Electrolyte Blood Press.
2007 Dec;5(2):116-125. 10.5049/EBP.2007.5.2.116.
Electrolyte and Acid-Base Disturbances Associated with Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junephro@snug.org
- KMID: 2052294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2007.5.2.116
Abstract
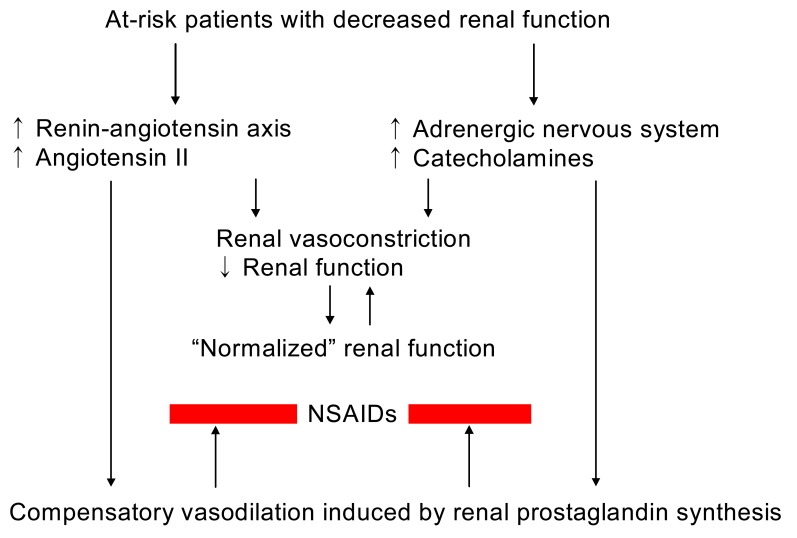
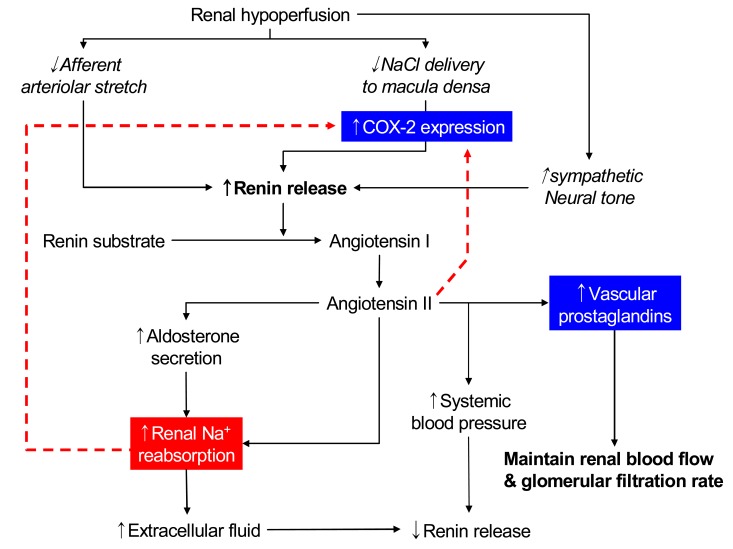
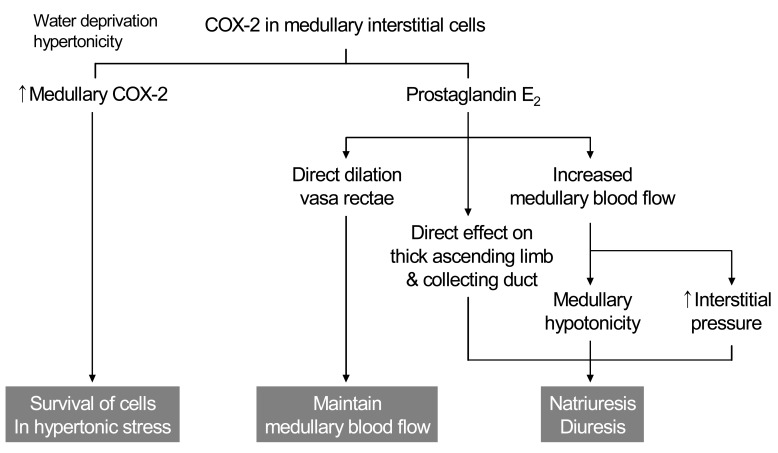
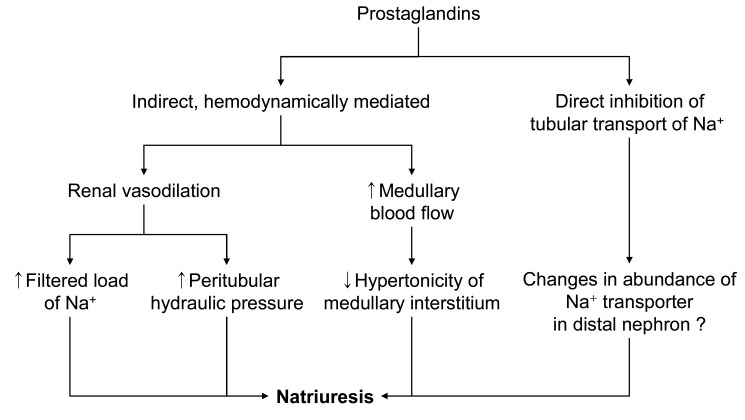
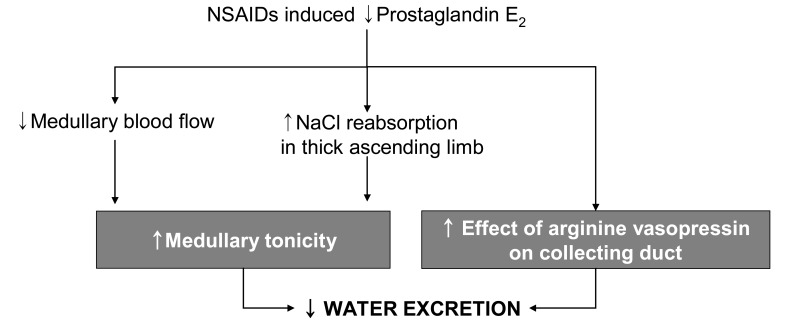
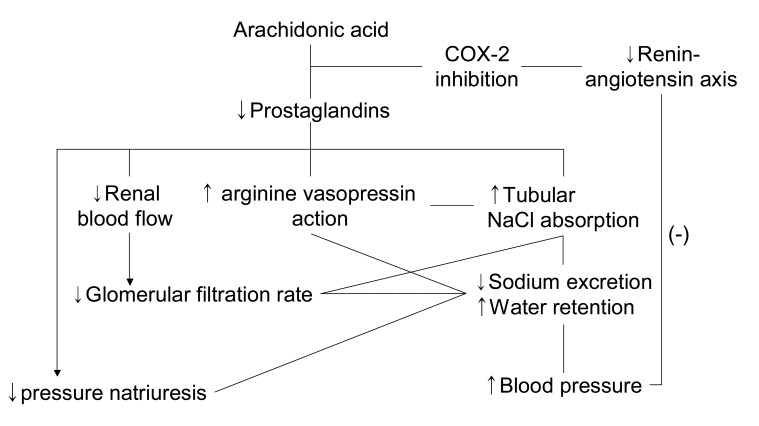
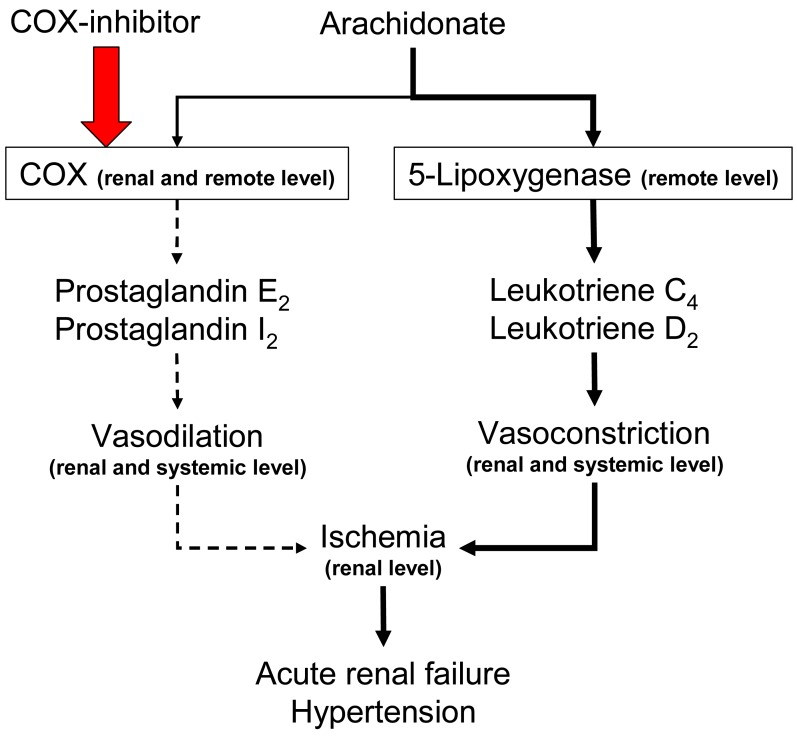
- Inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) causes various electrolyte and acid-base disturbances including sodium retention (edema, hypertension), hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and decreased renal function. Decreased sodium excretion can result in weight gain, peripheral edema, attenuation of the effects of antihypertensive agents, and rarely aggravation of congestive heart failure. Although rare, NSAIDs can cause hyponatremia by reducing renal free water clearance. Hyperkalemia could occur to a degree sufficient to cause cardiac arrhythmias. Renal function can decline sufficiently enough to cause acute renal failure. NSAIDs associated electrolyte and acid-base disturbances are