Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2015 Nov;19(6):499-506. 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.6.499.
Pitavastatin Regulates Ang II Induced Proliferation and Migration via IGFBP-5 in VSMC
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu 42415, Korea. yjkang@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2School of Food Science & Biotechnology, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Korea.
- KMID: 2070789
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.6.499
Abstract
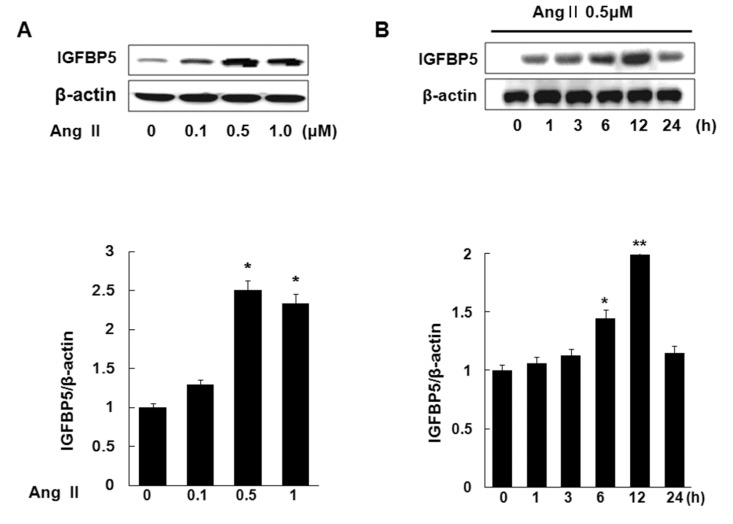
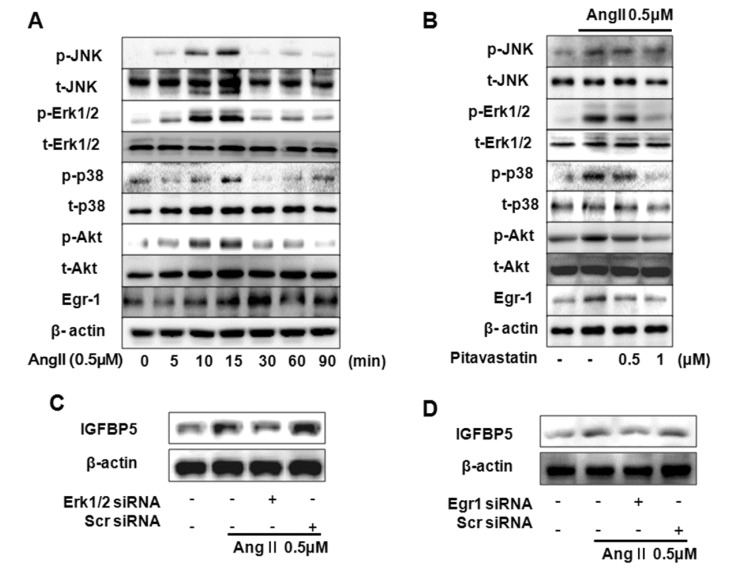
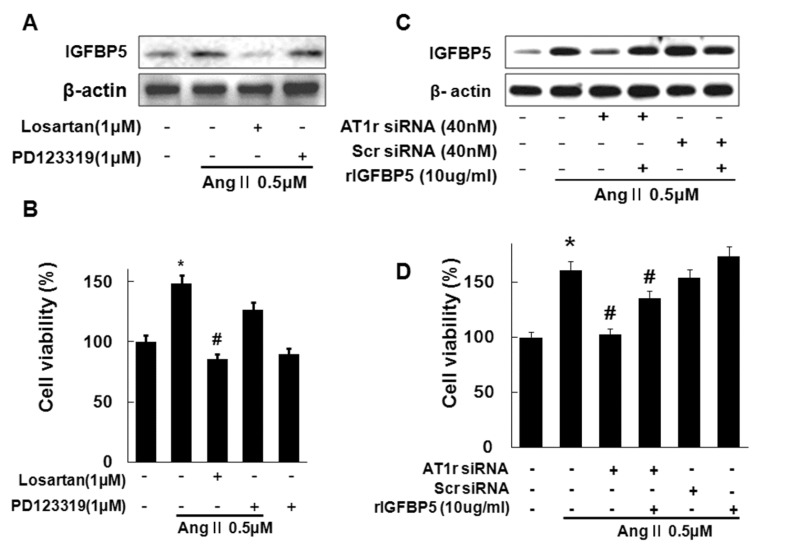
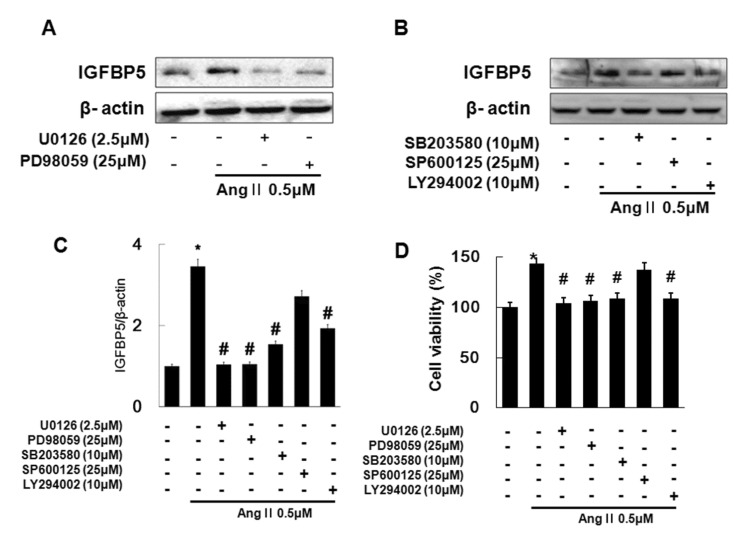
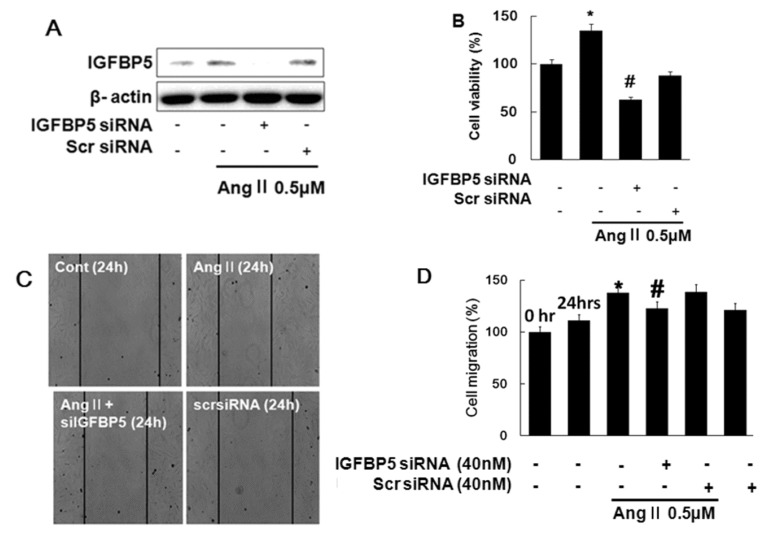
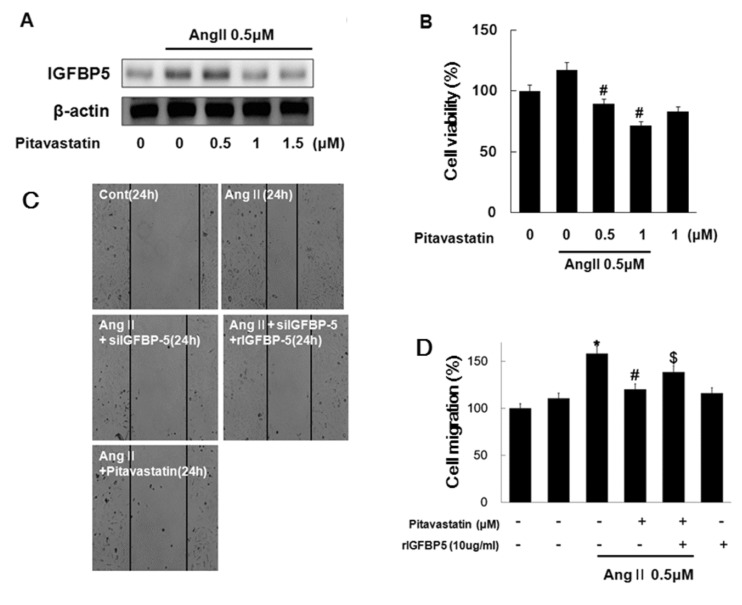
- Angiotensin II (Ang II), a key mediator of hypertensive, causes structural changes in the arteries (vascular remodeling), which involve alterations in cell growth, vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) hypertrophy. Ang II promotes fibrotic factor like IGFBP5, which mediates the profibrotic effects of Ang II in the heart and kidneys, lung and so on. The purpose of this study was to identify the signaling pathway of IGFBP5 on cell proliferation and migration of Ang II-stimulated VSMC. We have been interested in Ang II-induced IGFBP5 and were curious to determine whether a Pitavastatin would ameliorate the effects. Herein, we investigated the question of whether Ang II induced the levels of IGFBP5 protein followed by proliferation and migration in VSMC. Pretreatment with the specific Angiotensin receptor type 1 (AT1) inhibitor (Losartan), Angiotensin receptor type 2 (AT2) inhibitor (PD123319), MAPK inhibitor (U0126), ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059), P38 inhibitor (SB600125) and PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) resulted in significantly inhibited IGFBP5 production, proliferation, and migration in Ang II-stimulated VSMC. In addition, IGFBP5 knockdown resulted in modulation of Ang II induced proliferation and migration via IGFBP5 induction. In addition, Pitavastatin modulated Ang II induced proliferation and migration in VSMC. Taken together, our results indicated that Ang II induces IGFBP5 through AT1, ERK1/2, P38, and PI3K signaling pathways, which were inhibited by Pitavastatin. These findings may suggest that Pitavastatin has an effect on vascular disease including hypertension.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Fluvastatin inhibits advanced glycation end products-induced proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting connective tissue growth factor
Ae-Rang Hwang, Ju-Ock Nam, Young Jin Kang
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(2):193-201. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.2.193.
Reference
-
1. Hwa V, Oh Y, Rosenfeld RG. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr Rev. 1999; 20:761–787. PMID: 10605625.
Article2. Kim HS, Nagalla SR, Oh Y, Wilson E, Roberts CT Jr, Rosenfeld RG. Identification of a family of low-affinity insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs): characterization of connective tissue growth factor as a member of the IGFBP superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997; 94:12981–12986. PMID: 9371786.
Article3. Baxter RC, Meka S, Firth SM. Molecular distribution of IGF binding protein-5 in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:271–276. PMID: 11788658.
Article4. Green BN, Jones SB, Streck RD, Wood TL, Rotwein P, Pintar JE. Distinct expression patterns of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 2 and 5 during fetal and postnatal development. Endocrinology. 1994; 134:954–962. PMID: 7507840.
Article5. Stolf BS, Carvalho AF, Martins WK, Runza FB, Brun M, Hirata R Jr, Jordão Neves E, Soares FA, Postigo-Dias J, Kowalski LP, Reis LF. Differential expression of IGFBP-5 and two human ESTs in thyroid glands with goiter, adenoma and papillary or follicular carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2003; 191:193–202. PMID: 12618333.
Article6. Tsibris JC, Segars J, Coppola D, Mane S, Wilbanks GD, OBrien WF, Spellacy WN. Insights from gene arrays on the development and growth regulation of uterine leiomyomata. Fertil Steril. 2002; 78:114–121. PMID: 12095500.
Article7. Miyake H, Pollak M, Gleave ME. Castration-induced up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 potentiates insulin-like growth factor-I activity and accelerates progression to androgen independence in prostate cancer models. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:3058–3064. PMID: 10850457.8. Khan J, Bittner ML, Saal LH, Teichmann U, Azorsa DO, Gooden GC, Pavan WJ, Trent JM, Meltzer PS. cDNA microarrays detect activation of a myogenic transcription program by the PAX3-FKHR fusion oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:13264–13269. PMID: 10557309.
Article9. Li X, Cao X, Li X, Zhang W, Feng Y. Expression level of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 mRNA is a prognostic factor for breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007; 98:1592–1596. PMID: 17651454.
Article10. Liu B, Yu J, Taylor L, Zhou X, Polgar P. Microarray and phosphokinase screenings leading to studies on ERK and JNK regulation of connective tissue growth factor expression by angiotensin II 1a and bradykinin B2 receptors in Rat1 fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2006; 97:1104–1120. PMID: 16294326.
Article11. Tanno B, Cesi V, Vitali R, Sesti F, Giuffrida ML, Mancini C, Calabretta B, Raschellà G. Silencing of endogenous IGFBP-5 by micro RNA interference affects proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. Cell Death Differ. 2005; 12:213–223. PMID: 15618969.
Article12. Cobb LJ, Salih DA, Gonzalez I, Tripathi G, Carter EJ, Lovett F, Holding C, Pell JM. Partitioning of IGFBP-5 actions in myogenesis: IGF-independent anti-apoptotic function. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117:1737–1746. PMID: 15075235.
Article13. Perks CM, McCaig C, Clarke JB, Clemmons DR, Holly JM. Effects of a non-IGF binding mutant of IGFBP-5 on cell death in human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 294:995–1000. PMID: 12074575.
Article14. Arai T, Clarke J, Parker A, Busby W Jr, Nam T, Clemmons DR. Substitution of specific amino acids in insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein 5 alters heparin binding and its change in affinity for IGF-I response to heparin. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:6099–6106. PMID: 8626396.15. Nam TJ, Busby WH Jr, Rees C, Clemmons DR. Thrombospondin and osteopontin bind to insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-5 leading to an alteration in IGF-I-stimulated cell growth. Endocrinology. 2000; 141:1100–1106. PMID: 10698186.
Article16. Nam T, Moralez A, Clemmons D. Vitronectin binding to IGF binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) alters IGFBP-5 modulation of IGF-I actions. Endocrinology. 2002; 143:30–36. PMID: 11751588.
