Regional Distribution of Interstitial Cells of Cajal, (ICC) in Human Stomach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea. yunhyo@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 3Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea. physiokyc@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 4Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 5Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 7Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 8BK21 Chungbuk Biomedical Science Center, School of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 9Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai 200240, China.
- KMID: 2071700
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.5.317
Abstract
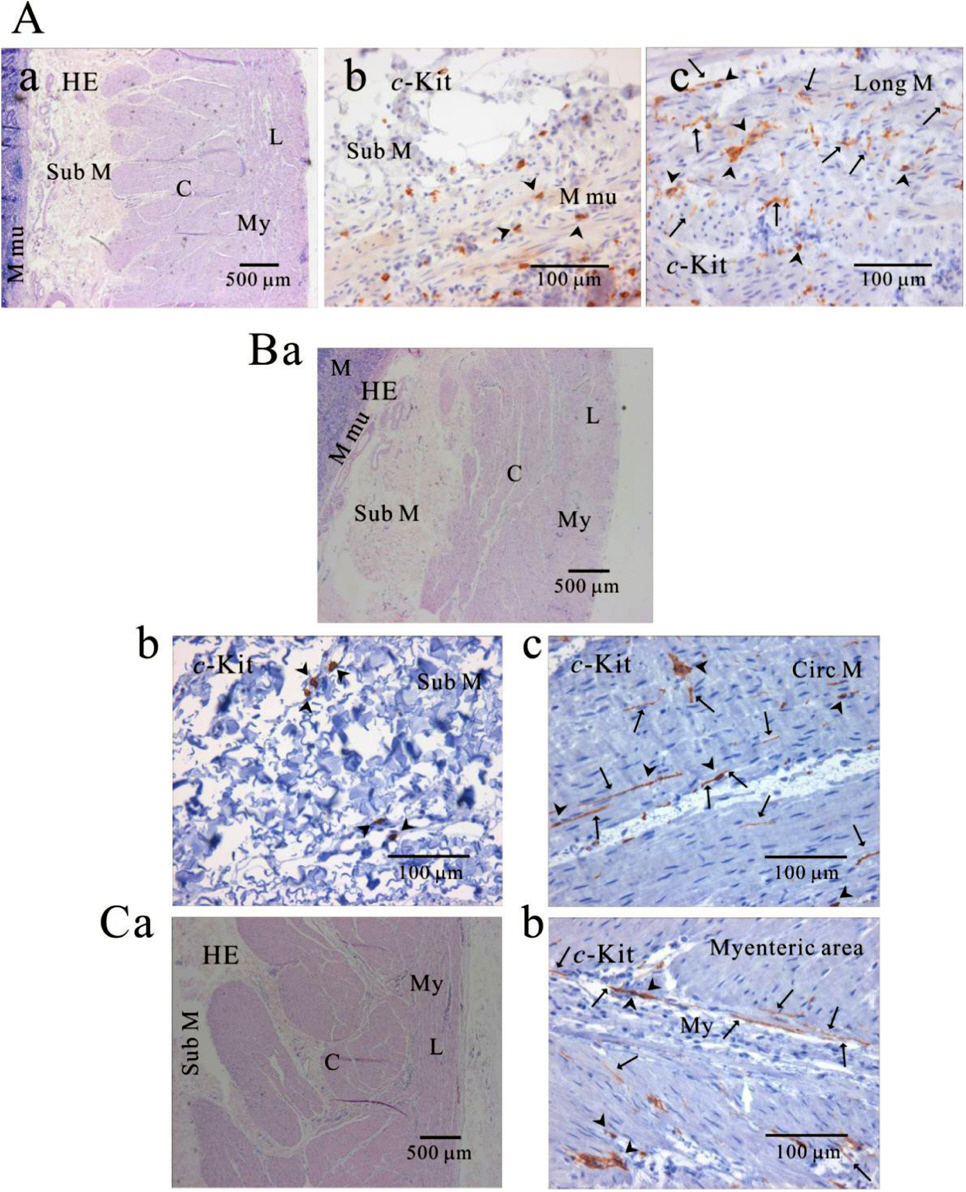
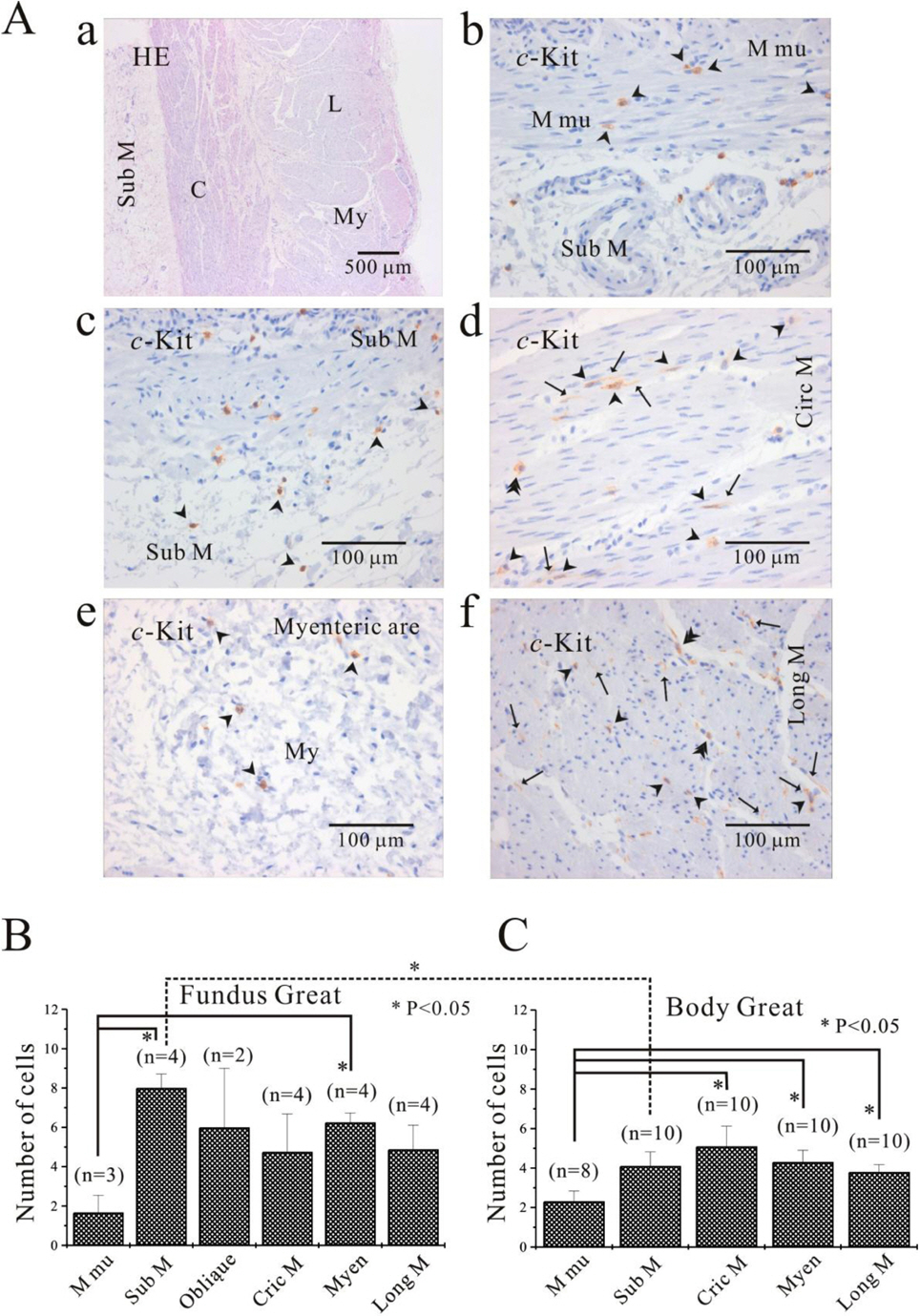
- We elucidated the distribution of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) in human stomach, using cryosection and c-Kit immunohistochemistry to identify c-Kit positive ICC. Before c-Kit staining, we routinely used hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining to identify every structure of human stomach, from mucosa to longitudinal muscle. HE staining revealed that the fundus greater curvature (GC) had prominent oblique muscle layer, and c-Kit immunostaining c-Kit positive ICC cells were found to have typical morphology of dense fusiform cell body with multiple processes protruding from the central cell body. In particular, we could observe dense processes and ramifications of ICC in myenteric area and longitudinal muscle layer of corpus GC. Interestingly, c-Kit positive ICC-like cells which had morphology very similar to ICC were found in gastric mucosa. We could not find any significant difference in the distribution of ICC between fundus and corpus, except for submucosa where the density of ICC was much higher in gastric fundus than corpus. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in the density of ICC between each area of fundus and corpus, except for muscularis mucosa. Finally, we also found similar distribution of ICC in normal and cancerous tissue obtained from a patient who underwent pancreotomy and gastrectomy. In conclusion, ICC was found ubiquitously in human stomach and the density of ICC was significantly lower in the muscularis mucosa of both fundus/corpus and higher in the submucosa of gastric fundus than corpus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Association between interstitial cells of Cajal and anti-vinculin antibody in human stomach
