Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2010 Dec;14(6):399-405. 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.399.
The Development of Phasic and Tonic Inhibition in the Rat Visual Cortex
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea. djrhie@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Catholic Neuroscience Center, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea.
- KMID: 2071712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.399
Abstract
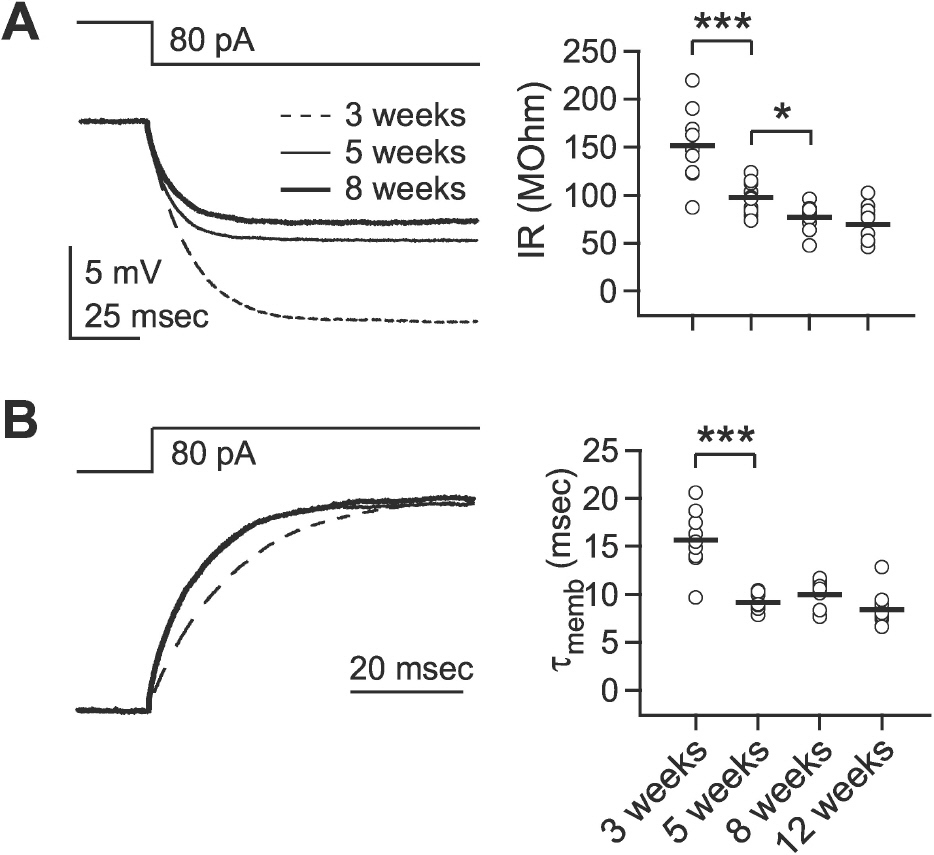
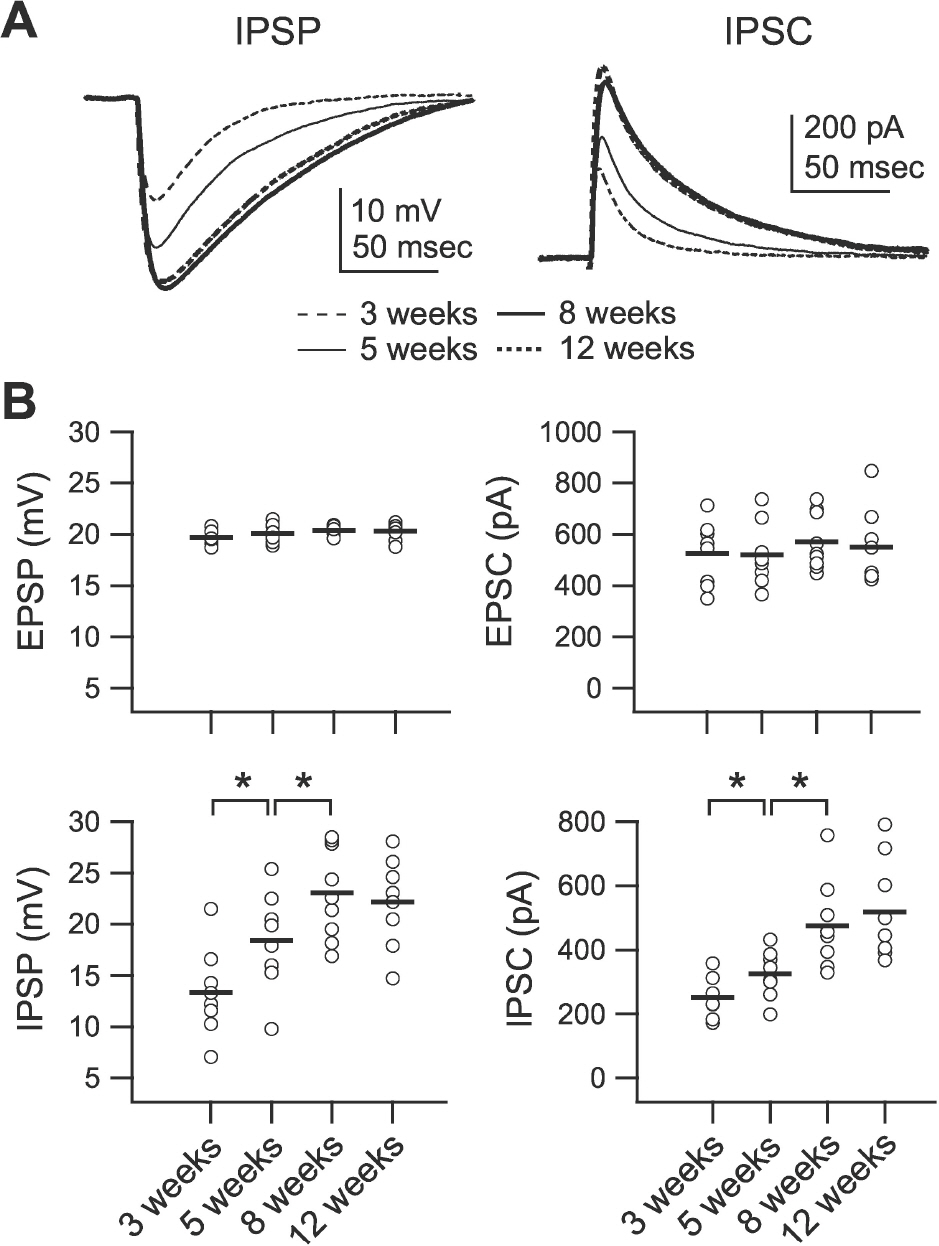
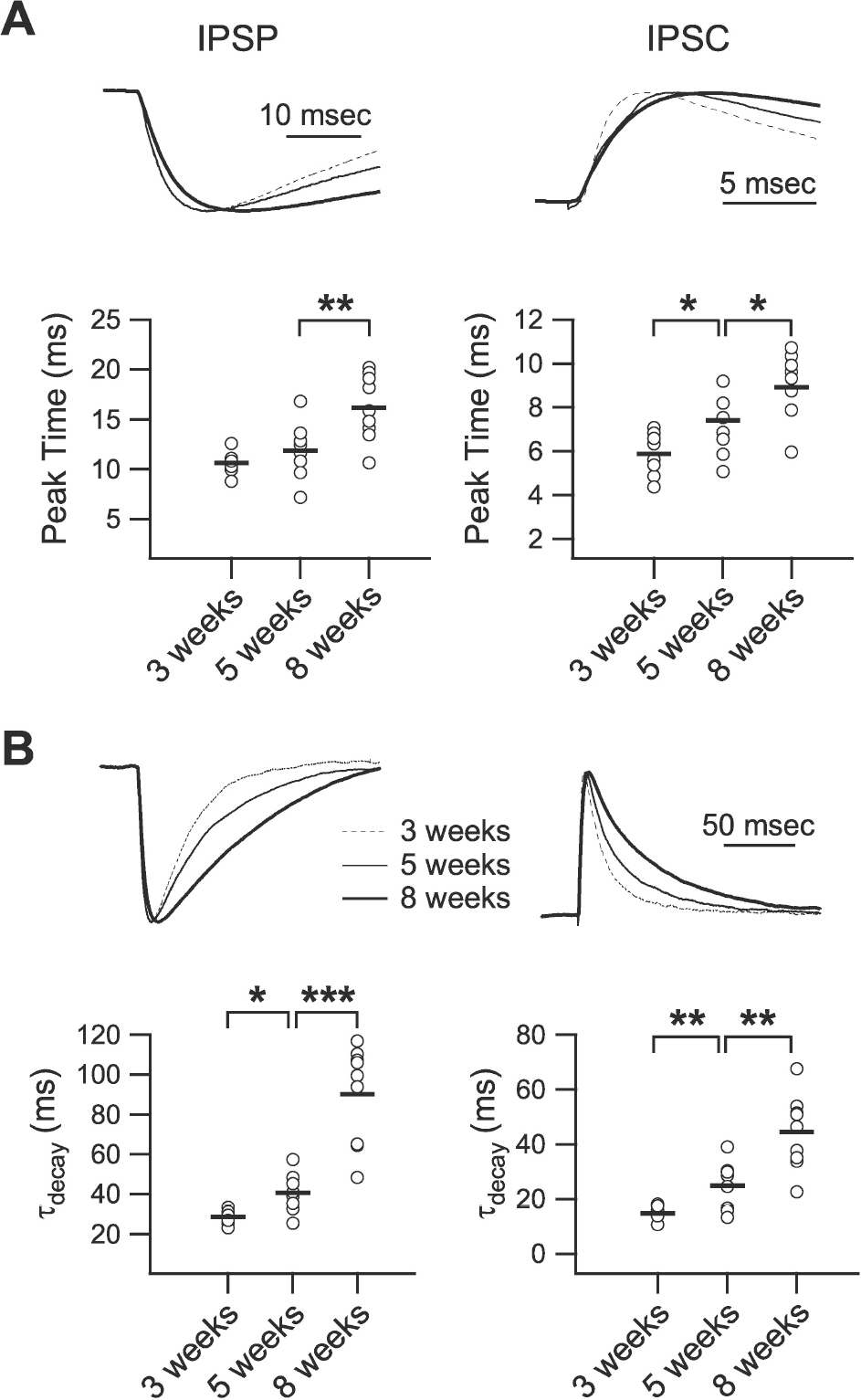
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic inhibition is important in the function of the visual cortex. In a previous study, we reported a developmental increase in GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in the rat visual cortex from 3 to 5 weeks of age. Because this developmental increase is crucial to the regulation of the induction of long-term synaptic plasticity, in the present study we investigated in detail the postnatal development of phasic and tonic inhibition. The amplitude of phasic inhibition evoked by electrical stimulation increased during development from 3 to 8 weeks of age, and the