Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Nov;73(5):278-281. 10.4046/trd.2012.73.5.278.
A Case of Tracheobronchial Aspergillosis Resolved Spontaneously in an Immunocompetent Host
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, St. Paul's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. mdlee@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2050681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2012.73.5.278
Abstract
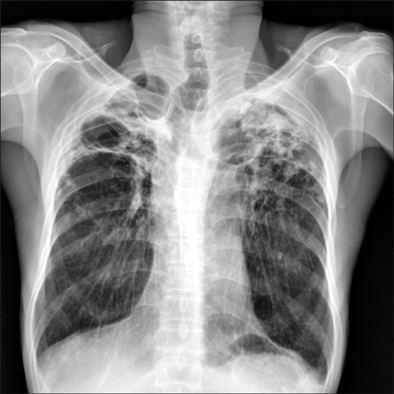
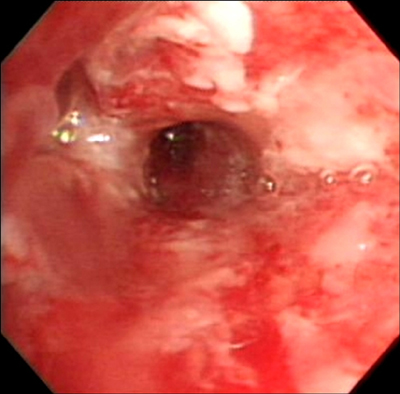
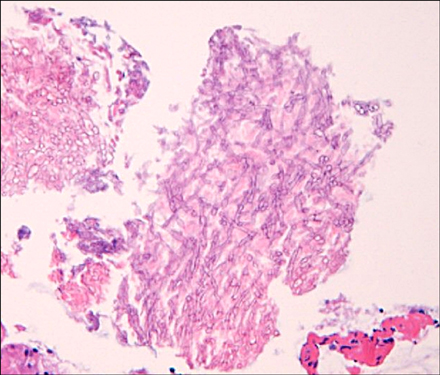
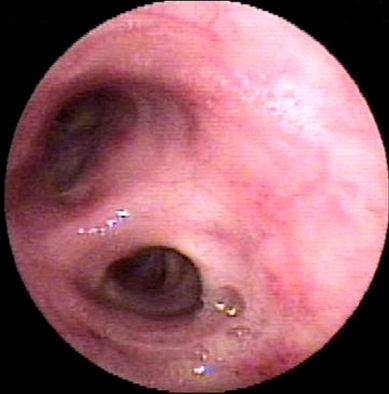
- A 47-year old man visited our hospital because of purulent sputum for 3 months. Chest X-ray showed destruction of both the upper lungs, and bronchoscopy revealed inflammatory change with whitish plaque on the left main bronchus through upper division of the left upper lobe. Tracheobronchial aspergillosis (TBA) was finally diagnosed as a result of histologic and microbiologic examination. However, he went abroad without medication before the diagnosis was made and visited again 10 months later. Follow-up bronchoscopy showed complete regression of the previously noted endobronchial lesion. We describe this case to consider the role of antifungal treatment in immunocompetent hosts, as well as to discuss a rare condition; TBA resolved spontaneously.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002. 121:1988–1999.2. Dagenais TR, Keller NP. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009. 22:447–465.3. McCormick A, Loeffler J, Ebel F. Aspergillus fumigatus: contours of an opportunistic human pathogen. Cell Microbiol. 2010. 12:1535–1543.4. Wu N, Huang Y, Li Q, Bai C, Huang HD, Yao XP. Isolated invasive Aspergillus tracheobronchitis: a clinical study of 19 cases. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. 16:689–695.5. Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, et al. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:327–360.6. Kramer MR, Denning DW, Marshall SE, Ross DJ, Berry G, Lewiston NJ, et al. Ulcerative tracheobronchitis after lung transplantation: a new form of invasive aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 144(3 Pt 1):552–556.7. Pornsuriyasak P, Murgu S, Colt H. Pseudomembranous Aspergillus tracheobronchitis superimposed on post-tuberculosis tracheal stenosis. Respirology. 2009. 14:144–147.8. Garcia-Olivé I, Andreo F, Rosiñol O, Sanz-Santos J, Font A, Monsó E. Bronchial stump aspergillosis after lobectomy for lung cancer as an unusual cause of false positive fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011. 5:72.9. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:1813–1821.10. Krenke R, Grabczak EM. Tracheobronchial manifestations of Aspergillus infections. ScientificWorldJournal. 2011. 11:2310–2329.11. Kim JS, Rhee Y, Kang SM, Ko WK, Kim YS, Lee JG, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma. Yonsei Med J. 2000. 41:422–425.12. Kim TH, Yong BJ, Kim YK, Lee YM, Kim KU, Uh ST, et al. A case of endobronchial aspergilloma with massive hemoptysis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2004. 57:589–593.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Case of Pseudomembranous Necrotizing Tracheobronchial Aspergillosis in an Immunocompetent Host
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Invaded to Thoracic Vertebra in a Immunocompetent Host: A case report
- Aspergillosis of Central Nervous System in Immunocompetent Host
- A Case of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in an Jmmunocompetent Host
- Concurrent Nocardia Related Brain Abscess and Semi-Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in an Immunocompetent Patient