J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Jun;80(Suppl 1):S59-S62. 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.Suppl1.S59.
Laparoscopic splenectomy for sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of the spleen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. sshamee@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2096653
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.80.Suppl1.S59
Abstract
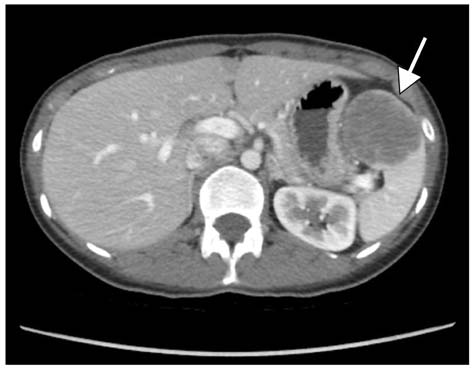
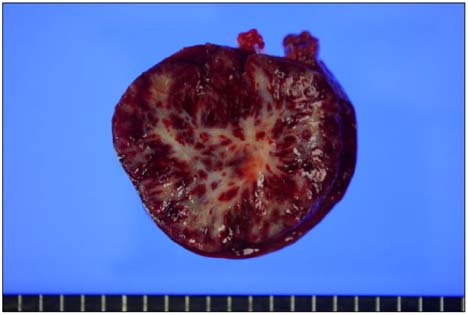
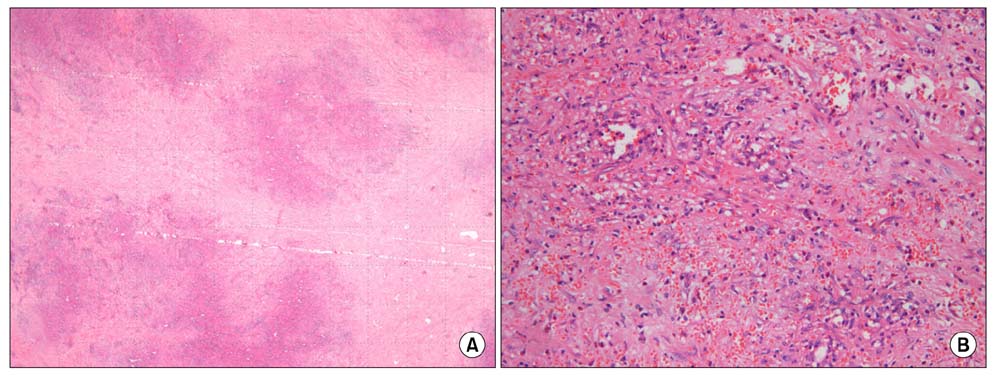
- Primary splenic tumors are rare and mainly found incidentally on radiologic studies. Among them, sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation (SANT) of the spleen is a new entity defined as a benign pathologic lesion. Most SANTs have no clinical symptoms and are occasionally accompanied by other splenic diseases such as malignancies. So, the exact diagnosis of the nature of the splenic tumor is mandatory for further treatment. But, preoperative diagnosis is not easy since it is difficult to obtain the tissue from the spleen for pathological study. Recently, laparoscopic splenectomy has become the more standard procedure for the spleen for diagnosis and treatment. Here, we report a rare case of SANT diagnosed following laparoscopic splenectomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moriyama S, Inayoshi A, Kurano R. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the spleen: report of a case. Surg Today. 2000. 30:942–946.2. Caraway NP, Fanning CV. Use of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the evaluation of splenic lesions in a cancer center. Diagn Cytopathol. 1997. 16:312–316.3. Stephens BJ, Justice JL, Sloan DA, Yoder JA. Elective laparoscopic splenectomy for hematologic disorders. Am Surg. 1997. 63:700–703.4. Walsh RM, Brody F, Brown N. Laparoscopic splenectomy for lymphoproliferative disease. Surg Endosc. 2004. 18:272–275.5. Martel M, Cheuk W, Lombardi L, Lifschitz-Mercer B, Chan JK, Rosai J. Sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation (SANT): report of 25 cases of a distinctive benign splenic lesion. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. 28:1268–1279.6. Teng X, Yu X, Wang G, Xu L, Lai M. Sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of the spleen. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2008. 30:125–132.7. Delaitre B, Maignien B. Splenectomy by the laparoscopic approach: report of a case. Presse Med. 1991. 20:2263.8. Rosen M, Brody F, Walsh RM, Tarnoff M, Malm J, Ponsky J. Outcome of laparoscopic splenectomy based on hematologic indication. Surg Endosc. 2002. 16:272–279.9. Lee SG, Kim MC, Kim HH, Kwon HC, Jung GJ. Treatment result of laparoscopic versus open splenectomy in benign splenic diseases. J Korean Surg Soc. 2005. 68:230–234.10. Bellows CF, Sweeney JF. Laparoscopic splenectomy: present status and future perspective. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2006. 3:95–104.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Splenic Sclerosing Angiomatoid Nodular Transformation in an 8-Year-Old Child
- CT and MRI Findings of Sclerosing Angiomatoid Nodular Transformation of the Spleen: Spoke Wheel Pattern
- A Case of Sclerosing Angiomatoid Nodular Transformation of the Spleen: Spoke Wheel Pattern on Computed Tomography
- Sclerosing Angiomatoid Nodular Transformation (SANT) in Spleen: A Case Report
- Laparoscopic Splenectomy in a Case of Stable Blunt Abdominal Trauma