peak time and decay kinetics of inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) and current (IPSC) slowed progressively. Since the membrane time constant decreased during this period, passive membrane properties might not be involved in the kinetic changes of IPSP and IPSC. Tonic inhibition, another mode of GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition, also increased developmentally and reached a plateau at 5 weeks of age. These results indicate that the time course of the postnatal development of GABAergic inhibition matched well that of the functional maturation of the visual cortex. Thus, the present study provides significant insight into the roles of inhibitory development in the functional maturation of the visual cortical circuits.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Phasic and Tonic Inhibition are Maintained Respectively by CaMKII and PKA in the Rat Visual Cortex
Kayoung Joo, Shin Hee Yoon, Duck-Joo Rhie, Hyun-Jong Jang
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(6):517-524. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.6.517.
Reference
-
References
1. Pouille F, Scanziani M. Enforcement of temporal fidelity in pyramidal cells by somatic feed-forward inhibition. Science. 2001; 293:1159–1163.
Article2. Whittington MA, Traub RD. Interneuron diversity series: inhibitory interneurons and network oscillations in vitro. Trends Neurosci. 2003; 26:676–682.
Article3. Cobb SR, Buhl EH, Halasy K, Paulsen O, Somogyi P. Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature. 1995; 378:75–78.
Article4. Hensch TK, Stryker MP. Columnar architecture sculpted by GABA circuits in developing cat visual cortex. Science. 2004; 303:1678–1681.
Article5. Gray CM. The temporal correlation hypothesis of visual feature integration: still alive and well. Neuron. 1999; 24:31–47.6. Jang HJ, Cho KH, Kim HS, Hahn SJ, Kim MS, Rhie DJ. Age-dependent decline in supragranular long-term synaptic plasticity by increased inhibition during the critical period in the rat primary visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2009; 101:269–275.
Article7. Hensch TK, Fagiolini M, Mataga N, Stryker MP, Baekkeskov S, Kash SF. Local GABA circuit control of experience-dependent plasticity in developing visual cortex. Science. 1998; 282:1504–1508.
Article8. Komatsu Y. Development of cortical inhibition in kitten striate cortex investigated by a slice preparation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1983; 8:136–139.