Ji Hyun Kim, Seung-Joo Nam, Sung Chul Park, Sang Hoon Lee, Tae Suk Kim, Minjong Lee, Jin Myung Park, Dae Hee Choi, Chang Don Kang, Sung Joon Lee, Young Joon Ryu, Kyungyul Lee, So Young Park
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;24(2):185-191. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.2.185.Nitric Oxide-mediated Relaxation by High K+ in Human Gastric Longitudinal Smooth Muscle
Young Chul Kim, Woong Choi, Hyo-Young Yun, Rohyun Sung, Ra Young Yoo, Seon-Mee Park, Sei Jin Yun, Mi-Jung Kim, Young-Jin Song, Wen-Xie Xu, Sang Jin Lee
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011;15(6):405-413. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.6.405.Mechanism of Relaxation Via TASK-2 Channels in Uterine Circular Muscle of Mouse
Seung Hwa Hong, Rohyun Sung, Young Chul Kim, Hikaru Suzuki, Woong Choi, Yeon Jin Park, Ill Woon Ji, Chan Hyung Kim, Sun Chul Myung, Moo Yeol Lee, Tong Mook Kang, Ra Young You, Kwang Ju Lee, Seung Woon Lim, Hyo-Yung Yun, Young-Jin Song, Wen-Xie Xu, Hak Soon Kim, Sang Jin Lee
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17(4):359-365. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.4.359.H2 Receptor-Mediated Relaxation of Circular Smooth Muscle in Human Gastric Corpus: the Role of Nitric Oxide (NO)
Sang Eok Lee, Dae Hoon Kim, Young Chul Kim, Joung-Ho Han, Woong Choi, Chan Hyung Kim, Hye Won Jeong, Seon-Mee Park, Sei Jin Yun, Song-Yi Choi, Rohyun Sung, Young Ho Kim, Ra Young Yoo, Park Hee Sun, Heon Kim, Young-Jin Song, Wen-Xie Xu, Hyo-Yung Yun, Sang Jin Lee
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(5):425-430. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.5.425.
Reference
-
References
1. Cajal SR. Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés. 2nd ed.Paris: Maloine;1911. p. 891–942.2. Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Cortesini C. Ultrastructural features and localization of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the smooth muscle coat of human esophagus. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1985; 17:187–197.3. Hagger R, Gharaie S, Finlayson C, Kumar D. Regional and transmural density of interstitial cells of Cajal in human colon and rectum. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275:G1309–G1316.
