Anat Cell Biol.
2012 Sep;45(3):155-159. 10.5115/acb.2012.45.3.155.
TonEBP and SMIT expression in human placenta
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hylee38@ewha.ac.kr
- 2School of Nano-Bioscience and Chemical Engineering, Ulsan National Institute and Science and Technology, Ulsan, Korea.
- 3School of Mechanical and Advanced Materials Engineering, Ulsan National Institute and Science and Technology, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2046742
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2012.45.3.155
Abstract
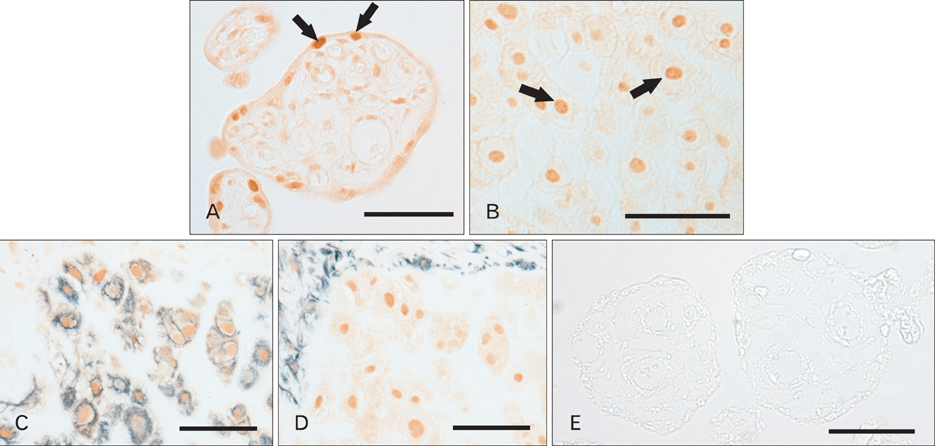
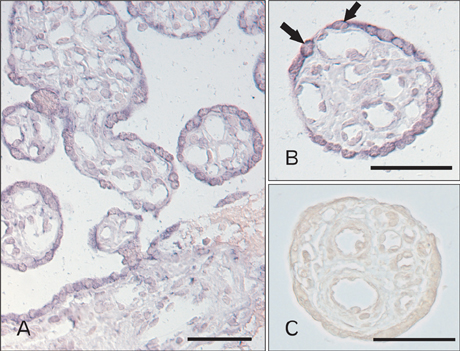
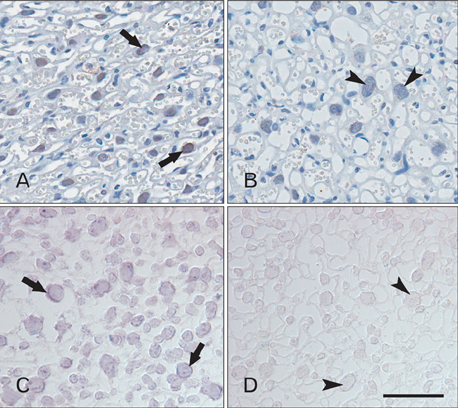
- Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein (TonEBP) is a signal transcription factor of transporters such as sodium-myo-inositol cotransporter (SMIT), aldose reductase. TonEBP has a variety of functions such as control of intracellular osmolytes and immunomodulating. It is known that TonEBP is abundant in the placenta, but location and function aren't known. The aim of this study is to describe the localization of TonEBP in the placenta. We assayed the immunohistochemistry of TonEBP and performed in situ hybridization of SMIT in normal human full term placenta. In normal human full term placenta, TonEBP was in villous trophoblasts, extravillous trophoblasts and some endothelial cells. The result of the in situ hybridization of SMIT was similar to that of immunohistochemistry of TonEBP. Neither TonEBP nor SMIT was present in TonEBP knockout mouse placenta. This shows TonEBP is a key factor in SMIT transcription. TonEBP may play an important role in transporting of inositol to fetus in placenta.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miyakawa H, Woo SK, Dahl SC, Handler JS, Kwon HM. Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein, a rel-like protein that stimulates transcription in response to hypertonicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. 96:2538–2542.2. Na KY, Woo SK, Lee SD, Kwon HM. Silencing of TonEBP/NFAT5 transcriptional activator by RNA interference. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. 14:283–288.3. Woo SK, Lee SD, Kwon HM. TonEBP transcriptional activator in the cellular response to increased osmolality. Pflugers Arch. 2002. 444:579–585.4. Dahl SC, Handler JS, Kwon HM. Hypertonicity-induced phosphorylation and nuclear localization of the transcription factor TonEBP. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001. 280:C248–C253.5. Trama J, Go WY, Ho SN. The osmoprotective function of the NFAT5 transcription factor in T cell development and activation. J Immunol. 2002. 169:5477–5488.6. Trama J, Lu Q, Hawley RG, Ho SN. The NFAT-related protein NFATL1 (TonEBP/NFAT5) is induced upon T cell activation in a calcineurin-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2000. 165:4884–4894.7. Dawson RM, Freinkel N. The distribution of free mesoinositol in mammalian tissues, including some observations on the lactating rat. Biochem J. 1961. 78:606–610.8. Stokes CE, Gillon KR, Hawthorne JN. Free and total lipid myo-inositol concentrations decrease with age in human brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983. 753:136–138.9. Godfrey DA, Hallcher LM, Laird MH, Matschinsky FM, Sherman WR. Distribution of myo-inositol in the cat cochlear nucleus. J Neurochem. 1982. 38:939–947.10. Fisher SK, Novak JE, Agranoff BW. Inositol and higher inositol phosphates in neural tissues: homeostasis, metabolism and functional significance. J Neurochem. 2002. 82:736–754.11. Berry GT, Wu S, Buccafusca R, Ren J, Gonzales LW, Ballard PL, Golden JA, Stevens MJ, Greer JJ. Loss of murine Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter leads to brain myo-inositol depletion and central apnea. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:18297–18302.12. Buccafusca R, Venditti CP, Kenyon LC, Johanson RA, Van Bockstaele E, Ren J, Pagliardini S, Minarcik J, Golden JA, Coady MJ, Greer JJ, Berry GT. Characterization of the null murine sodium/myo-inositol cotransporter 1 (Smit1 or Slc5a3) phenotype: myo-inositol rescue is independent of expression of its cognate mitochondrial ribosomal protein subunit 6 (Mrps6) gene and of phosphatidylinositol levels in neonatal brain. Mol Genet Metab. 2008. 95:81–95.13. Berry GT, Mallee JJ, Kwon HM, Rim JS, Mulla WR, Muenke M, Spinner NB. The human osmoregulatory Na+/myo-inositol cotransporter gene (SLC5A3): molecular cloning and localization to chromosome 21. Genomics. 1995. 25:507–513.14. Benirschke K, Kaufmann P, Baergen RN. Pathology of the human placenta. 2006. 5th ed. New York: Springer;24–29.15. Guo W, Shimada S, Tajiri H, Yamauchi A, Yamashita T, Okada S, Tohyama M. Developmental regulation of Na+ / myo-inositol cotransporter gene expression. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997. 51:91–96.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Abundance and Nuclear Distribution of TonEBP in Response to Changes of Tonicity in Hyperglycemic Cells
- Alteration of Hypertonic Responses in Hyperglycemic Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial and Placental Cells
- TonEBP suppresses adipocyte differentiation via modulation of early signaling in 3T3-L1 cells
- Expression of TonEBP by Hypertonic and Hyperosmolar Stress in RGC-5 Cells
- Alternative Isoforms of TonEBP with Variable N-termini are Expressed in Mammalian Cells