Article9. Morales B, Choi SY, Kirkwood A. Dark rearing alters the development of GABAergic transmission in visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:8084–8090.
Article10. Fagiolini M, Hensch TK. Inhibitory threshold for critical-period activation in primary visual cortex. Nature. 2000; 404:183–186.
Article11. Jang HJ, Cho KH, Park SW, Kim MJ, Yoon SH, Rhie DJ. Effects of serotonin on the induction of long-term depression in the rat visual cortex. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010; 14:337–343.
Article12. Bosman LW, Rosahl TW, Brussaard AB. Neonatal development of the rat visual cortex: synaptic function of GABAA receptor alpha subunits. J Physiol. 2002; 545:169–181.13. Kapur A, Lytton WW, Ketchum KL, Haberly LB. Regulation of the NMDA component of EPSPs by different components of postsynaptic GABAergic inhibition: computer simulation analysis in piriform cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1997; 78:2546–2559.
Article14. Perkel DJ, Petrozzino JJ, Nicoll RA, Connor JA. The role of Ca2+ entry via synaptically activated NMDA receptors in the induction of long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1993; 11:817–823.15. Bear MF, Kleinschmidt A, Gu QA, Singer W. Disruption of experience-dependent synaptic modifications in striate cortex by infusion of an NMDA receptor antagonist. J Neurosci. 1990; 10:909–925.
Article16. Mulkey RM, Malenka RC. Mechanisms underlying induction of homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron. 1992; 9:967–975.
Article17. Kirkwood A, Lee HK, Bear MF. Co-regulation of long-term potentiation and experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in visual cortex by age and experience. Nature. 1995; 375:328–331.
Article18. Farrant M, Nusser Z. Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABAA receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005; 6:215–229.19. Semyanov A, Walker MC, Kullmann DM. GABA uptake regulates cortical excitability via cell type-specific tonic inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2003; 6:484–490.
Article20. Glykys J, Mody I. The main source of ambient GABA responsible for tonic inhibition in the mouse hippocampus. J Physiol. 2007; 582:1163–1178.
Article21. Birnir B, Everitt AB, Lim MS, Gage PW. Spontaneously opening GABAA channels in CA1 pyramidal neurones of rat hippocampus. J Membr Biol. 2000; 174:21–29.22. McCartney MR, Deeb TZ, Henderson TN, Hales TG. Tonically active GABAA receptors in hippocampal pyramidal neurons exhibit constitutive GABA-independent gating. Mol Pharmacol. 2007; 71:539–548.23. Semyanov A, Walker MC, Kullmann DM, Silver RA. Tonically active GABAA receptors: modulating gain and maintaining the tone. Trends Neurosci. 2004; 27:262–269.24. Yamada J, Furukawa T, Ueno S, Yamamoto S, Fukuda A. Molecular basis for the GABAA receptor-mediated tonic inhibition in rat somatosensory cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2007; 17:1782–1787.25. Spruston N, Jaffe DB, Johnston D. Dendritic attenuation of synaptic potentials and currents: the role of passive membrane properties. Trends Neurosci. 1994; 17:161–166.
Article26. Grashow R, Brookings T, Marder E. Compensation for variable intrinsic neuronal excitability by circuit-synaptic interactions. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:9145–9156.
Article27. Vicini S, Ferguson C, Prybylowski K, Kralic J, Morrow AL, Homanics GE. GABAA receptor alpha1 subunit deletion prevents developmental changes of inhibitory synaptic currents in cerebellar neurons. J Neurosci. 2001; 21:3009–3016.28. Moreau AW, Amar M, Le Roux N, Morel N, Fossier P. Serotoninergic fine-tuning of the excitation-inhibition balance in rat visual cortical networks. Cereb Cortex. 2010; 20:456–467.29. Fagiolini M, Pizzorusso T, Berardi N, Domenici L, Maffei L. Functional postnatal development of the rat primary visual cortex and the role of visual experience: dark rearing and monocular deprivation. Vision Res. 1994; 34:709–720.
Article30. Guire ES, Lickey ME, Gordon B. Critical period for the monocular deprivation effect in rats: assessment with sweep visually evoked potentials. J Neurophysiol. 1999; 81:121–128.
Article31. Alitto HJ, Dan Y. Function of inhibition in visual cortical processing. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010; 20:340–346.