Article4. Radenkovic G, Savic V, Mitic D, Grahovac S, Bjelakovic M, Krstic M. Development of c-Kit immunopositive interstitial cells of Cajal in the human stomach. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14:1125–1134.5. Romert P, Mikkelsen HB. c-Kit immunoreactive cells of Cajal in the human small and large intestine. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998; 109:195–202.6. Torihashi S, Horisawa M, Watanabe Y. c-Kit immunoreactive interstitial cells in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1999; 75:38–50.7. Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A. W/Kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature. 1995; 373:347–349.8. Torihashi S, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Development of c-Kit-positive cells and the onset of electrical rhythmicity in murine small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:144–155.9. Nemeth L, Maddeur S, Puri P. Immunolocalization of the gap junction protein connexin 43 in the interstitial cells of Cajal in the normal and Hirschsprung's disease bowel. J Pediatr Surg. 2000; 35:823–828.10. Klüppel M, Huizinga JD, Malysz J, Bernstein A. Developmental origin and Kit- dependent development of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the mammalian small intestine. Dev Dyn. 1998; 211:60–71.11. Maeda H, Yamagata A, Nishikawa S, Yoshinaga K, Kobayashi S, Nishi K, Nishikawa S. Requirement of c-Kit for development of intestinal pacemaker system. Development. 1992; 116:369–375.12. Ördög T, Redelman D, Horváth VJ, Miller LJ, Horowitz B, Sanders KM. Qunatitative analysis by flow cytometry of interstitial cells of Cajal, pacemakers, and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Cytometry A. 2004; 62:139–149.13. Burns AJ, Lomax AE, Torihashi S, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Interstitial cells of Cajal mediated inhibitory neurotransmission in the stomach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996; 93:12008–12013.14. Goyal RK, Chaudhury A. Mounting evidence against the role of ICC in neurotransmission to smooth muscle in the gut. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010; 298:G10–G13.
Article15. Wang XY, Paterson C, Huizinga JD. Cholinergic and nitrergic innervation of ICC-DMP and ICC-IM in the human small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2003; 15:531–543.
Article16. Nakahara M, Isozaki K, Hirota S, Vanderwinden JM, Takakura R, Kinoshita K, Miyagawa J, Chen H, Miyazaki Y, Kiyohara T, Shinomura Y, Matsuzawa Y. Deficiency of Kit-positive cells in the colon of patients with diabetes mellitus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002; 17:666–670.
Article17. Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ. Interstitial cells of Cajal in human gut and gastrointestinal disease. Microsc Res Tech. 1999; 47:344–360.
