case reports
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Korean Woman with Osteoporosis Treated with Oral Bisphosphonate: Case Report
- A Case of Intractable Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Treated with Teriparatide