J Korean Med Assoc.
2009 Jun;52(6):611-626. 10.5124/jkma.2009.52.6.611.
New Antiepileptic Drugs in Childhood Epilepsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyunghee University College of Medicine, Korea. sajchung@khmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2065056
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2009.52.6.611
Abstract
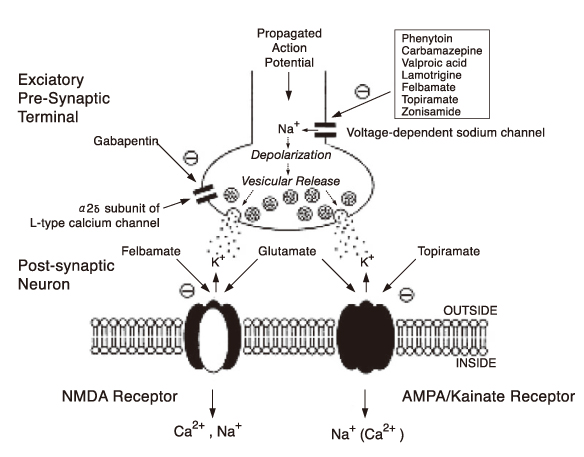
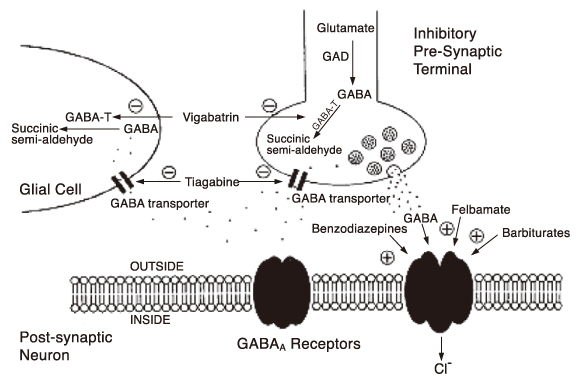
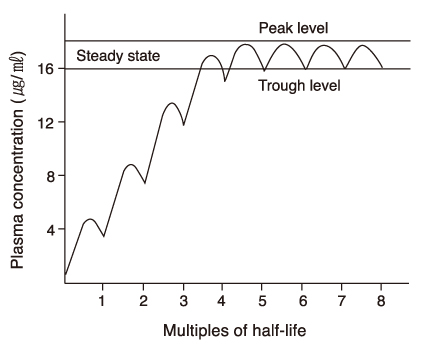
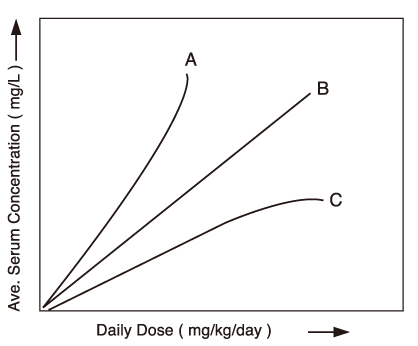
- Many new antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) have been developed in the last two decades, contributing to the optimal treatment for childhood epilepsy. The goal of the treatment is to achieve seizure-free without any side effects, that deteriorates the quality of life by causing negative consequences. The new AEDs have not shown better efficacy, but generally seem to be better tolerated, having fewer systemic reactions and better pharmacokinetics than the established AEDs. The new AEDs have a broad spectrum of activities, which offer new opportunities to patients who have not shown any favorable responses to the established ones. There are more choices when trying to select AEDs for epileptic seizures and syndromes. Majority of the new AEDs have more than one action mechanism. AEDs acting selectively through the GABAergic system are tiagabine and vigabatrin; acting by inhibition of voltagedependent Na+ and Ca2+ channels are lamotirigine, oxcabarbazepine and topiramate; and acting by inhibition of glutamate-mediated excitation are felbamate, topiramate. The pharmacokinetic parameters of the new AEDs compared to the established AEDs, new AEDs have improved in terms of longer half-lives, permitting less frequent daily dosing, reduced potential for drug interactions. Considerations in selecting an AEDs are not only dependent on seizure types or syndromes, side effect profile, action mechanism, drug interaction, pharmacokinetic profile, facility of drug initiation, but also on age and sex of patients. Patients with worsened seizurefrequency or development of new types of seizure after the introduction of AEDs, should be questioned on the previously diagnosed seizure types or syndromes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ben-Menachem E. Strategy for utilization of new antiepileptic drugs. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008. 21:167–172.
Article2. Rho JM, Sanker R. The pharmacologic basis of antiepileptic drug action. Epilepsia. 1999. 40:1471–1483.
Article3. Meldrum BS. Update on the mechanism of action of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 1996. 37:S6. S4–S11.
Article4. Bourgeois BFD. Wyllie E, editor. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antiepileptic drugs. The treatment odepilepsy. practice & practice. 2001. 3rd ed. Pholadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;729–757.5. French JA, Kanner AM, Bautista J, Abou-Khalil B, Browne T, Harden CL, Theodore WH, Bazil C, Stern J, Schachter SC, Bergen D, Hirtz D, Montouris GD, Nespeca M, Gidal B, Marks WJ Jr, Turk WR, Fischer JH, Bourgeois B, Wilner A, Faught RE Jr, Sachdeo RC, Beydoun A, Glauser TA. Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. American Epilepsy Society. Efficacy and tolerability of the new antiepileptic drugs I: treament of new onset epilepsy. Neurology. 2004. 62:1252–1260.
Article6. Beyenburg S, Bauer J, Reuber M. New drugs for treatment of epilepsy: a practical approach. Postgrad Med J. 2004. 80:581–587.7. Brodie MJ, Schachter SC, Kwan P. Fast Facts:Epilepsy. 2005. 3rd ed. Oxford: Health Press.8. O'Dell C, Shinnar S. Initiation and discontinuation of antiepileptic drugs. Neurol Clin. 2001. 19:289–311.9. Sankar R. Initial treatment of epilepsy with antiepileptic drugs; Pedaitric issues. Neurology. 2004. 63:S4. S30–S39.10. Wolfig AA. Monotherapy in children and infants. Neurology. 2007. 69:S3. 17–22.
Article11. Sazgar M, Bourgois BFD. Aggravation of epilepsy by abtiepileptic drugs. Pediatr Neurol. 2005. 33:227–234.