Yonsei Med J.
2014 Jul;55(4):886-894. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.886.
A Novel Synthetic Compound 3-Amino-3-(4-Fluoro-Phenyl)-1H-Quinoline-2,4-Dione (KR22332) Exerts a Radioprotective Effect via the Inhibition of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. ostium@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Center for Cell Death Regulating Biodrug, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 4Bio-Organic Science Division, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- 5Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei Head and Neck Cancer Clinic, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2130811
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.886
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Acute side effects of radiation such as oral mucositis are observed in most patients. Although several potential radioprotective agents have been proposed, no effective agent has yet been identified. In this study, we investigated the effectiveness of synthetic compound 3-amino-3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-1H-quinoline-2,4-dione (KR22332) as a radioprotective agent.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell viability, apoptosis, the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential changes, and changes in apoptosis-related signaling were examined in human keratinocyte (HaCaT).
RESULTS
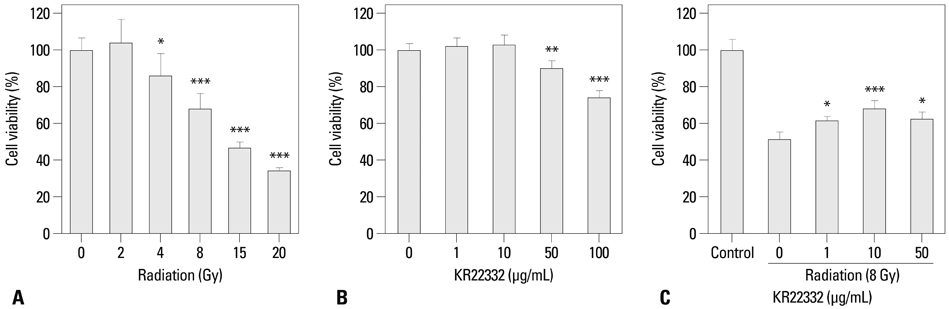
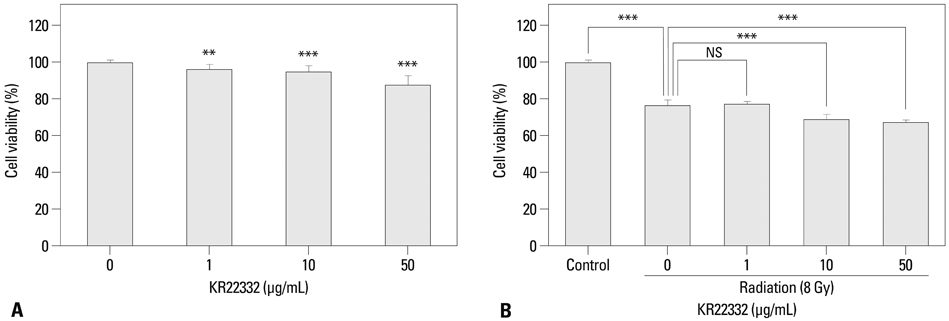
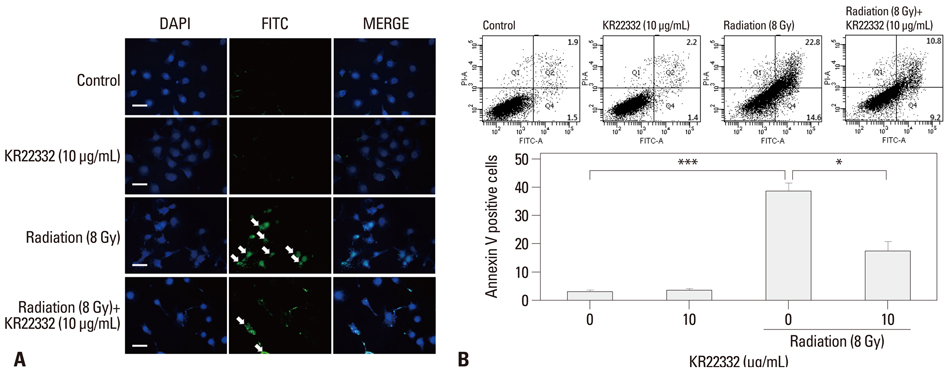
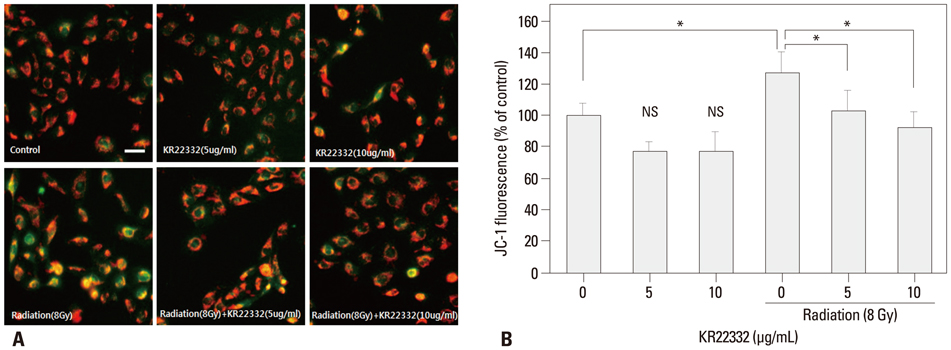
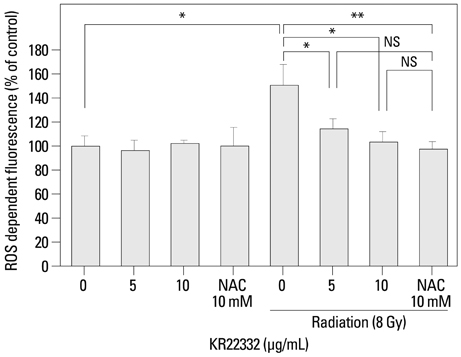
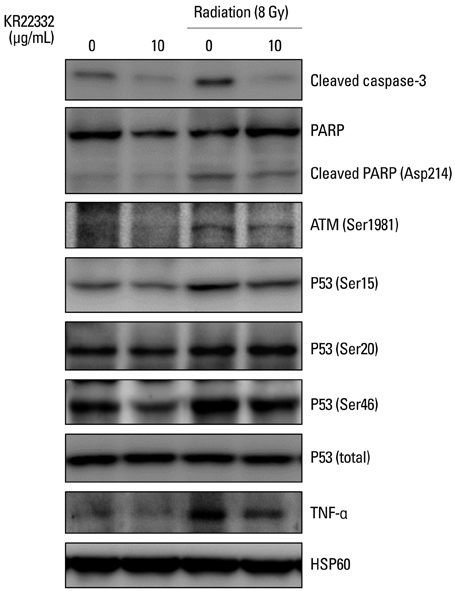
