J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Feb;42(1):98-105. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.1.98.
Scoliosis Correction with Thoracic Pedicle Screws: Posteroanterior C-arm Rotation Method
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, Ulsan University, Korea. cslee@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2106382
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.1.98
Abstract
-
Purpose: This study evaluated a practical, safe and accurate method of thoracic pedicle screw insertion for the surgical treatment of scoliosis using the posteroanterior C-arm fluoroscopy rotation method.
Materials and Methods
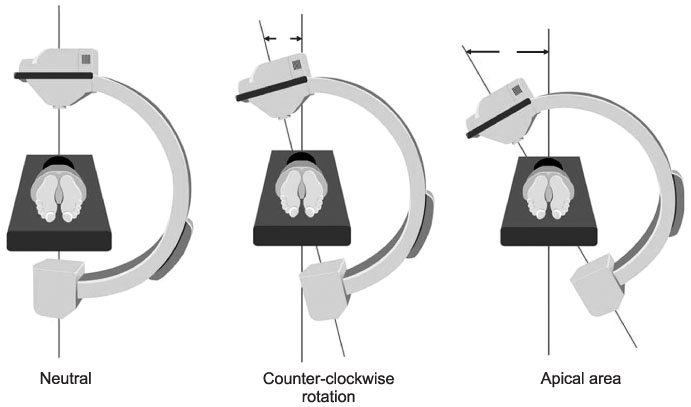
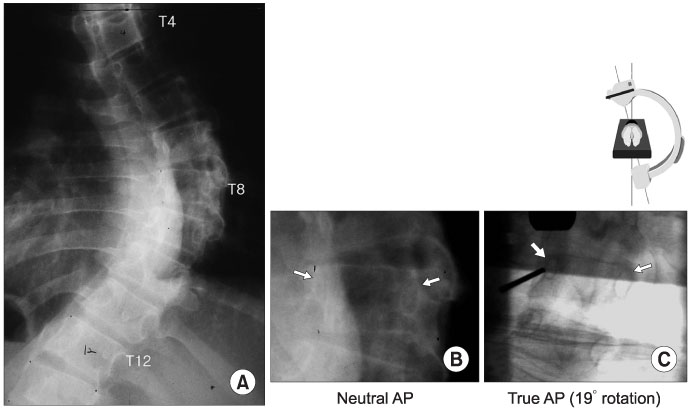
A total of 611 thoracic pedicle screws were inserted in 45 patients using the posteroanterior (PA) C-arm rotation method. CT scans were taken postoperatively in the transverse and sagittal sections to evaluate the pedicle screw placement.
Results
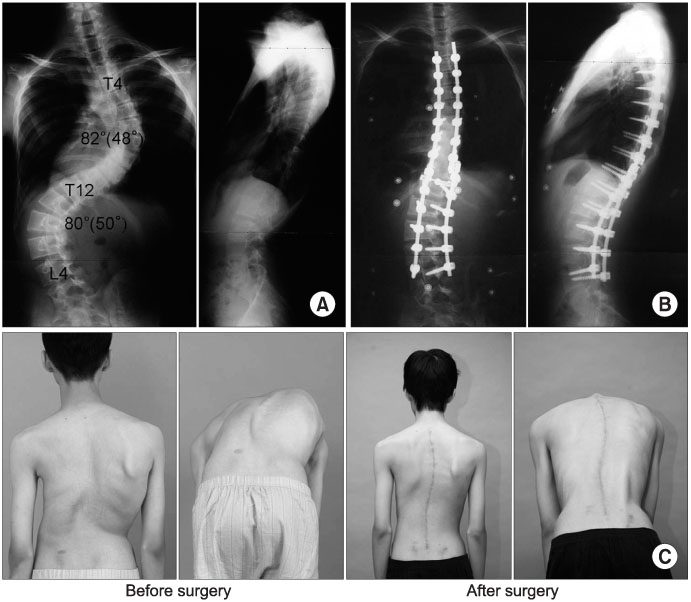
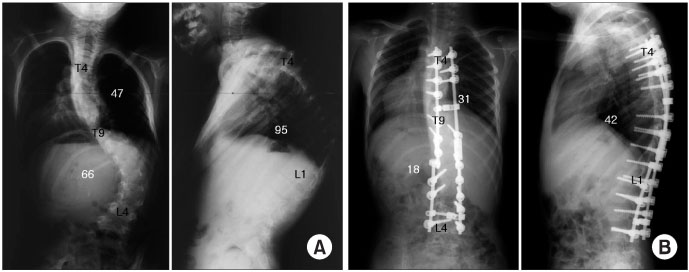
A mean preoperative curve of 57.7o was corrected to 17.1o (range, 3o-45o) in the coronal plane. The postoperative CT scans revealed that 10 screws (1.6%) had penetrated the medial cortex by a mean distance of 3.0 mm and 56 screws (9.2%) penetrated the lateral cortex by a mean distance of 3.5 mm. No screw penetrated the inferior or superior cortex in the sagittal plane. However, 21 screws (3.4%) penetrated the anterior cortex. No neurological or vascular complications were encountered, and none of the screws required replacement.
