Yonsei Med J.
2015 Mar;56(2):550-555. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.550.
Comparison of MALDI-TOF MS, Housekeeping Gene Sequencing, and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing for Identification of Aeromonas Clinical Isolates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leekcp@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Hanyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2070037
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.550
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The genus Aeromonas is a pathogen that is well known to cause severe clinical illnesses, ranging from gastroenteritis to sepsis. Accurate identification of A. hydrophila, A. caviae, and A. veronii is important for the care of patients. However, species identification remains difficult using conventional methods. The aim of this study was to compare the accuracy of different methods of identifying Aeromonas at the species level: a biochemical method, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry-time of flight (MALDI-TOF MS), 16S rRNA sequencing, and housekeeping gene sequencing (gyrB, rpoB).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed 65 Aeromonas isolates recovered from patients at a university hospital in Korea between 1996 and 2012. The isolates were recovered from frozen states and tested using the following four methods: a conventional biochemical method, 16S rRNA sequencing, housekeeping gene sequencing with phylogenetic analysis, and MALDI-TOF MS.
RESULTS
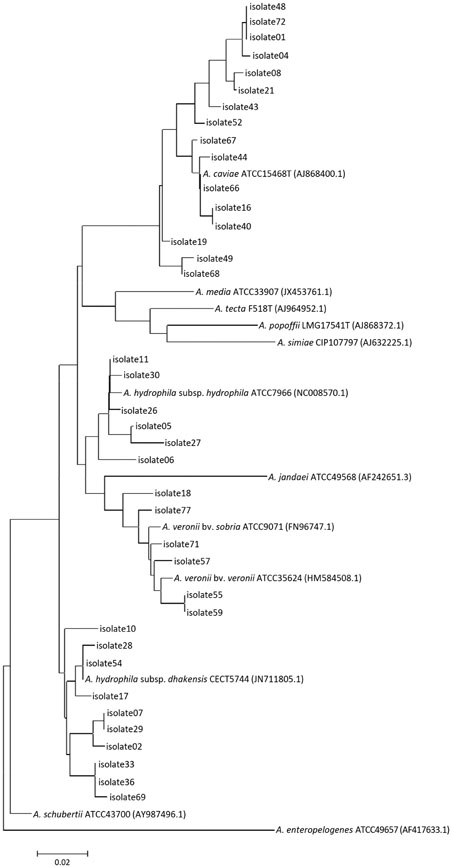
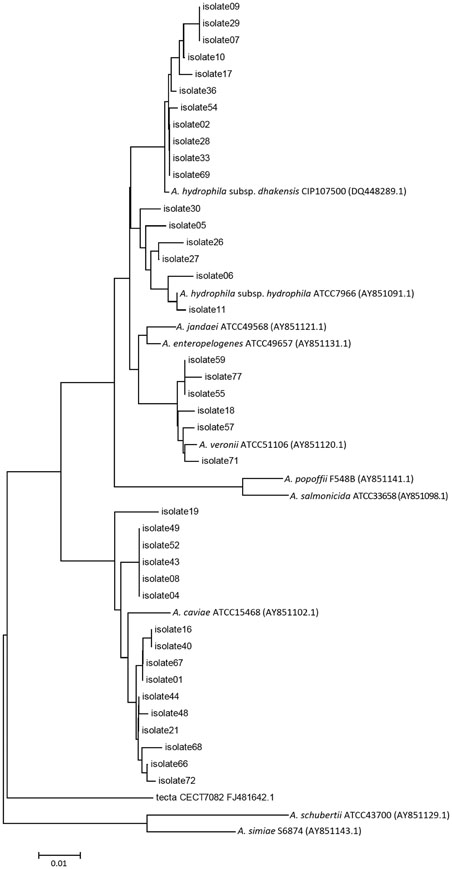
The conventional biochemical method and 16S rRNA sequencing identified Aeromonas at the genus level very accurately, although species level identification was unsatisfactory. MALDI-TOF MS system correctly identified 60 (92.3%) isolates at the species level and an additional four (6.2%) at the genus level. Overall, housekeeping gene sequencing with phylogenetic analysis was found to be the most accurate in identifying Aeromonas at the species level.
CONCLUSION
The most accurate method of identification of Aeromonas to species level is by housekeeping gene sequencing, although high cost and technical difficulty hinder its usage in clinical settings. An easy-to-use identification method is needed for clinical laboratories, for which MALDI-TOF MS could be a strong candidate.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aeromonas/classification/*genetics/isolation & purification
DNA, Bacterial/genetics
Genes, Essential/*genetics
Humans
Molecular Typing/*methods
Phylogeny
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S/*genetics
Republic of Korea
Sensitivity and Specificity
Sequence Analysis, DNA/*methods
Spectrometry, Mass, Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption-Ionization/*methods
DNA, Bacterial
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S
Figure
Reference
-
1. Steinberg J, Burd EM. Other Gram-Negative and Gram-Variable Bacilli. In : Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 7th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;2010. p. 465–478.2. Janda JM, Abbott SL. The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010; 23:35–73.