Article18. Der T, Bercik P, Donnelly G, Jackson T, Berezin I, Collins SM, Huizinga JD. Interstitial cells of Cajal and inflammation-induced motor dysfunction in the mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology. 2000; 119:1590–1599.
Article19. Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Cretoiu D, Radu E. The connective connection: interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells establish synapses with immunoreactive cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2005; 9:714–730.20. Hassan S, Kinoshita Y, Kawanami C, Kishi K, Matsushima Y, Ohashi A, Funasaka Y, Maekawa T, He-Yao W, Chuba T. Expression of protooncogene c-Kit and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) in gastric carcinoma cell lines. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 1998; 43:8–14.21. Kunisawa Y, Komuro T. Interstitial cells of Cajal associated with submucosal plexus of the guinea-pig stomach. Neuroscience Letters. 2008; 434:273–276.22. Torihashi S, Yokoi K, Nagaya H, Aoki K, Fujimoto T. New monoclonal antibody (AIC) identifies interstitial cells of Cajal in the musculature of the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Auton Neurosci. 2004; 113:16–23.
Article23. Reed J, Ouban A, Schickor FK, Muraca P, Yeatman T, Coppola D. Immunohistochemical staining for c-Kit (CD117) is a rare event in human colorectal carcinoma. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2002; 2:119–122.24. Ashman LK. The biology of stem cell factor and its receptor C-kit. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999; 31:1037–1051.25. Rygaard K, Nakamura T, Spang Thomsen M. Expression of the proto-oncogene c-met and c-Kit and their ligands, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter facter and stem cell factor, in SCLS cell lines and xenografts. Br J Cancer. 1993; 67:37–46.26. Hibi K, Takahashi T, Sekido Y, Ueda R, Hida T, Ariyoshi Y, Takagi H, Takahashi T. Coexpression of the stem cell factor and the c-Kit genes in small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1991; 6:2291–2296.27. Fujiwara T, Motoyama T, Ishihara N, Watanabe H, Kumanishi T, Kato K, Ichinose H, Nagatsu T. Characterization of four new cell lines derived from small-cell gastrointestinal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993; 54:965–971.
Article28. Song G, Hirst GDS, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Regional variation in ICC distribution, pacemaking activity and neural responses in the longitudinal muscle of the murine stomach. J Physiol. 2005; 564:523–540.
Article29. Hirst GDS, Beckett EAH, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Regional variation in contribution of myenteric and intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal to generation of slow waves in mouse gastric antrum. J Physiol. 2002; 540:1003–1012.
Article30. Han J, Shen WH, Jiang YZ, Yu B, He YT, Mei F. Distribution, development and proliferation of interstitial cells of Cajal in murine colon: an immunohistochemical study from neonatal to adult life. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010; 133:163–175.
Article31. Ibba Manneschi L, Pacini S, Corsani L, Cechi P, Faussone-Pellegrini MS. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the human stomach: distribution and relationship with enteric innervation. Histol Histopathol. 2004; 19:1153–1164.32. Nemeth L, Puri P. Three-demensional morphology of c-Kit-positive cellular network and nitrergic innervation in the human gut. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2001; 125:899–904.33. Burns AJ, Herbert TM, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract as revealed by c-Kit immunohistochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1997; 290:11–20.34. Horiguchi K, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Enteric motor neurons from synaptic-like junctions with interstitial cells of Cajal in the canine gastric antrum. Cell Tissue Res. 2003; 311:299–313.35. Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Pantalone D, Cortesini C. An ultra-structural study of the interstitial cells of Cajal of the human stomach. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1989; 21:439–460.36. Abrahamsson H. Studies on the inhibitory nervous control of gastric motility. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1973; 390:1–38.37. Percy WH, Warren JM, Brunz JT. Characteristics of the muscularis mucosae in the acid-secreting region of the rabbit stomach. Am J Physiol. 1999; 276:G1213–G1220.38. Synnerstad I, Ekblad E, Sundler F, Holm L. Gastric mucosal smooth muscles may explain oscillations in glandular pressure: role of vasocative intestinal peptide. Gastroenterology. 1998; 114:284–294.39. Moskalewski S, Biernacka-Wawrzonek D, Klimkiewicz J, Zdun R. Venous outflow system in rabbit gastric mucosa. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2004; 63:151–157.40. Fawcett DW. A Textbook of Histology. 12th ed.New York, London: Chapman & Hall;1994. p. 617–651.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Interstitial Cells of Cajal-opathy Present in Gastroparesis?
- The Pharmacological Regulation of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Small Intestine
- Association between interstitial cells of Cajal and anti-vinculin antibody in human stomach
- Voltage-dependent Ca2+ Current Identified in Freshly Isolated Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC) of Guinea-pig Stomach
- Morphology of the c-Kit-Immunoreactive Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC) in the Mouse Intestine