Tuberc Respir Dis.
2007 Feb;62(2):144-148. 10.4046/trd.2007.62.2.144.
Acute Respiratory Failure Developed in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Gefitinib
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, South Korea. jsryu@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, South Korea.
- KMID: 2114603
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2007.62.2.144
Abstract
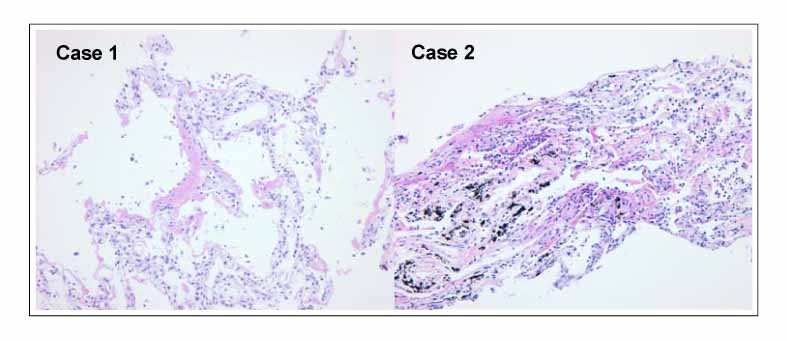
- Gefitinib is an oral selective inhibitor that targets the tyrosine kinase of the epidermal growth factor receptor. The prevalence of interstitial lung disease is 2% in Japan and 0.3% in the USA with a mortality rate of up to one third. We describe two non-small cell lung cancer patients who developed acute respiratory failure after gefitinib, and suggest that clinicians take extreme caution when deciding to treat patients with gefitinib.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ando M, Okamoto I, Yamamoto N, Takeda K, Tamura K, Seto T, et al. Predictive factors for interstitial lung disease, antitumor response, and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:2549–2556.2. Cohen MH, Williams GA, Sridhara R, Chen G, McGuinn WD Jr, Morse D, et al. United States Food and Drug Administration Drug Approval summary: Gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) tablets. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:1212–1218.3. Takano T, Ohe Y, Kusumoto M, Tateishi U, Yamamoto S, Nokihara H, et al. Risk factors for interstitial lung disease and predictive factors for tumor response in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with gefitinib. Lung Cancer. 2004. 45:93–104.4. Inoue A, Saijo Y, Maemondo M, Gomi K, Tokue Y, Kimura Y, et al. Severe acute interstitial pneumonia and gefitinib. Lancet. 2003. 361:137–139.5. Seto T, Seki N, Uematsu K, Tanigaki T, Shioya S, Koboyashi T, et al. Gefitinib-induced lung injury successfully treated with high-dose corticosteroids. Respirology. 2006. 11:113–116.6. Ohyanagi F, Ando Y, Nagashima F, Narabayashi M, Sasaki Y. Acute gefitinib-induced pneumonitis. Int J Clin Oncol. 2004. 9:406–409.7. Rabinowits G, Herchenhorn D, Rabinowits M, Weatge D, Torres W. Fatal pulmonary toxicity in a patient treated with gefitinib for non-small cell lung cancer after previous hemolytic-uremic syndrome due to gemcitabine. Anticancer Drugs. 2003. 14:665–668.8. Ieki R, Saitoh E, Shibuya M. Acute lung injury as a possible adverse drug reaction related to gefitinib. Eur Respir J. 2003. 22:179–181.9. Okamoto I, Fujii K, Matsumoto M, Terasaki Y, Kihara N, Kohrogi H, et al. Diffuse alveolar damage after ZD1839 therapy in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2003. 40:339–342.10. Inomata S, Takahashi H, Nagata M, Yamada G, Shiratori M, Tanaka H, et al. Acute lung injury as an adverse event of gefitinib. Anticancer Drugs. 2004. 15:461–467.11. Nagaria NC, Cogswell J, Choe JK, Kasimis B. Side effects and good effects from new chemotherapeutic agents: case 1. Gefitinib-induced interstitial fibrosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:2423–2424.12. Sumpter K, Harper-Wynne C, O'Brien M, Congleton J. Severe acute interstitial pneumonia and gefitinib. Lung Cancer. 2004. 43:367–368.13. Suzuki H, Aoshiba K, Yokohori N, Nagai A. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition augments a murine model of pulmonary fibrosis. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:5054–5059.14. Ishii Y, Fujimoto S, Fukuda T. Gefitinib prevents bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. 174:550–556.15. Fujiwara Y, Kiura K, Toyooka S, Takigawa N, Tokumo M, Hotta K, et al. Relationship between epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and the severity of adverse events by gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2006. 52:99–103.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gefitinib-induced Acute Fatal Respiratory Failure in a Woman who Never Smoked and had Adenocarinoma of the Lung with EGFR Mutation
- A case of leptomeningeal metastasis from adenocarcinoma of the lung improved by treatment with Gefitinib
- The Effectiveness of Gefitinib on Spinal Metastases of Lung Cancer: Report of Two Cases
- Comparison of Gefitinib versus Docetaxel in Patients with Pre-Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Gefitinib-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease in Korean Lung Cancer Patients