Korean Circ J.
2010 Mar;40(3):141-142. 10.4070/kcj.2010.40.3.141.
High Plasma Levels of the B-type Natriuretic Peptide in Patients Without Heart Failure: Is There Clinical Significance?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. kimmh@dau.ac.kr
- 2Regional Clinical Trial Center, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2094075
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2010.40.3.141
Abstract
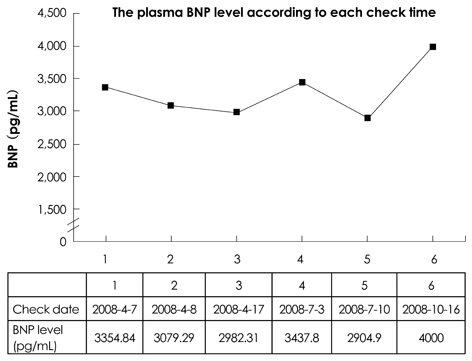
- We report a case of a 19-year-old female with an elevated plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) level, but without evidence of heart failure (HF). She presented with non-specific chest pain and a high level of the B-type natriuretic peptide, despite having unremarkable findings on physical examination, laboratory analysis, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, chest X-ray, chest computed tomography, whole body scan, and coronary angiography. We attribute this finding to a genetic variation in the synthesis and cleavage of the natriuretic peptides.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Horio T, Kawano Y. Bio-molecular markers for cardiovascular disease: significance of natriuretic peptides and adrenomedullin. Korean Circ J. 2008. 38:507–513.2. Yasue H, Yoshimura M, Sumida H, et al. Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation. 1994. 90:195–203.3. Hunt PJ, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG, Richards AM, Espiner EA. The amino-terminal portion of pro-brain natriuretic peptide (Pro-BNP) circulates in human plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995. 214:1175–1183.4. Lainchbury JG, Campbell E, Frampton CM, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG, Richards AM. Brain natriuretic peptide and N terminal brain natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of heart failure in patients with acute shortness of breath. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. 42:728–735.5. Nishikimi T, Yoshihara F, Morimoto A, et al. Relationship between left ventricular geometry and natriuretic peptide levels in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1996. 28:22–30.6. Troughton RW, Prior DL, Pereira JJ, et al. Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels in systolic heart failure: importance of left ventricular diastolic function and right ventricular systolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. 43:416–422.7. Baggish AL, van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL Jr. The differential diagnosis of an elevated amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide level. Am J Cardiol. 2008. 101:43–48.8. Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, et al. Heritability and genetic linkage of plasma natriuretic peptide levels. Circulation. 2003. 108:13–16.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure: Focus on B-type Natriuretic Peptide
- Serial Monitoring of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Heart Failure Patients
- Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic Peptides and Adrenomedullin
- Clinical Implication of B-type Natriuretic Peptide in the Elderly
- Plasma Atrial Natriuertic Peptide (ANP) Levels and Hemodynamic Data in Patient with Heart Disease