Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Sep;8(3):275-280. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.275.
Prognostic Significance of Serine-Phosphorylated STAT3 Expression in pT1-T2 Oral Tongue Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosciences DNS, Otolaryngology Section, University of Padova, Padova, Italy. elena.fasanaro@alice.it
- 2Department of Neurosciences DNS, Otolaryngology Section, Treviso Hospital Branch, University of Padova, Treviso, Italy.
- 3Department of Medicine DIMED, University of Padova, Padova, Italy.
- 4School of Dentistry, University of Padova, Padova, Italy.
- 5Department of Neurosciences, Odontostomatology Institute, University of Padova, Padova, Italy.
- KMID: 2117524
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.275
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Phosphorylated (activated) STAT3 (pSTAT3) is a regulator of numerous genes that play an essential part in the onset, development and progression of cancer; it is involved in cell proliferation and preventing apoptosis, and in invasion, angiogenesis, and the evasion of immune surveillance. This study aimed mainly to investigate the potential prognostic role of pSTAT3 expression in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
METHODS
Phospho-ser727 STAT3 immunolabeling was correlated with prognostic parameters in 34 consecutive cases of pT1-T2 tongue SCCs undergoing primary surgery. Computer-based image analysis was used for the immunohistochemical reactions analysis.
RESULTS
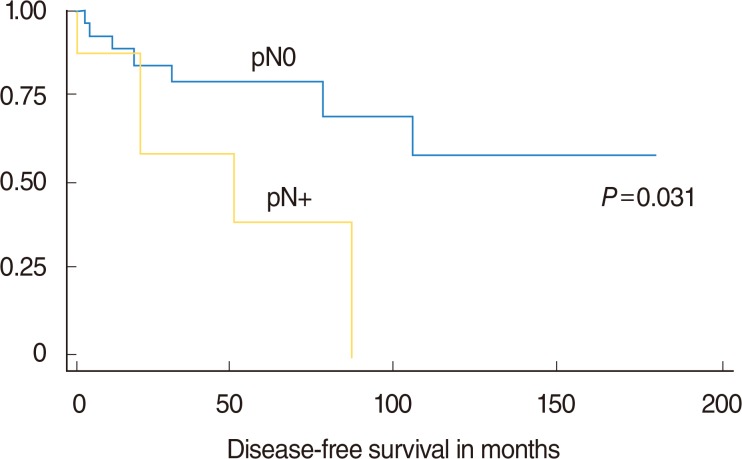
Statistical analysis showed a difference in disease-free survival (DFS) when patients were stratified by pN status (P=0.031). Most tumors had variable degrees (mean+/-SD, 80.7%+/-23.8%) of intense nuclear immunoreaction to pSTAT3. Our findings rule out any significant association of serine-phosphorylated nuclear STAT3 expression with tumor stage, grade, lymph node metastasis, recurrence rate, or DFS.
CONCLUSION
In spite of these results, it is worth further investigating the role of pSTAT3 (serine- and tyrosine-pSTAT3) in oral tongue SCC in larger series because preclinical models are increasingly showing that several anticancer strategies would benefit from STAT3 phosphorylation inhibition.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010; 12. 127(12):2893–2917. PMID: 21351269.
Article2. Wang X, Crowe PJ, Goldstein D, Yang JL. STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in human cancers (review). Int J Oncol. 2012; 10. 41(4):1181–1191. PMID: 22842992.3. Manni S, Brancalion A, Mandato E, Tubi LQ, Colpo A, Pizzi M, et al. Protein kinase CK2 inhibition down modulates the NF-κB and STAT3 survival pathways, enhances the cellular proteotoxic stress and synergistically boosts the cytotoxic effect of bortezomib on multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma cells. PLoS One. 2013; 9. 8(9):e75280. PMID: 24086494.
Article4. Siveen KS, Sikka S, Surana R, Dai X, Zhang J, Kumar AP, et al. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014; 1845:136–154. PMID: 24388873.
Article5. Dobi E, Monnien F, Kim S, Ivanaj A, N'Guyen T, Demarchi M, et al. Impact of STAT3 phosphorylation on the clinical effectiveness of anti-EGFR-based therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2013; 3. 12(1):28–36. PMID: 23083634.
Article6. Marioni G, Nucci R, Marino F, Cappellesso R, Pillon M, Zanoletti E, et al. Evaluation of the prognostic role of pSTAT3 expression in temporal bone squamous cell carcinoma. Otol Neurotol. 2013; 10. 34(8):1476–1482. PMID: 24005169.
Article7. Tsien CI, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Ramanand SG, Chepeha DB, Worden FP, et al. Effect of erlotinib on epidermal growth factor receptor and downstream signaling in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2013; 9. 35(9):1323–1330. PMID: 22907806.
Article8. Marioni G, Staffieri A, Fasanaro E, Stramare R, Giacomelli L, Bernardi E, et al. The role of angiogenin in pT1-T2 tongue carcinoma neo-angiogenesis and cell proliferation: an exploratory study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2013; 9. 42(8):606–611. PMID: 23432607.