Article3. Benagli C, Demarta A, Caminada A, Ziegler D, Petrini O, Tonolla M. A rapid MALDI-TOF MS identification database at genospecies level for clinical and environmental Aeromonas strains. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e48441.4. Nhung PH, Hata H, Ohkusu K, Noda M, Shah MM, Goto K, et al. Use of the novel phylogenetic marker dnaJ and DNA-DNA hybridization to clarify interrelationships within the genus Aeromonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007; 57(Pt 6):1232–1237.
Article5. Küpfer M, Kuhnert P, Korczak BM, Peduzzi R, Demarta A. Genetic relationships of Aeromonas strains inferred from 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoB gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006; 56(Pt 12):2743–2751.
Article6. Lamy B, Kodjo A, Laurent F. ColBVH Study Group. Identification of Aeromonas isolates by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 71:1–5.
Article7. Murray PR. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: usefulness for taxonomy and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010; 16:1626–1630.
Article8. Yáñez MA, Catalán V, Apráiz D, Figueras MJ, Martínez-Murcia AJ. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003; 53(Pt 3):875–883.
Article9. Korczak B, Christensen H, Emler S, Frey J, Kuhnert P. Phylogeny of the family Pasteurellaceae based on rpoB sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004; 54(Pt 4):1393–1399.
Article10. Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011; 28:2731–2739.
Article11. Mellmann A, Cloud J, Maier T, Keckevoet U, Ramminger I, Iwen P, et al. Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry in comparison to 16S rRNA gene sequencing for species identification of nonfermenting bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:1946–1954.
Article12. Chong Y, Yi KN, Lee SY. Cultural and biochemical characteristics of clinical isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila. Yonsei Med J. 1980; 21:52–57.
Article13. Kwak CG, Chong Y, Lee SY, Hong CS, Koh CM. Species and antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas strains isolated from patients and environmental sources. Korean J Infect Dis. 1987; 19:167–177.14. Janda JM, Abbott SL. Evolving concepts regarding the genus Aeromonas: an expanding Panorama of species, disease presentations, and unanswered questions. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 27:332–344.
Article15. Soler L, Yáñez MA, Chacon MR, Aguilera-Arreola MG, Catalán V, Figueras MJ, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas based on two housekeeping genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004; 54(Pt 5):1511–1519.
Article16. Horneman AJ, Ali A. Aeromonas. In : Versalovic J, Carroll KC, Funke G, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Warnock DW, editors. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 10th ed. Washington D.C.: ASM Press;2011. p. 658–665.17. Martinez-Murcia AJ, Benlloch S, Collins MD. Phylogenetic interrelationships of members of the genera Aeromonas and Plesiomonas as determined by 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing: lack of congruence with results of DNA-DNA hybridizations. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992; 42:412–421.
Article18. Blondiaux N, Gaillot O, Courcol RJ. [MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry to identify clinical bacterial isolates: evaluation in a teaching hospital in Lille]. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2010; 58:55–57.19. Saavedra MJ, Figueras MJ, Martínez-Murcia AJ. Updated phylogeny of the genus Aeromonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006; 56(Pt 10):2481–2487.20. Abbott SL, Cheung WK, Janda JM. The genus Aeromonas: biochemical characteristics, atypical reactions, and phenotypic identification schemes. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:2348–2357.
Article21. Morandi A, Zhaxybayeva O, Gogarten JP, Graf J. Evolutionary and diagnostic implications of intragenomic heterogeneity in the 16S rRNA gene in Aeromonas strains. J Bacteriol. 2005; 187:6561–6564.
Article22. Donohue MJ, Smallwood AW, Pfaller S, Rodgers M, Shoemaker JA. The development of a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry-based method for the protein fingerprinting and identification of Aeromonas species using whole cells. J Microbiol Methods. 2006; 65:380–389.
Article23. Martínez-Murcia A, Monera A, Alperi A, Figueras MJ, Saavedra MJ. Phylogenetic evidence suggests that strains of Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. dhakensis belong to the species Aeromonas aquariorum sp. nov. Curr Microbiol. 2009; 58:76–80.
Article24. Sandrin TR, Goldstein JE, Schumaker S. MALDI TOF MS profiling of bacteria at the strain level: a review. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2013; 32:188–217.
Article25. Shin GW, You MJ, Cho HS, Yi SW, Lee CS. Severe sepsis due to Aeromonas aquariorum in a patient with liver cirrhosis. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2013; 66:519–522.
Article26. Puthucheary SD, Puah SM, Chua KH. Molecular characterization of clinical isolates of Aeromonas species from Malaysia. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e30205.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Taxonomic Identification of Bacillus Species Using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
- Resource Development and Investigation of Novel Species from Unidentified Pathogens in NCCP using MALDI-TOF MS and 16S rRNA Gene Analysis
- Comparison between the Rapid ID 32 Strep test system and 16S rRNA gene sequencing for the identification of α-hemolytic streptococci
- A Case of Klebsiella pneumoniae Unidentified by Conventional Biochemical Tests
- Five Cases of the Gram Variable Bacterium Paenibacillus urinalis Isolated from Clinical Specimens and its Clinical Significance