not uncommon in some clinical situations. Adverse renal effects of NSAIDs are generally associated with prostaglandin dependent states such as volume-contracted states, low cardiac output, or other conditions that tend to compromise renal perfusion. All NSAIDs seem to share these adverse effects. In view of many NSAIDs users' susceptibility to renal adverse effects due to their underlying disease or condition, physicians should be cautious in prescribing NSAIDs to susceptible patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oates JA, FitzGerald GA, Branch RA, Jackson EK, Knapp HR, Roberts LJ 2nd. Clinical implications of prostaglandin and thromboxane A2 formation (2). N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:761–767. PMID: 3045551.2. Oates JA, FitzGerald GA, Branch RA, Jackson EK, Knapp HR, Roberts LJ 2nd. Clinical implications of prostaglandin and thromboxane A2 formation (1). N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:689–698. PMID: 3045550.3. Bush TM, Shlotzhauer TL, Imai K. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Proposed guidelines for monitoring toxicity. West J Med. 1991; 155:39–42. PMID: 1877228.4. Whelton A. Renal aspects of treatment with con ventional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus cyclooxygenase-2-specific inhibitors. Am J Med. 2001; 110(Suppl 3A):33S–42S. PMID: 11173048.5. Currie MG, Needleman P. Renal arachidonic acid metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984; 46:327–341. PMID: 6370112.
Article6. Xie WL, Chipman JG, Robertson DL, Erikson RL, Simmons DL. Expression of a mitogen-responsive gene encoding prostaglandin synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991; 88:2692–2696. PMID: 1849272.
Article7. Smith WL, Bell TG. Immunohistochemical localization of the prostaglandin-forming cyclooxygenase in renal cortex. Am J Physiol. 1978; 235:F451–F457. PMID: 103439.
Article8. Schlondorff D. Renal complications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Kidney Int. 1993; 44:643–653. PMID: 8231040.
Article9. Satoh T, Cohen HT, Katz AI. Intracellular signaling in the regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase. I. Role of cyclic AMP and phospholipase A2. J Clin Invest. 1992; 89:1496–1500. PMID: 1349027.
Article10. Anderson RJ, Berl T, McDonald KM, Schrier RW. Prostaglandins: effects on blood pressure, renal blood flow, sodium and water excretion. Kidney Int. 1976; 10:205–215. PMID: 972441.
Article11. Breyer MD, Breyer RM. Prostaglandin E receptors and the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 279:F12–F23. PMID: 10894784.