KR22332 inhibited irradiation-induced apoptosis and intracellular ROS generation, and it markedly attenuated the changes in mitochondrial membrane potential in primary human keratinocytes. Moreover, KR22332 significantly reduced the protein expression levels of ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein, p53, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha compared to significant increases observed after radiation treatment.
CONCLUSION
KR22332 significantly inhibited radiation-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes in vitro, indicating that it might be a safe and effective treatment for the prevention of radiation-induced mucositis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis/drug effects/physiology
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Survival/drug effects/physiology
Humans
Keratinocytes/metabolism
Membrane Potential, Mitochondrial/drug effects/physiology
Radiation-Protective Agents/chemistry/*pharmacology
Reactive Oxygen Species/metabolism
Radiation-Protective Agents
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sonis ST, Fey EG. Oral complications of cancer therapy. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002; 16:680–686.2. Denham JW, Hauer-Jensen M. The radiotherapeutic injury--a complex "wound". Radiother Oncol. 2002; 63:129–145.3. Rose-Ped AM, Bellm LA, Epstein JB, Trotti A, Gwede C, Fuchs HJ. Complications of radiation therapy for head and neck cancers. The patient's perspective. Cancer Nurs. 2002; 25:461–467.4. Dörr W, Hamilton CS, Boyd T, Reed B, Denham JW. Radiation-induced changes in cellularity and proliferation in human oral mucosa. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 52:911–917.
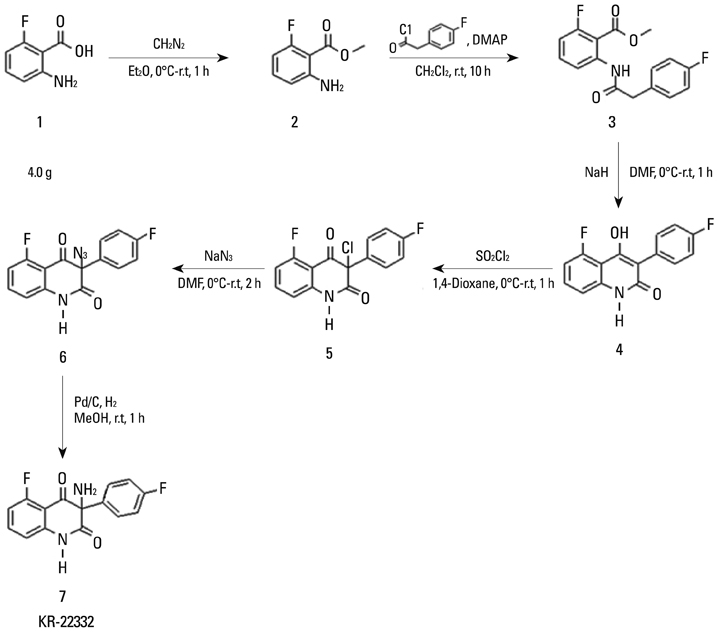
Article5. Shin YS, Song SJ, Kang SU, Hwang HS, Choi JW, Lee BH, et al. A novel synthetic compound, 3-amino-3-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-1H-quinoline-2,4-dione, inhibits cisplatin-induced hearing loss by the suppression of reactive oxygen species: in vitro and in vivo study. Neuroscience. 2012; 232C:1–12.