Article9. Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C, editors. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 7th ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell;2009.10. National Comprehensive Cancer Network clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Head and neck cancers. ver. 2. 2013 [Internet]. Fort Wathington: National Comprehensive Cancer Network;c2015. cited 2015 Jun 10. Available from: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp.11. Rosato A, Menin C, Boldrin D, Dalla Santa S, Bonaldi L, Scaini MC, et al. Survivin expression impacts prognostically on NSCLC but not SCLC. Lung Cancer. 2013; 2. 79(2):180–186. PMID: 23218791.
Article12. Garcia R, Bowman TL, Niu G, Yu H, Minton S, Muro-Cacho CA, et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation of human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2001; 5. 20(20):2499–2513. PMID: 11420660.
Article13. de Sousa SF, Gleber-Netto FO, de Oliveira-Neto HH, Batista AC, Nogueira Guimarães, de Aguiar MC. Lymphangiogenesis and podoplanin expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma and the associated lymph nodes. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2012; 12. 20(6):588–594. PMID: 22495364.
Article14. Song JI, Grandis JR. STAT signaling in head and neck cancer. Oncogene. 2000; 5. 19(21):2489–2495. PMID: 10851047.
Article15. Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer: new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 2. 4(2):97–105. PMID: 14964307.16. Buettner R, Mora LB, Jove R. Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 2002; 4. 8(4):945–954. PMID: 11948098.17. Li L, Shaw PE. Autocrine-mediated activation of STAT3 correlates with cell proliferation in breast carcinoma lines. J Biol Chem. 2002; 5. 277(20):17397–17405. PMID: 11859072.
Article18. Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Chakraborty A, Zhou MY, Zeng Q, Pitt AS, et al. Requirement of Stat3 but not Stat1 activation for epidermal growth factor receptor- mediated cell growth in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1998; 10. 102(7):1385–1392. PMID: 9769331.
Article19. Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Zeng Q, Watkins SC, Melhem MF, Endo S, et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling abrogates apoptosis in squamous cell carcinogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 4. 97(8):4227–4232. PMID: 10760290.
Article20. Grandis JR, Tweardy DJ. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 1993; 8. 53(15):3579–3584. PMID: 8339264.21. Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, Day R, Holst VA, Wagener MM, et al. Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 6. 90(11):824–832. PMID: 9625170.22. Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Barnes EL, Tweardy DJ. Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 1996; 9. 78(6):1284–1292. PMID: 8826952.23. Naher L, Kiyoshima T, Kobayashi I, Wada H, Nagata K, Fujiwara H, et al. STAT3 signal transduction through interleukin-22 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2012; 11. 41(5):1577–1586. PMID: 22922995.
Article24. Seethala RR, Gooding WE, Handler PN, Collins B, Zhang Q, Siegfried JM, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of phosphotyrosine signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine signaling pathways in head and neck cancers and metastatic lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 3. 14(5):1303–1309. PMID: 18316548.
Article25. Macha MA, Matta A, Kaur J, Chauhan SS, Thakar A, Shukla NK, et al. Prognostic significance of nuclear pSTAT3 in oral cancer. Head Neck. 2011; 4. 33(4):482–489. PMID: 20652980.
Article26. Zhao Y, Zhang J, Xia H, Zhang B, Jiang T, Wang J, et al. Stat3 is involved in the motility, metastasis and prognosis in lingual squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012; 6. 30(4):340–346. PMID: 22302289.
Article27. Sriuranpong V, Park JI, Amornphimoltham P, Patel V, Nelkin BD, Gutkind JS. Epidermal growth factor receptor-independent constitutive activation of STAT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by the autocrine/paracrine stimulation of the interleukin 6/gp130 cytokine system. Cancer Res. 2003; 6. 63(11):2948–2956. PMID: 12782602.28. Squarize CH, Castilho RM, Sriuranpong V, Pinto DS Jr, Gutkind JS. Molecular cross-talk between the NFkappaB and STAT3 signaling pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia. 2006; 9. 8(9):733–746. PMID: 16984731.29. Xi S, Zhang Q, Dyer KF, Lerner EC, Smithgall TE, Gooding WE, et al. Src kinases mediate STAT growth pathways in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Biol Chem. 2003; 8. 278(34):31574–31583. PMID: 12771142.
Article30. Arredondo J, Chernyavsky AI, Jolkovsky DL, Pinkerton KE, Grando SA. Receptor-mediated tobacco toxicity: cooperation of the Ras/Raf-1/MEK1/ERK and JAK-2/STAT-3 pathways downstream of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in oral keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2006; 10. 20(12):2093–2101. PMID: 17012261.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase Activation Is Required for Serine 727 Phosphorylation of STAT3 in Schwann Cells in vitro and in vivo
- Activated Rac1 regulates the degradation of IκBα and the nuclear translocation of STAT3–NFκB complexes in starved cancer cells
- Enhanced Protein Expression of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 and Protein Kinase Substrate p36 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The Expression of STAT3 in Skin Tumors
- Expression of E-Cadherin and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue