J Vet Sci.
2014 Dec;15(4):575-578. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.4.575.
Induction of antibody and interferon-gamma production in mice immunized with virus-like particles of swine hepatitis E virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea. ischoi@konkuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Public Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea.
- 3Department of Biomedical Science and Technology, SMART Institute of Advanced Biomedical Science, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea.
- 4Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Anyang 430-855, Korea.
- 5Veterinary Science Research Institute, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea.
- KMID: 2070246
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.4.575
Abstract
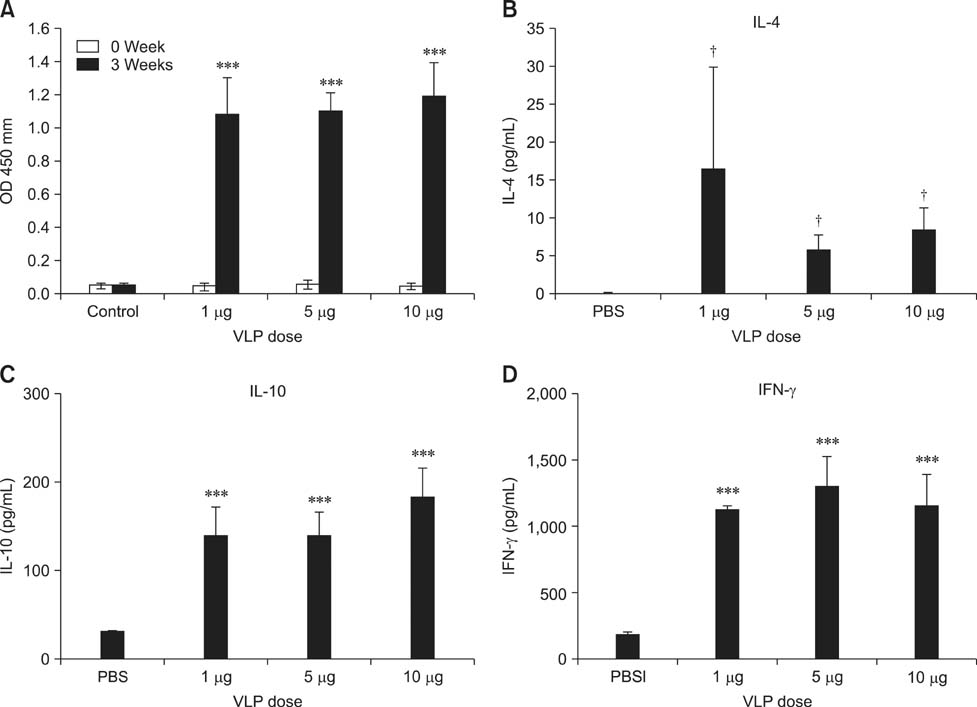
- Virus-like particles (VLPs) composed of the truncated capsid protein of swine hepatitis E virus (HEV) were developed and immune responses of mice immunized with the VLPs were evaluated. IgG titers specific for the capsid protein of swine HEV were significantly higher for all groups of mice immunized with the VLPs than those of the negative control mice. Splenocytes from mice immunized with the VLPs also produced significantly greater quantities of interferon (IFN)-gamma than interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10. These newly developed swine HEV VLPs have the capacity to induce antigen-specific antibody and IFN-gamma production in immunized mice.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies, Viral/blood
Capsid Proteins/immunology
Female
Hepatitis E/immunology/*veterinary/virology
Hepatitis E virus/*immunology
Immunization/*veterinary
Interferon-gamma/blood
Mice
Mice, Inbred BALB C
Swine
Swine Diseases/*immunology/virology
Vaccines, Virus-Like Particle/immunology
Viral Hepatitis Vaccines/*immunology
Antibodies, Viral
Capsid Proteins
Interferon-gamma
Vaccines, Virus-Like Particle
Viral Hepatitis Vaccines
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arankalle VA, Chadha MS, Tsarev SA, Emerson SU, Risbud AR, Banerjee K, Purcell RH. Seroepidemiology of water-borne hepatitis in India and evidence for a third enterically-transmitted hepatitis agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91:3428–3432.
Article2. Bright RA, Carter DM, Daniluk S, Toapanta FR, Ahmad A, Gavrilov V, Massare M, Pushko P, Mytle N, Rowe T, Smith G, Ross TM. Influenza virus-like particles elicit broader immune responses than whole virion inactivated influenza virus or recombinant hemagglutinin. Vaccine. 2007; 25:3871–3878.
Article3. Brun A, Bárcena J, Blanco E, Borrego B, Dory D, Escribano JM, Le Gall-Reculé G, Ortego J, Dixon LK. Current strategies for subunit and genetic viral veterinary vaccine development. Virus Res. 2011; 157:1–12.
Article4. Kirnbauer R, Booy F, Cheng N, Lowy DR, Schiller JT. Papillomavirus L1 major capsid protein self-assembles into virus-like particles that are highly immunogenic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89:12180–12184.
Article5. Matsuda H, Okada K, Takahashi K, Mishiro S. Severe hepatitis E virus infection after ingestion of uncooked liver from a wild boar. J Infect Dis. 2003; 188:944.
Article6. Mayo MA, Ball LA. ICTV in San Francisco: a report from the plenary session. Arch Virol. 2006; 151:413–422.
Article7. Meng XJ, Halbur PG, Shapiro MS, Govindarajan S, Bruna JD, Mushahwar IK, Purcell RH, Emerson SU. Genetic and experimental evidence for cross-species infection by swine hepatitis E virus. J Virol. 1998; 72:9714–9721.
Article8. Meng XJ, Purcell RH, Halbur PG, Lehman JR, Webb DM, Tsareva TS, Haynes JS, Thacker BJ, Emerson SU. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997; 94:9860–9865.
Article9. Mori Y, Matsuura Y. Structure of heapatitis E viral particle. Virus Res. 2011; 161:59–64.10. Nam HM, Chae KS, Song YJ, Lee NH, Lee JB, Park SY, Song CS, Seo KH, Kang SM, Kim MC, Choi IS. Immune responses in mice vaccinated with virus-like particles composed of the GP5 and M proteins of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Arch Virol. 2013; 158:1275–1285.
Article11. Song YJ, Jeong HJ, Kim YJ, Lee SW, Lee JB, Park SY, Song CS, Park HM, Choi IS. Analysis of complete genome sequences of swine hepatitis E virus and possible risk factors for transmission of HEV to humans in Korea. J Med Virol. 2010; 82:583–591.
Article12. Song YJ, Park WJ, Park BJ, Lee JB, Park SY, Song CS, Lee NH, Seo KH, Kang YS, Choi IS. Hepatitis E virus infections in humans and animals. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2014; 3:29–36.
Article13. Tam AW, Smith MM, Guerra ME, Huang CC, Bradley DW, Fry KE, Reyes GR. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology. 1991; 185:120–131.
Article14. Vitral CL, Yoshida CF, Gaspar AM. The use of non-human primates as animal models for the study of hepatitis viruses. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998; 31:1035–1048.
Article15. Zhou YH, Purcell RH, Emerson SU. A truncated ORF2 protein contains the most immunogenic site on ORF2: antibody responses to non-vaccine sequences following challenge of vaccinated and non-vaccinated macaques with hepatitis E virus. Vaccine. 2005; 23:3157–3165.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- Characterization of Monoclonal Antibody Specific for Hepatitis C Virus E2 Envelope Protein
- Generation, characterization, and application in serodiagnosis of recombinant swine vesicular disease virus-like particles
- Randomized, controlled trial of recombinant human gamma-interferon in chronic hepatitis B infection
- Expression of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein in Hepatocytes Suppresses CD8+ T Cell Activity