Article32. Mohler H. GABAA receptor diversity and pharmacology. Cell Tissue Res. 2006; 326:505–516.33. Tia S, Wang JF, Kotchabhakdi N, Vicini S. Developmental changes of inhibitory synaptic currents in cerebellar granule neurons: role of GABAA receptor alpha 6 subunit. J Neurosci. 1996; 16:3630–3640.34. Xiang Z, Huguenard JR, Prince DA. Synaptic inhibition of pyramidal cells evoked by different interneuronal subtypes in layer v of rat visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2002; 88:740–750.
Article35. Karayannis T, Elfant D, Huerta-Ocampo I, Teki S, Scott RS, Rusakov DA, Jones MV, Capogna M. Slow GABA transient and receptor desensitization shape synaptic responses evoked by hippocampal neurogliaform cells. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:9898–9909.
Article36. Hefti BJ, Smith PH. Distribution and kinetic properties of GABAergic inputs to layer V pyramidal cells in rat auditory cortex. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2003; 4:106–121.
Article37. Sceniak MP, Maciver MB. Slow GABAA mediated synaptic transmission in rat visual cortex. BMC Neurosci. 2008; 9:8.38. Klostermann O, Wahle P. Patterns of spontaneous activity and morphology of interneuron types in organotypic cortex and thalamus-cortex cultures. Neuroscience. 1999; 92:1243–1259.
Article39. Chattopadhyaya B, Di Cristo G, Higashiyama H, Knott GW, Kuhlman SJ, Welker E, Huang ZJ. Experience and activity-dependent maturation of perisomatic GABAergic innervation in primary visual cortex during a postnatal critical period. J Neurosci. 2004; 24:9598–9611.
Article40. Okaty BW, Miller MN, Sugino K, Hempel CM, Nelson SB. Transcriptional and electrophysiological maturation of neocortical fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons. J Neurosci. 2009; 29:7040–7052.
Article41. Huang ZJ, Kirkwood A, Pizzorusso T, Porciatti V, Morales B, Bear MF, Maffei L, Tonegawa S. BDNF regulates the maturation of inhibition and the critical period of plasticity in mouse visual cortex. Cell. 1999; 98:739–755.
Article42. Jiang B, Huang S, de Pasquale R, Millman D, Song L, Lee HK, Tsumoto T, Kirkwood A. The maturation of GABAergic transmission in visual cortex requires endocannabinoid-mediated LTD of inhibitory inputs during a critical period. Neuron. 2010; 66:248–259.
Article43. Jiang B, Sohya K, Sarihi A, Yanagawa Y, Tsumoto T. Laminar-specific maturation of GABAergic transmission and susceptibility to visual deprivation are related to endocannabinoid sensitivity in mouse visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:14261–14272.
Article44. Carmignoto G, Vicini S. Activity-dependent decrease in NMDA receptor responses during development of the visual cortex. Science. 1992; 258:1007–1011.
Article45. Nase G, Weishaupt J, Stern P, Singer W, Monyer H. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of NMDA receptor expression in the rat visual cortex. Eur J Neurosci. 1999; 11:4320–4326.
Article46. Flint AC, Maisch US, Weishaupt JH, Kriegstein AR, Monyer H. NR2A subunit expression shortens NMDA receptor synaptic currents in developing neocortex. J Neurosci. 1997; 17:2469–2476.
Article47. Mitchell SJ, Silver RA. Shunting inhibition modulates neuronal gain during synaptic excitation. Neuron. 2003; 38:433–445.
Article48. Pavlov I, Savtchenko LP, Kullmann DM, Semyanov A, Walker MC. Outwardly rectifying tonically active GABAA receptors in pyramidal cells modulate neuronal offset, not gain. J Neurosci. 2009; 29:15341–15350.49. Hausser M, Clark BA. Tonic synaptic inhibition modulates neuronal output pattern and spatiotemporal synaptic integration. Neuron. 1997; 19:665–678.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phasic and Tonic Inhibition are Maintained Respectively by CaMKII and PKA in the Rat Visual Cortex
- Role of Nitric Oxide in the Motor Activity of Rat Vas Deferens
- Changes of beta-Adrenergic Receptor mRNA in the Visual Cortex and Superior Colliculus of Monocular Deprivated Rat
- Effects of Relief of Bladder Outlet Obstruction on the Detrusor Contractility in Rat
- The Effects of Partial Outlet Obstruction on Bladder Strip Sensitivity to Glucose Deprivation: An In-Vitro Study in the Rat