Article6. Chang JW, Park KH, Hwang HS, Shin YS, Oh YT, Kim CH. Protective effects of Korean red ginseng against radiation-induced apoptosis in human HaCaT keratinocytes. J Radiat Res. 2014; 55:245–256.
Article7. Spielberger R, Stiff P, Bensinger W, Gentile T, Weisdorf D, Kewalramani T, et al. Palifermin for oral mucositis after intensive therapy for hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:2590–2598.
Article8. Buentzel J, Micke O, Adamietz IA, Monnier A, Glatzel M, de Vries A. Intravenous amifostine during chemoradiotherapy for head-and-neck cancer: a randomized placebo-controlled phase III study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 64:684–691.
Article9. Donetti E, Bedoni M, Capone P, Gualerzi A, Tartaglia G, Sforza C. An in vitro model of human oral explants to study early effects of radiation mucositis. Eur J Oral Sci. 2009; 117:169–174.
Article10. Connolly L, Lasarev M, Jordan R, Schwartz JL, Turker MS. Atm haploinsufficiency does not affect ionizing radiation mutagenesis in solid mouse tissues. Radiat Res. 2006; 166(1 Pt 1):39–46.
Article11. Tobita T, Izumi K, Feinberg SE. Development of an in vitro model for radiation-induced effects on oral keratinocytes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 39:364–370.
Article12. Naidu MU, Ramana GV, Rani PU, Mohan IK, Suman A, Roy P. Chemotherapy-induced and/or radiation therapy-induced oral mucositis--complicating the treatment of cancer. Neoplasia. 2004; 6:423–431.
Article13. Chung YM, Park SH, Tsai WB, Wang SY, Ikeda MA, Berek JS, et al. FOXO3 signalling links ATM to the p53 apoptotic pathway following DNA damage. Nat Commun. 2012; 3:1000.
Article14. Korwek Z, Sewastianik T, Bielak-Zmijewska A, Mosieniak G, Alster O, Moreno-Villanueva M, et al. Inhibition of ATM blocks the etoposide-induced DNA damage response and apoptosis of resting human T cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012; 11:864–873.
Article15. Kang SU, Lee BS, Lee SH, Baek SJ, Shin YS, Kim CH. Expression of NSAID-activated gene-1 by EGCG in head and neck cancer: involvement of ATM-dependent p53 expression. J Nutr Biochem. 2013; 24:986–999.
Article16. Makovski A, Yaffe E, Shpungin S, Nir U. Down-regulation of Fer induces ROS levels accompanied by ATM and p53 activation in colon carcinoma cells. Cell Signal. 2012; 24:1369–1374.
Article17. Inagaki-Ohara K, Yada S, Takamura N, Reaves M, Yu X, Liu E, et al. p53-dependent radiation-induced crypt intestinal epithelial cells apoptosis is mediated in part through TNF-TNFR1 system. Oncogene. 2001; 20:812–818.18. Kim JJ, Lee SB, Park JK, Yoo YD. TNF-alpha-induced ROS production triggering apoptosis is directly linked to Romo1 and Bcl-X(L). Cell Death Differ. 2010; 17:1420–1434.19. Curra M, Martins MA, Lauxen IS, Pellicioli AC, Sant'Ana Filho M, Pavesi VC, et al. Effect of topical chamomile on immunohistochemical levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in 5-fluorouracil-induced oral mucositis in hamsters. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013; 71:293–299.
Article20. Gao MC, Jia XD, Wu QF, Cheng Y, Chen FR, Zhang J. Silencing Prx1 and/or Prx5 sensitizes human esophageal cancer cells to ionizing radiation and increases apoptosis via intracellular ROS accumulation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011; 32:528–536.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epilepsy, Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitochondria
- Inhibition of Oxidative Tissue Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction by Glycyrrhizin in the 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease
- Differential Inhibition of MPP+- or 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced Cell Viability Loss in PC12 Cells by Trifluoperazine and W-7
- Cytotoxic Mechanism of FK506 on Human T Lymphocytes
- The role of mitochondrial DNA mutation on neurodegenerative diseases