J Adv Prosthodont.
2013 Aug;5(3):234-240. 10.4047/jap.2013.5.3.234.
A comparison of retentive strength of implant cement depending on various methods of removing provisional cement from implant abutment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Republic of Korea. syshin@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2118161
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2013.5.3.234
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study evaluated the effectiveness of various methods for removing provisional cement from implant abutments, and what effect these methods have on the retention of prosthesis during the definitive cementation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty implant fixture analogues and abutments were embedded in resin blocks. Forty cast crowns were fabricated and divided into 4 groups each containing 10 implants. Group A was cemented directly with the definitive cement (Cem-Implant). The remainder were cemented with provisional cement (Temp-Bond NE), and classified according to the method for cleaning the abutments. Group B used a plastic curette and wet gauze, Group C used a rubber cup and pumice, and Group D used an airborne particle abrasion technique. The abutments were observed using a stereomicroscope after removing the provisional cement. The tensile bond strength was measured after the definitive cementation. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance test (alpha=.05).
RESULTS
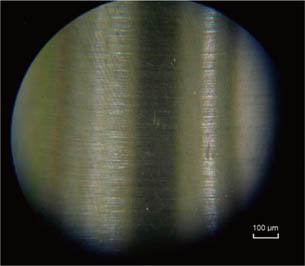
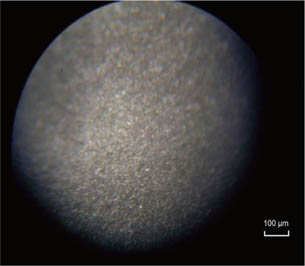
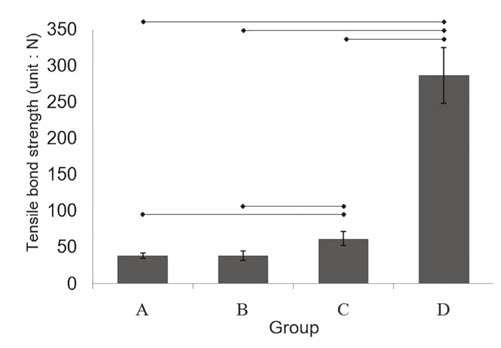
Group B clearly showed provisional cement remaining, whereas the other groups showed almost no cement. Groups A and B showed a relatively smooth surface. More roughness was observed in Group C, and apparent roughness was noted in Group D. The tensile bond strength tests revealed Group D to have significantly the highest tensile bond strength followed in order by Groups C, A and B.
CONCLUSION
A plastic curette and wet gauze alone cannot effectively remove the residual provisional cement on the abutment. The definitive retention increased when the abutments were treated with rubber cup/pumice or airborne particle abraded to remove the provisional cement.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hebel KS, Gajjar RC. Cement-retained versus screw-retained implant restorations: achieving optimal occlusion and esthetics in implant dentistry. J Prosthet Dent. 1997; 77:28–35.2. Chee W, Felton DA, Johnson PF, Sullivan DY. Cemented versus screw-retained implant prostheses: which is better? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999; 14:137–141.3. Taylor TD, Agar JR, Vogiatzi T. Implant prosthodontics: current perspective and future directions. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000; 15:66–75.4. Michalakis KX, Hirayama H, Garefis PD. Cement-retained versus screw-retained implant restorations: a critical review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003; 18:719–728.5. Vigolo P, Givani A, Majzoub Z, Cordioli G. Cemented versus screw-retained implant-supported single-tooth crowns: a 4-year prospective clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004; 19:260–265.6. Weber HP, Sukotjo C. Does the type of implant prosthesis affect outcomes in the partially edentulous patient? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007; 22:140–172.7. Michalakis KX, Pissiotis AL, Hirayama H. Cement failure loads of 4 provisional luting agents used for the cementation of implant-supported fixed partial dentures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000; 15:545–549.8. Breeding LC, Dixon DL, Bogacki MT, Tietge JD. Use of luting agents with an implant system: Part I. J Prosthet Dent. 1992; 68:737–741.9. Mehl C, Harder S, Wolfart M, Kern M, Wolfart S. Retrievability of implant-retained crowns following cementation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008; 19:1304–1311.10. Schneider RL. Evaluation of the retention of castings to endosseous dental implants. J Prosthet Dent. 1987; 58:73–78.11. Rosenstiel SF, Land MF, Fujimoto J. Contemporary fixed prosthodontics. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2006. p. 229.12. Covey DA, Kent DK, St Germain HA Jr, Koka S. Effects of abutment size and luting cement type on the uniaxial retention force of implant-supported crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 2000; 83:344–348.13. Akça K, Iplikçioğlu H, Cehreli MC. Comparison of uniaxial resistance forces of cements used with implant-supported crowns. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002; 17:536–542.14. Juntavee N, Millstein PL. Effect of surface roughness and cement space on crown retention. J Prosthet Dent. 1992; 68:482–486.15. Tuntiprawon M. Effect of tooth surface roughness on marginal seating and retention of complete metal crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1999; 81:142–147.16. Oilo G, Jørgensen KD. The influence of surface roughness on the retentive ability of two dental luting cements. J Oral Rehabil. 