Korean J Radiol.
2015 Apr;16(2):357-362. 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.2.357.
Comparison of Radiation Exposure during Fluoroscopy-Guided Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections at Different Vertebral Levels
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea. mhlee625@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Gachon University Gil Hospital, Incheon 405-760, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan 612-896, Korea.
- KMID: 2070180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.2.357
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
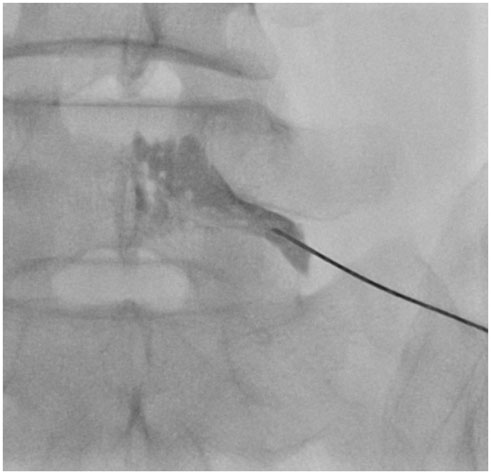
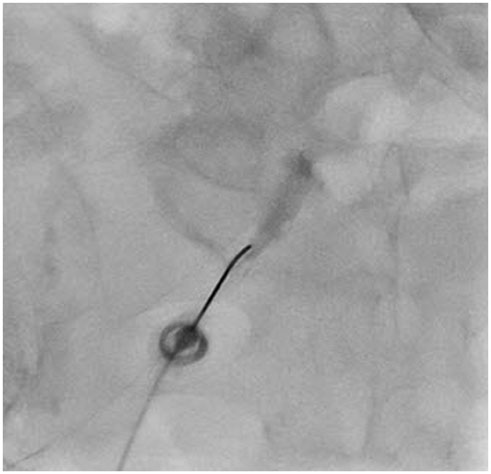
To estimate and compare radiation exposure during transforaminal fluoroscopy-guided epidural steroid injection (TFESI) at different vertebral levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fluoroscopy-guided TFESI was performed in 181 patients. The patients were categorized into three groups according to the injected lumbosacral nerve level of L2-4, L5, or S1. Fluoroscopy time (FT) and dose area product (DAP) were recorded for all patients; correlations between FT and DAP were determined at each level, and both FT and DAP were compared between the different vertebral levels.
RESULTS
The numbers of patients who received ESI at L2-4, L5, and S1 were 29, 123, and 29. Mean FT was 44 seconds at L2-4, 33.5 seconds at L5, and 37.7 seconds at S1. Mean DAP was 138.6 microGy.m2 at L2-4, 100.6 microGy.m2 at L5, and 72.1 microGy.m2 at S1. FT and DAP were positively correlated in each group (p values < 0.001). FT was significantly shorter at L5 than that at L2-4 (p = 0.004) but was not significantly different between S1 and L2-4 or L5 (p values = 0.286 and 0.532, respectively). DAP was significantly smaller at L5 and S1 than that at L2-4, but L5 and S1 were not significantly different. After correcting for FT, DAP was significantly smaller at S1 than that at either L2-4 or L5 (p values = 0.001 and 0.010).
CONCLUSION
The radiation dose was small during a single procedure of ESI and showed differences between different lumbosacral spine levels.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stout A. Epidural steroid injections for low back pain. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2010; 21:825–834.2. Fink GE. Radiation safety in fluoroscopy for neuraxial injections. AANA J. 2009; 77:265–269.3. Riew KD, Yin Y, Gilula L, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Lauryssen C, et al. The effect of nerve-root injections on the need for operative treatment of lumbar radicular pain. A prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82-A:1589–1593.4. Friedly J, Chan L, Deyo R. Geographic variation in epidural steroid injection use in medicare patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:1730–1737.5. Hoang JK, Yoshizumi TT, Toncheva G, Gray L, Gafton AR, Huh BK, et al. Radiation dose exposure for lumbar spine epidural steroid injections: a comparison of conventional fluoroscopy data and CT fluoroscopy techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:778–782.6. Zhou Y, Singh N, Abdi S, Wu J, Crawford J, Furgang FA. Fluoroscopy radiation safety for spine interventional pain procedures in university teaching hospitals. Pain Physician. 2005; 8:49–53.7. Hanu-Cernat DE, Duarte R, Raphael JH, Mutagi H, Kapur S, Senthil L. Type of interventional pain procedure, body weight, and presence of spinal pathology are determinants of the level of radiation exposure for fluoroscopically guided pain procedures. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:434–439.8. Miller DL, Balter S, Schueler BA, Wagner LK, Strauss KJ, Vañó E. Clinical radiation management for fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures. Radiology. 2010; 257:321–332.9. Fletcher DW, Miller DL, Balter S, Taylor MA. Comparison of four techniques to estimate radiation dose to skin during angiographic and interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:391–397.10. Axelsson B. Optimisation in fluoroscopy. Biomed Imaging Interv J. 2007; 3:e47.11. Hirshfeld JW Jr, Balter S, Brinker JA, Kern MJ, Klein LW, Lindsay BD, et al. ACCF/AHA/HRS/SCAI clinical competence statement on physician knowledge to optimize patient safety and image quality in fluoroscopically guided invasive cardiovascular procedures: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association/American College of Physicians Task Force on Clinical Competence and Training. Circulation. 2005; 111:511–532.12. Miller DL, Kwon D, Bonavia GH. Reference levels for patient radiation doses in interventional radiology: proposed initial values for U.S. practice. Radiology. 2009; 253:753–764.13. Stecker MS, Balter S, Towbin RB, Miller DL, Vañó E, Bartal G, et al. Guidelines for patient radiation dose management. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:7 Suppl. S263–S273.14. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, Moss TL, Rivera J, Pampati V. Risk of whole body radiation exposure and protective measures in fluoroscopically guided interventional techniques: a prospective evaluation. BMC Anesthesiol. 2003; 3:2.15. Fish DE, Lee PC, Marcus DB. The S1 "Scotty dog": report of a technique for S1 transforaminal epidural steroid injection. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:1730–1733.16. Schueler BA. The AAPM/RSNA physics tutorial for residents: general overview of fluoroscopic imaging. Radiographics. 2000; 20:1115–1126.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of incidence of intravascular injections during transforaminal epidural steroid injection using different needle types
- Oblique interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: A case report
- Accuracy of Live Fluoroscopy to Detect Intravascular Injection During Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections
- An Analysis of Pattern of Transforaminal Epidurography
- Epidural hematoma treated by aspiration after transforaminal epidural steroid injection - A case report -