Article12. Good DW, George T. Regulation of HCO-3 absorption by prostaglandin E2 and G proteins in rat medullary thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1996; 270:F711–F717. PMID: 8928831.13. Hébert RL, Jacobson HR, Breyer MD. PGE2 inhibits AVP-induced water flow in cortical collecting ducts by protein kinase C activation. Am J Physiol. 1990; 259:F318–F325. PMID: 2167017.14. Guan Y, Chang M, Cho W, Zhang Y, Redha R, Davis L, Chang S, DuBois RN, Hao CM, Breyer M. Cloning, expression, and regulation of rabbit cyclooxygenase-2 in renal medullary interstitial cells. Am J Physiol. 1997; 273:F18–F26. PMID: 9249588.
Article15. Hao CM, Yull F, Blackwell T, Kömmhoff M, Davis LS, Breyer MD. Dehydration activates an NF-kappaB-driven, COX2-dependent survival mechanism in renal medullary interstitial cells. J Clin Invest. 2000; 106:973–982. PMID: 11032857.16. Roman RJ, Lianos E. Influence of prostaglandins on papillary blood flow and pressure-natriuretic response. Hypertension. 1990; 15:29–35. PMID: 2295512.
Article17. Cowley AW Jr, Mattson DL, Lu S, Roman RJ. The renal medulla and hypertension. Hypertension. 1995; 25:663–673. PMID: 7721413.
Article18. Brater DC. Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on renal function: focus on cyclooxygenase-2-selective inhibition. Am J Med. 1999; 107:65S–70S. discussion 70S-71S. PMID: 10628595.19. Harris RC, Zhang MZ, Cheng HF. Cyclooxygenase-2 and the renal renin-angiotensin system. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004; 181:543–547. PMID: 15283769.
Article20. Fernández-Llama P, Ecelbarger CA, Ware JA, Andrews P, Lee AJ, Turner R, Nielsen S, Knepper MA. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors increase Na-K-2Cl cotransporter abundance in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1999; 277:F219–F226. PMID: 10444576.21. Kramer HJ, Glänzer K, Düsing R. Role of prostaglandins in the regulation of renal water excretion. Kidney Int. 1981; 19:851–859. PMID: 7021956.
Article22. Davis DP, Videen JS, Marino A, Vilke GM, Dunford JV, Van Camp SP, Maharam LG. Exercise-associated hyponatremia in marathon runners: a two-year experience. J Emerg Med. 2001; 21:47–57. PMID: 11399389.
Article23. Hew TD, Chorley JN, Cianca JC, Divine JG. The incidence, risk factors, and clinical manifestations of hyponatremia in marathon runners. Clin J Sport Med. 2003; 13:41–47. PMID: 12544163.
Article24. Page AJ, Reid SA, Speedy DB, Mulligan GP, Thompson J. Exercise-associated hyponatremia, renal function, and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use in an ultraendurance mountain run. Clin J Sport Med. 2007; 17:43–48. PMID: 17304005.
Article25. Collins R, Peto R, MacMahon S, Hebert P, Fiebach NH, Eberlein KA, Godwin J, Qizilbash N, Taylor JO, Hennekens CH. Blood pressure, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Part 2, Short-term reductions in blood pressure: overview of randomised drug trials in their epidemiological context. Lancet. 1990; 335:827–838. PMID: 1969567.26. Stokes JB. Patterns of K+ permeation following inhibition of Na+ transport in rabbit cortical ncollecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986; 250:F120–F126. PMID: 3455800.27. Perazella MA, Eras J. Are selective COX-2 inhibitors nephrotoxic? Am J Kidney Dis. 2000; 35:937–940. PMID: 10793030.
Article28. Swan SK, Rudy DW, Lasseter KC, Ryan CF, Buechel KL, Lambrecht LJ, Pinto MB, Dilzer SC, Obrda O, Sundblad KJ, Gumbs CP, Ebel DL, Quan H, Larson PJ, Schwartz JI, Musliner TA, Gertz BJ, Brater DC, Yao SL. Effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition on renal function in elderly persons receiving a low-salt diet. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2000; 133:1–9. PMID: 10877734.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial-induced Electrolyte and Acid-Base Disturbances
- Updates of Spondyloarthrothy Treatment
- Current Guidelines for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Experimental study of the effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents used in dental clinic on orthodontic tooth movement in rats