1978; 5:377–389.17. Felton DA, Kanoy BE, White JT. The effect of surface roughness of crown preparations on retention of cemented castings. J Prosthet Dent. 1987; 58:292–296.18. Ayad MF, Rosenstiel SF, Salama M. Influence of tooth surface roughness and type of cement on retention of complete cast crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1997; 77:116–121.19. Ramp MH, Dixon DL, Ramp LC, Breeding LC, Barber LL. Tensile bond strengths of provisional luting agents used with an implant system. J Prosthet Dent. 1999; 81:510–514.20. Grasso CA, Caluori DM, Goldstein GR, Hittelman E. In vivo evaluation of three cleansing techniques for prepared abutment teeth. J Prosthet Dent. 2002; 88:437–441.21. Erkut S, Küçükesmen HC, Eminkahyagil N, Imirzalioglu P, Karabulut E. Influence of previous provisional cementation on the bond strength between two definitive resin-based luting and dentin bonding agents and human dentin. Oper Dent. 2007; 32:84–93.22. Peutzfeldt A, Asmussen E. Influence of eugenol-containing temporary cement on efficacy of dentin-bonding systems. Eur J Oral Sci. 1999; 107:65–69.23. Lingard GL, Davies EH, von Fraunhofer JA. The interaction between lining materials and composite resin restorative materials. J Oral Rehabil. 1981; 8:121–129.24. Marshall SJ, Marshall GW Jr, Harcourt JK. The influence of various cavity bases on the micro-hardness of composites. Aust Dent J. 1982; 27:291–295.25. Kanakuri K, Kawamoto Y, Matsumura H. Influence of temporary cement remnant and surface cleaning method on bond strength to dentin of a composite luting system. J Oral Sci. 2005; 47:9–13.26. Koka S, Ewoldsen NO, Dana CL, Beatty MW. The effect of cementing agent and technique on the retention of a CeraOne gold cylinder: a pilot study. Implant Dent. 1995; 4:32–35.27. Dudley JE, Richards LC, Abbott JR. Retention of cast crown copings cemented to implant abutments. Aust Dent J. 2008; 53:332–339.28. Button GL, Barnes RF, Moon PC. Surface preparation and shear bond strength of the casting-cement interface. J Prosthet Dent. 1985; 53:34–38.29. Cobb DS, Vargas MA, Fridrich TA, Bouschlicher MR. Metal surface treatment: characterization and effect on compositeto-metal bond strength. Oper Dent. 2000; 25:427–433.30. Al-Zain SA. The effect of different metal cleaning methods on retention of cast crowns. Egypt Dent J. 2006; 52:2087–2092.31. Mosharraf R. A simple method for cleaning zinc oxide-eugenol provisional cement residues from the intaglio surface of casting restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 91:200.32. Homiak AW, Cook PA, DeBoer J. Effect of hygiene instrumentation on titanium abutments: a scanning electron microscopy study. J Prosthet Dent. 1992; 67:364–369.33. Speelman JA, Collaert B, Klinge B. Evaluation of different methods to clean titanium abutments. A scanning electron microscopic study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1992; 3:120–127.34. Brookshire FV, Nagy WW, Dhuru VB, Ziebert GJ, Chada S. The qualitative effects of various types of hygiene instrumentation on commercially pure titanium and titanium alloy implant abutments: an in vitro and scanning electron microscope study. J Prosthet Dent. 1997; 78:286–294.35. Mengel R, Buns CE, Mengel C, Flores-de-Jacoby L. An in vitro study of the treatment of implant surfaces with different instruments. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998; 13:91–96.36. Bain CA. An in vitro and in vivo evaluation of various implant-cleaning instruments. Quintessence Int. 1998; 29:423–427.37. Razzoog ME, Koka S. In vitro analysis of the effects of two air-abrasive prophylaxis systems and inlet air pressure on the surface of titanium abutment cylinders. J Prosthodont. 1994; 3:103–107.38. Augthun M, Tinschert J, Huber A. In vitro studies on the effect of cleaning methods on different implant surfaces. J Periodontol. 1998; 69:857–864.39. Dario LJ. Implant angulation and position and screw or cement retention: clinical guidelines. Implant Dent. 1996; 5:101–104.40. Kreisler M, Kohnen W, Christoffers AB, Götz H, Jansen B, Duschner H, d'Hoedt B. In vitro evaluation of the biocompatibility of contaminated implant surfaces treated with an Er : YAG laser and an air powder system. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005; 16:36–43.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A modified technique for extraoral cementation of implant retained restorations for preventing excess cement around the margins
- A literature review on cementation of implant prosthesis
- Effects of various cements and thermocycling on retentive strengths of cemented implant-supported prostheses
- Effect of different surface treatments on the shear bond strength of luting cements used with implant-supported prosthesis: An in vitro study
- A technique for fabricating abutment replica with hot melt adhesive material to minimize residual cement in implant restoration: a case report