Article17. Lee DH, Kim JE, Kang YJ. Insulin like growth factor binding protein-5 regulates excessive vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in spontaneously hypertensive rats via ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013; 17:157–162. PMID: 23626478.
Article18. Kuemmerle JF, Zhou H. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) stimulates growth and IGF-I secretion in human intestinal smooth muscle by Ras-dependent activation of p38 MAP kinase and Erk1/2 pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:20563–20571. PMID: 11923300.
Article19. Lan TH, Huang XQ, Tan HM. Vascular fibrosis in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013; 22:401–407. PMID: 23375582.
Article20. Ross R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:115–126. PMID: 9887164.21. Novo G, Guttilla D, Fazio G, Cooper D, Novo S. The role of the renin-angiotensin system in atrial fibrillation and the therapeutic effects of ACE-Is and ARBS. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008; 66:345–351. PMID: 18782141.
Article22. Sasaki K, Yamano Y, Bardhan S, Iwai N, Murray JJ, Hasegawa M, Matsuda Y, Inagami T. Cloning and expression of a complementary DNA encoding a bovine adrenal angiotensin II type-1 receptor. Nature. 1991; 351:230–233. PMID: 2041569.
Article23. Kambayashi Y, Bardhan S, Takahashi K, Tsuzuki S, Inui H, Hamakubo T, Inagami T. Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1993; 268:24543–24546. PMID: 8227011.
Article24. Stegbauer J, Coffman TM. New insights into angiotensin receptor actions: from blood pressure to aging. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011; 20:84–88. PMID: 21076298.
Article25. Eguchi S, Matsumoto T, Motley ED, Utsunomiya H, Inagami T. Identification of an essential signaling cascade for mitogenactivated protein kinase activation by angiotensin II in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Possible requirement of Gq-mediated p21ras activation coupled to a Ca2+/calmodulin-sensitive tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:14169–14175. PMID: 8662912.26. Mehta PK, Griendling KK. Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007; 292:C82–C97. PMID: 16870827.
Article27. Khachigian LM. Early growth response-1 in cardiovascular pathobiology. Circ Res. 2006; 98:186–191. PMID: 16456111.
Article28. Cheyou ES, Srivastava A. Angiotensin-II-induced expression of the early growth response protein 1 is mediated by CaMKIIdependent pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. 2014; 28:1011.29. Day FL, Rafty LA, Chesterman CN, Khachigian LM. Angiotensin II (ATII)-inducible platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene expression is p42/44 extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 and Egr-1-dependent and mediated via the ATII type 1 but not type 2 receptor. Induction by ATII antagonized by nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:23726–23733. PMID: 10446131.30. Santiago FS, Atkins DG, Khachigian LM. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and regrowth after mechanical injury in vitro are Egr-1/NGFI-A-dependent. Am J Pathol. 1999; 155:897–905. PMID: 10487847.
Article31. Zhang YH, Fang LH, Ku BS. Fangchinoline inhibits rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and cell cycle progression through inhibition of ERK1/2 activation and c-fos expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003; 66:1853–1860. PMID: 14563495.
Article32. Takahashi T, Taniguchi T, Konishi H, Kikkawa U, Ishikawa Y, Yokoyama M. Activation of Akt/protein kinase B after stimulation with angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1999; 276:H1927–H1934. PMID: 10362672.33. Prospective Studies Collaboration. Lewington S, Whitlock G, Clarke R, Sherliker P, Emberson J, Halsey J, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000 vascular deaths. Lancet. 2007; 370:1829–1839. PMID: 18061058.34. Dechend R, Müller D, Park JK, Fiebeler A, Haller H, Luft FC. Statins and angiotensin II-induced vascular injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002; 17:349–353. PMID: 11865073.
Article35. Delbosc S, Cristol JP, Descomps B, Mimran A, Jover B. Simvastatin prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiac alteration and oxidative stress. Hypertension. 2002; 40:142–147. PMID: 12154104.
Article36. Yamakawa T, Tanaka S, Kamei J, Kadonosono K, Okuda K. Pitavastatin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by inactivating extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2003; 10:37–42. PMID: 12621163.
Article37. Resink TJ, Scott-Burden T, Baur U, Bühler FR. Increased proliferation fate and phosphoinositide turnover in cultured smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens Suppl. 1987; 5:S145–S148. PMID: 2832572.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-5 Regulates Excessive Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats via ERK 1/2 Phosphorylation
- Effect of Age on Proliferation of Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Stimulated with Fetal Bovine Serum, Angiotensin II and Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate
- Insulin Enhances Suppressive Effect of Lipopolysaccharide on Glucose-induced Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- Involvement of betaPIX in angiotensin II-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells
- Effect of Carvedilol Alone or with Cyclosporine on the Migration of Cultured Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell