Electrolyte Blood Press.
2009 Dec;7(2):51-57. 10.5049/EBP.2009.7.2.51.
Hyponatremia in Patients with Neurologic Disorders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junephro@snuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2052319
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2009.7.2.51
Abstract
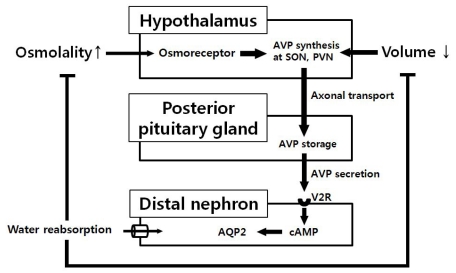
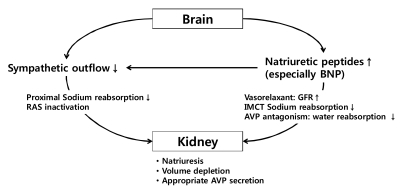
- The kidney and the brain play a major role in maintaining normal homeostasis of the extracellular fluid by neuroendocrine regulation of sodium and water balance. Therefore, disturbances of sodium balance are common in patients with central nervous system (CNS) disorders and clinicians should focus not only on the CNS lesion, but also on the potentially deleterious complications. Hyponatremia is the most common and important electrolyte disorder affecting patients with critical neurologic diseases. In these patients, the maladaptation to hyponatremia by impaired osmoregulation in pathologic lesions of brain may cause more aggressive cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure due to hypoosmolality induced by hyponatremia. Furthermore, hyponatremia accompanied by CNS disorders has shown to increase delayed cerebral ischemia and mortality rates. Two main pathophysiologies of hyponatremia, excluding iatrogenic causes, are inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) and cerebral salt wasting (CSW) syndrome. Differential diagnosis between these two entities can be difficult due to considerable overlap in the laboratory findings and clinical situations. SIADH is in a volume expanded status due to inappropriately secreted arginine vasopressin (AVP) and requires water restriction. However, CSW syndrome is characterized by renal sodium wasting mainly due to increased natriuretic peptides resulting in volume depletion and follows appropriate secretion of AVP. Therefore, maintenance of volume status and sodium replacement is the mainstay of treatment in CSW syndrome. In this review, we aimed to describe the regulation of sodium and water balance, and pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia in neurologic patients, especially focusing on SIADH and CSW syndrome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Arginine Vasopressin
Brain
Brain Edema
Brain Ischemia
Central Nervous System
Diagnosis, Differential
Extracellular Fluid
Homeostasis
Humans
Hyponatremia
Inappropriate ADH Syndrome
Intracranial Pressure
Kidney
Natriuretic Peptides
Nervous System Diseases
Sodium
Water-Electrolyte Balance
Arginine Vasopressin
Natriuretic Peptides
Sodium
Water-Electrolyte Balance
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Syndrome of Inappropriate Scretion of Anti-Diuretic Hormone Associated with Sodium Valproate
Hong Joo Lee, Jung Kook Wi, Ju Young Moon, Kyung Hwan Jeong, Chun Gyoo Ihm, Sang Ho Lee, Tae Won Lee
Electrolyte Blood Press. 2012;10(1):31-34. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2012.10.1.31.
Reference
-
1. Piek J. Medical complications in severe head injury. New Horiz. 1995; 3:534–538. PMID: 7496764.2. Arango MF, Andrews PJ. Systemic complications of neurologic diseases. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2001; 7:61–67. PMID: 11373512.
Article3. Tisdall M, Crocker M, Watkiss J, Smith M. Disturbances of sodium in critically ill adult neurologic patients: a clinical review. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2006; 18:57–63. PMID: 16369141.4. Davenport A. The brain and the kidney--organ cross talk and interactions. Blood Purif. 2008; 26:526–536. PMID: 18987466.5. Swaab DF, Nijveldt F, Pool CW. Distribution of oxytocin and vasopressin in the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nucleus. J Endocrinol. 1975; 67:461–462. PMID: 1206330.
Article6. Sachs H, Poryanova R, Haller EW, Share L. Cellular processes concerned with vasopressin biosynthesis, storage and release. Neurosecretion. 1967. 1st ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;p. 146–154.
Article7. Robertson GL. Antidiuretic hormone. Normal and disordered function. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001; 30:671–694. PMID: 11571936.8. Robertson GL, Aycinena P, Zerbe RL. Neurogenic disorders of osmoregulation. Am J Med. 1982; 72:339–353. PMID: 7036730.
Article9. Landry DW, Oliver JA. The pathogenesis of vasodilatory shock. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:588–595. PMID: 11529214.
Article10. McKinley MJ, Mathai ML, McAllen RM, et al. Vasopressin secretion: osmotic and hormonal regulation by the lamina terminalis. J Neuroendocrinol. 2004; 16:340–347. PMID: 15089972.
Article11. Baumann G, Dingman JF. Distribution, blood transport, and degradation of antidiuretic hormone in man. J Clin Invest. 1976; 57:1109–1116. PMID: 1262458.
Article12. Verbalis JG. Vasopressin V2 receptor antagonists. J Mol Endocrinol. 2002; 29:1–9. PMID: 12200224.
Article13. Nielsen S. Renal aquaporins: an overview. BJU Int. 2002; 90(Suppl 3):1–6. PMID: 12445090.
Article14. Flear CT, Gill GV, Burn J. Hyponatraemia: mechanisms and management. Lancet. 1981; 2:26–31. PMID: 6113402.
Article15. Waikar SS, Mount DB, Curhan GC. Mortality after hospitalization with mild, moderate, and severe hyponatremia. Am J Med. 2009; 122:857–865. PMID: 19699382.
Article16. Reeder RF, Harbaugh RE. Administration of intravenous urea and normal saline for the treatment of hyponatremia in neurosurgical patients. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70:201–206. PMID: 2913218.
Article17. Hasan D, Wijdicks EF, Vermeulen M. Hyponatremia is associated with cerebral ischemia in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Ann Neurol. 1990; 27:106–108. PMID: 2301918.
Article18. Karandanis D, Shulman JA. Recent survey of infectious meningitis in adults: review of laboratory findings in bacterial, tuberculous, and aseptic meningitis. South Med J. 1976; 69:449–457. PMID: 1265506.19. Sane T, Rantakari K, Poranen A, Tahtela R, Valimaki M, Pelkonen R. Hyponatremia after transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994; 79:1395–1398. PMID: 7962334.
Article20. Olson BR, Gumowski J, Rubino D, Oldfield EH. Pathophysiology of hyponatremia after transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. J Neurosurg. 1997; 87:499–507. PMID: 9322839.
Article22. Boulard G, Marguinaud E, Sesay M. Osmotic cerebral oedema: the role of plasma osmolarity and blood brain barrier. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2003; 22:215–219. PMID: 12747989.23. Wijdicks EF, Vermeulen M, Hijdra A, van Gijn J. Hyponatremia and cerebral infarction in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: is fluid restriction harmful? Ann Neurol. 1985; 17:137–140. PMID: 3977297.
Article24. Rabinstein AA, Wijdicks EF. Hyponatremia in critically ill neurological patients. Neurologist. 2003; 9:290–300. PMID: 14629783.
Article25. Robertson GL. Regulation of arginine vasopressin in the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. Am J Med. 2006; 119:S36–S42. PMID: 16843083.
Article26. Smith D, Moore K, Tormey W, Baylis PH, Thompson CJ. Downward resetting of the osmotic threshold for thirst in patients with SIADH. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 287:E1019–E1023. PMID: 15213060.
Article27. Palmer BF. Hyponatremia in patients with central nervous system disease: SIADH versus CSW. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 14:182–187. PMID: 12714279.
Article28. Maesaka JK, Imbriano LJ, Ali NM, Ilamathi E. Is it cerebral or renal salt wasting? Kidney Int. 2009; 76:934–938. PMID: 19641485.
Article29. Ellison DH, Berl T. Clinical practice. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:2064–2072. PMID: 17507705.30. Bhardwaj A. Neurological impact of vasopressin dysregulation and hyponatremia. Ann Neurol. 2006; 59:229–236. PMID: 16437573.
Article31. Casulari LA, Costa KN, Albuquerque RC, Naves LA, Suzuki K, Domingues L. Differential diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia following pituitary surgery. J Neurosurg Sci. 2004; 48:11–18. PMID: 15257260.32. Palmer BF, Gates JR, Lader M. Causes and management of hyponatremia. Ann Pharmacother. 2003; 37:1694–1702. PMID: 14565794.
Article33. Laureno R, Karp BI. Myelinolysis after correction of hyponatremia. Ann Intern Med. 1997; 126:57–62. PMID: 8992924.
Article34. Rabinstein AA. Vasopressin antagonism: potential impact on neurologic disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2006; 29:87–93. PMID: 16614541.35. Sherlock M, O'Sullivan E, Agha A, et al. The incidence and pathophysiology of hyponatraemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006; 64:250–254. PMID: 16487432.
Article36. Palmer BF. Hyponatraemia in a neurosurgical patient: syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion versus cerebral salt wasting. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000; 15:262–268. PMID: 10648680.
Article37. Berendes E, Walter M, Cullen P, et al. Secretion of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 1997; 349:245–249. PMID: 9014912.
Article38. Schweda F, Friis U, Wagner C, Skott O, Kurtz A. Renin release. Physiology (Bethesda). 2007; 22:310–319. PMID: 17928544.
Article39. Marin-Grez M, Fleming JT, Steinhausen M. Atrial natriuretic peptide causes pre-glomerular vasodilatation and postglomerular vasoconstriction in rat kidney. Nature. 1986; 324:473–476. PMID: 2946962.
Article40. Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:321–328. PMID: 9682046.
Article41. Maesaka JK, Gupta S, Fishbane S. Cerebral salt-wasting syndrome: does it exist? Nephron. 1999; 82:100–109. PMID: 10364700.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hyponatremia with Generalized Convulsion Following Sinus Surgery
- Initial Transient Neurologic Recovery Followed by Delayed Deterioration of Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome: A Case Report
- A Case of Severe Hyponatremia Induced by Radiographic Contrast Agent
- Acute Severe Symptomatic Hyponatremia Following Coronary Angiography
- Efficacy of Clozapine on Schizophrenia with Polydipsia: Two Cases Experience