Conclusion
Thoracic pedicle screw insertion in scoliosis patients using the posteroanterior C-arm rotation method is a practical, simple and safe technique that allows the en face visualization of both pedicles by rotating the C-arm to compensate for the rotational deformity.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, Dhawan A, Polly DW Jr. In vivo accuracy of thoracic pedicle screws. Spine. 2001. 26:2340–2346.
Article2. Cinotti G, Gumina S, Ripani M, Postacchini F. Pedicle instrumentation in the thoracic spine. A morphometric and cadaveric study for placement of screws. Spine. 1999. 24:114–119.3. Ebraheim NA, Jabaly G, Xu R, Yeasting RA. Anatomic relations of the thoracic pedicle to the adjacent neural structures. Spine. 1997. 22:1553–1556.
Article4. Foley KT, Simon DA, Rampersaud YR. Virtual fluoroscopy: computer-assisted fluoroscopic navigation. Spine. 2001. 26:347–351.
Article5. Gertzbein SD, Robbins SE. Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine. 1990. 15:11–14.
Article6. Kim KD, Patrick Johnson J, Bloch BS O, Masciopinto JE. Computer-assisted thoracic pedicle screw placement: an in vitro feasibility study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:360–364.7. Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cho YS, Riew KD. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine. 2004. 29:333–342.
Article8. Lenke LG, Rinella A, Kim YJ. Freehand thoracic pedicle screw placement. Seminars in Spine Surgery. 2002. 14:48–57.9. Liljenqvist UR, Allkemper T, Hackenberg L, link TM, Steinbeck J, Halm HF. Analysis of vertebral morphology in idiopathic scoliosis with use of magnetic resonance imaging and multiplanar reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:359–368.
Article10. Liljenqvist U, Hackenberg L, Link T, Halm H. Pullout strength of pedicle screws versus pedicle and laminar hooks in the thoracic spine. Acta Orthop Belg. 2001. 67:157–163.11. Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM. Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1997. 22:2239–2245.
Article12. Liljenqvist U, Lepsien U, Hackenberg L, Niemeyer T, Halm H. Comparative analysis of pedicle screw and hook instrumentation in posterior correction and fusion of idiopathic thoracic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2002. 11:336–343.
Article13. Liljenqvist UR, Link TM, Halm HF. Morphometric analysis of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2000. 25:1247–1253.
Article14. Mirza SK, Wiggins GC, Kuntz C 4th, et al. Accuracy of thoracic vertebral body screw placement using standard fluoroscopy, fluoroscopic image guidance, and computed tomographic image guidance: a cadaver study. Spine. 2003. 28:402–413.15. O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Mardjetko S, et al. Pedicle morphology in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: is pedicle fixation an anatomically viable technique? Spine. 2000. 25:2285–2293.16. Rampersaud YR. Advanced image guidance for the placement of thoracic pedicle screws. Seminars in Spine Surgery. 2002. 14:58–65.17. Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Kim JH, Chung ER. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities: are they really safe? Spine. 2001. 26:2049–2057.18. Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Balderston RA, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part II: An anatomical and radiographic assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:1200–1206.19. Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Ou Y, Yeasting RA. Anatomic considerations of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine. Roy-Camille technique versus open-lamina technique. Spine. 1998. 23:1065–1068.20. Youkilis AS, Quint DJ, McGillicuddy JE, Papadopoulos SM. Stereotactic navigation for placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Neurosurgery. 2001. 48:771–778.
Article21. Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Widell EH, et al. A biomechanical study of intrapeduncular screw fixation in the lumbosacral spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 203:99–112.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thoracic Pedicle Screw Insertion in Scoliosis Using Posteroanterior C-arm rotation Method
- Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of Thoracic idiopathic scoliosis
- Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: The Insertion Technique, the Fusion Levels and Direct Vertebral Rotation
- Effect of Direct Vertebral Rotation on the Uninstrumented Lumbar Curve in Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Clinical Results of Selective Thoracic Fusion by Segmental Pedicle Screws in King type II Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis ( AIS )