J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Jul;58(1):14-21. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.14.
The Effect of Early Intervention and Rehabilitation in the Expression of Aquaporin-4; and Ultrastructure Changes on Rat's Offspring's Damaged Brain Caused by Intrauterine Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Children Cerebral Palsy Unit One, College of Rehabilitation Medicine, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi, Heilongjiang, China. xiaojljms@vip.163.com
- KMID: 2067099
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.14
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To study the effect of early intervention and rehabilitation in the expression of aquaporin-4 and ultrastructure changes on cerebral palsy pups model induced by intrauterine infection.
METHODS
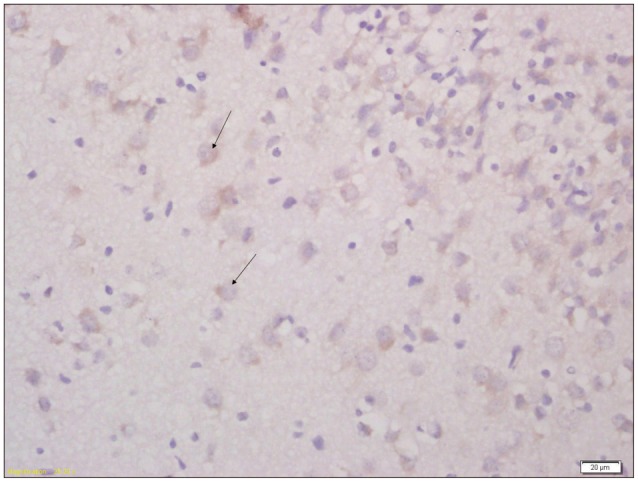
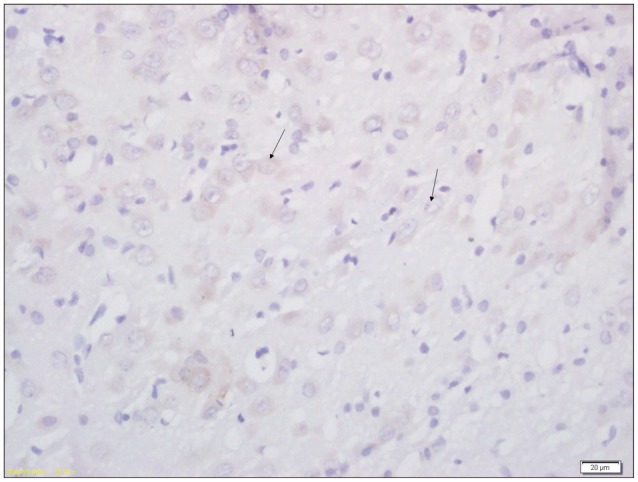
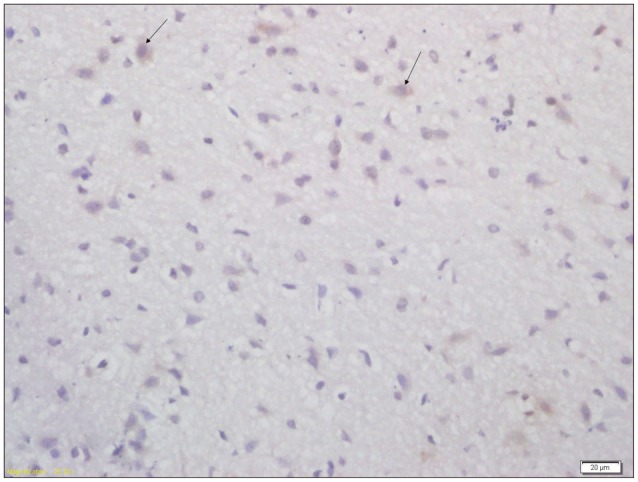
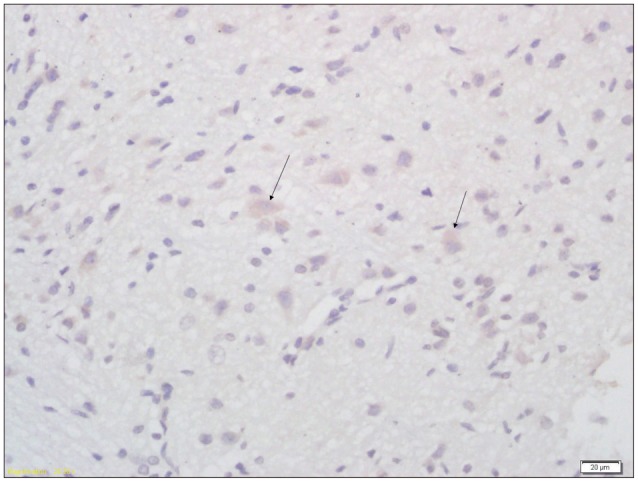
20 pregnant Wistar rats were consecutively injected with lipopolysaccharide intraperitoneally. 60 Pups born from lipopolysaccharide group were randomly divided into intervention group (n=30) and non-intervention group (n=30); intervention group further divided into early intervention and rehabilitation group (n=10), acupuncture group (n=10) and consolidate group (n=10). Another 5 pregnant rats were injected with normal saline intraperitoneally; 30 pups born from the normal saline group were taken as control group. The intervention group received early intervention, rehabilitation and acupuncture treatment. The motor functions of all pups were assessed via suspension test and modified BBB locomotor score. Aquaporin-4 expression in brain tissue was studied through immunohistochemical and western-blot analysis. Ultrastructure changes in damaged brain and control group were studied electron-microscopically.
RESULTS
The scores of suspension test and modified BBB locomotor test were significantly higher in the control group than the intervention and non intervention group (p<0.01); higher in the intervention group than the non-intervention group (p<0.01). The expression of Aquaporin-4 was lower in intervention and non intervention group than in the control group (p<0.01); also lower in non-intervention group than the intervention group (p<0.01). Marked changes were observed in ultrastructure of cortex and hippocampus CAI in brain damaged group.
CONCLUSION
Early intervention and rehabilitation training can improve the motor function in offspring with brain injury and reduce the expression of aquaporin-4 in damaged brain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, et al. Aquaporin water channels--from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol. 2002; 542(Pt 1):3–16. PMID: 12096044.2. Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP. The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003; 4:991–1001. PMID: 14682361.
Article3. Auguste KI, Jin S, Uchida K, Yan D, Manley GT, Papadopoulos MC, et al. Greatly impaired migration of implanted aquaporin-4-deficient astroglial cells in mouse brain toward a site of injury. FASEB J. 2007; 21:108–116. PMID: 17135365.
Article4. Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, et al. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005; 47:571–576. PMID: 16108461.
Article5. Guo Z, Li X, Pang W. Comparison of two kinds of evaluation for motor function of cerebral palsy neonatal rats caused by intrauterine infection. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract. 2010; 3:224–227.6. Hagberg B, Hagberg G, Beckung E, Uvebrant P. Changing panorama of cerebral palsy in Sweden. VIII. Prevalence and origin in the birth year period 1991-94. Acta Paediatr. 2001; 90:271–277. PMID: 11332166.
Article7. Hagberg H, Peebles D, Mallard C. Models of white matter injury : comparison of infectious, hypoxic-ischemic, and excitotoxic insults. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2002; 8:30–38. PMID: 11921384.
Article8. Jaworski J, Kapitein LC, Gouveia SM, Dortland BR, Wulf PS, Grigoriev I, et al. Dynamic microtubules regulate dendritic spine morphology and synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 2009; 61:85–100. PMID: 19146815.
Article9. Jiulai T. Conductive Education in latest research and trends in cerebral palsy rehabilitation management system. Chin Child Rehabil. 2009; 6:8–9.10. Kakizawa H, Matsui F, Tokita Y, Hirano K, Ida M, Nakanishi K, et al. Neuroprotective effect of nipradilol, an NO donor, on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury of neonatal rats. Early Hum Dev. 2007; 83:535–540. PMID: 17157452.
Article11. Kumral A, Uysal N, Tugyan K, Sonmez A, Yilmaz O, Gokmen N, et al. Erythropoietin improves long-term spatial memory deficits and brain injury following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2004; 153:77–86. PMID: 15219709.
Article12. Li X, Lv Z, Sun Z, Gao J. Effects of enriched environmental stimulation on brain development in cerebral palsy rats. Chin J Rehabil Med. 2006; 12:1061–1064.13. Liu Chuanjun GY, Li Yalu. Early intervention on hypoxic ischemic brain damage and effects of synaptic plasticity on cerebral cortex in newborn rat. Chin Matern Child Health. 2011; 26:1702–1705.14. Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, et al. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med. 2000; 6:159–163. PMID: 10655103.
Article15. Nelson KB, Willoughby RE. Infection, inflammation and the risk of cerebral palsy. Curr Opin Neurol. 2000; 13:133–139. PMID: 10987569.
Article16. Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bourque C, Agre P, Ottersen OP. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells : high-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1997; 17:171–180. PMID: 8987746.
Article17. Pang W, Li XJ, Zhang SL, Guo LM. Effects of early intervention on expression of S-100 protein and neurobehavioral change in offspring rats with brain injury induced by intrauterine infection. J Appl Clin Pediatr. 102; 2:96–98.18. Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Watanabe H, Yan D, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Involvement of aquaporin-4 in astroglial cell migration and glial scar formation. J Cell Sci. 2005; 118(Pt 24):5691–5698. PMID: 16303850.
Article19. Senger D, Cairncross JG, Forsyth PA. Long-term survivors of glioblastoma : statistical aberration or important unrecognized molecular subtype? Cancer J. 2003; 9:214–221. PMID: 12952306.20. Shepherd R. Cerebral palsy. Physiotherapy in paediatric. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinnemann;1995. p. 110–144.21. Tang Y, Wu P, Su J, Xiang J, Cai D, Dong Q. Effects of Aquaporin-4 on edema formation following intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp Neurol. 2010; 223:485–495. PMID: 20132816.
Article22. Venero JL, Vizuete ML, Machado A, Cano J. Aquaporins in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 2001; 63:321–336. PMID: 11115728.
Article23. Chen Y, Chen Y. Effect of exercise on mouse cerebellar cortex and age-related changes in the spinal cord and the synaptophysin. J Anat. 1994; 25:263–267.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Altered Expression of Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) in Hippocampal Formation after Systemic Hyponatremia
- Long-term effects of pro-opiomelanocortin methylation induced in food-restricted dams on metabolic phenotypes in male rat offspring
- Down-Regulation of Aquaporin 4 in the Lithium-Treated Rat Brain
- Increased Levels of C1q in the Prefrontal Cortex of Adult Offspring after Maternal Immune Activation: Prevention by 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone
- Loss of Caveolin 1 is Associated With the Expression of Aquaporin 1 and Bladder Dysfunction in Mice