J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Dec;79(Suppl 1):S16-S25. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.Suppl1.S16.
The Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in the Wall of Great Saphenous Vein in Patients with Varicose Veins
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Transplantation and Vascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. shuh@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Pohang St. Mary's Hospital, Pohang, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2040547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.Suppl1.S16
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although varicose veins are very common in adults, the mechanism of the disease has not been established. Degradation of the extracellular matrix is regulated by various matrix metallopreteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors tissue inhibitor of metallaproteinase (TIMPs). This study was performed to analyse the relationship between venous wall degeneration and expression of these matrix proteinases.
METHODS
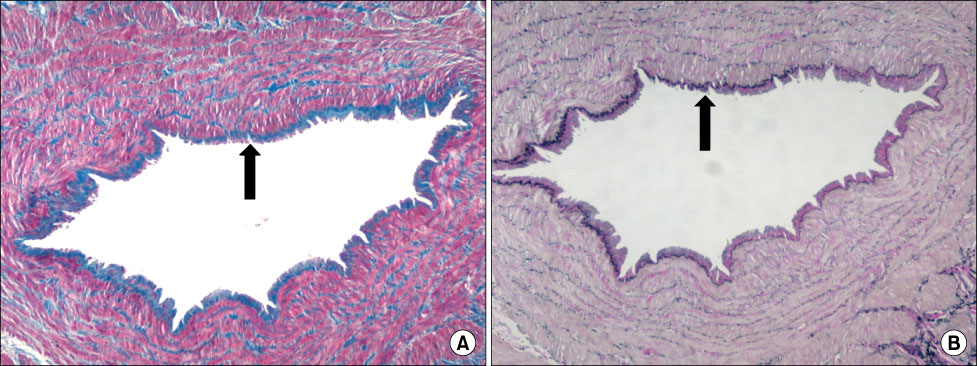
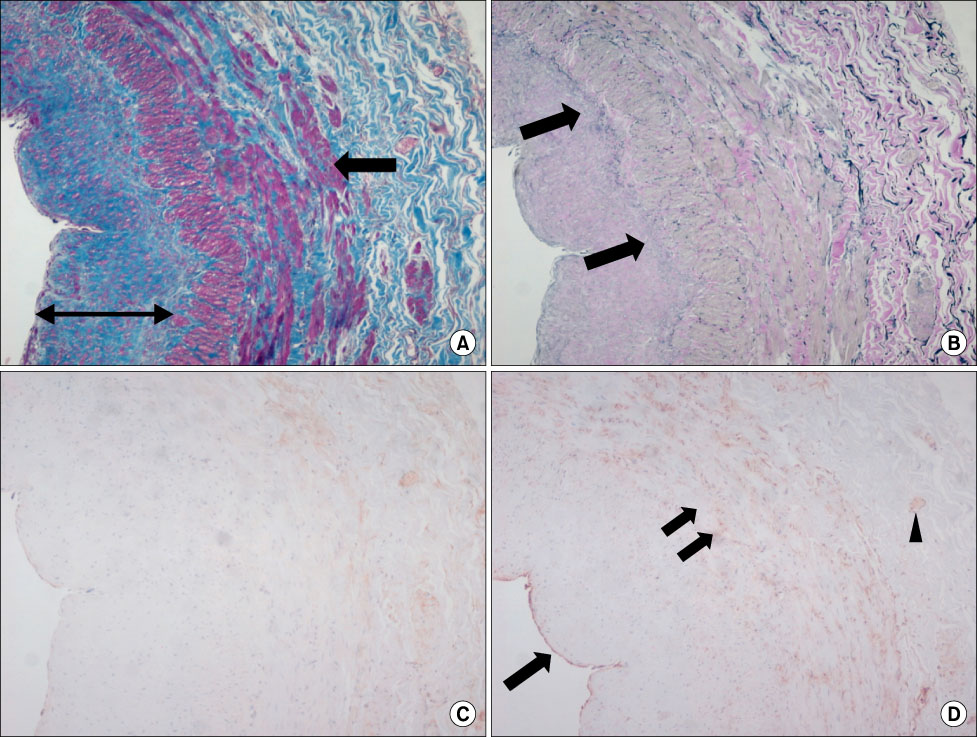
Twelve great saphenous vein (GSV) segments from 7 patients without varicose veins (control) and 86 GSV segments from 18 patients (22 limbs) with varicose veins (C2,4,5EPASPR) were used for this study. Light microscopic examination was used in the evaluation of vein wall degeneration, immunohistochemistry and Western blotting for the expression of MMPs (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-9 and MMP-13) and TIMPs (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2), and zymography for gelatinolytic activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were performed.
RESULTS
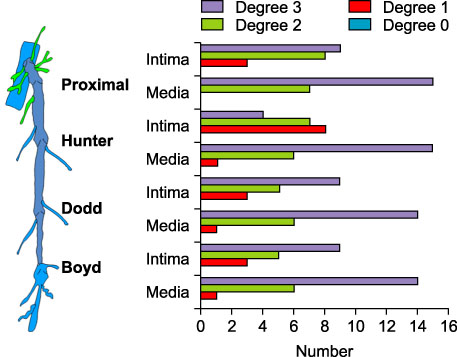
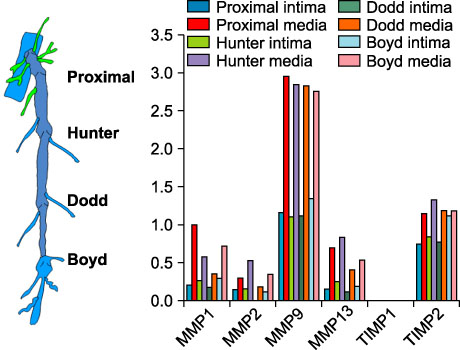
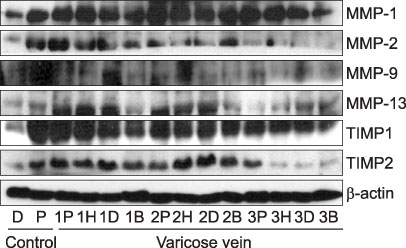
MMP-9 was more strongly expressed in the vein wall of both control and patient groups, especially in the endothelial cells and medial muscle layers and TIMP-2 followed. The expression of MMP-9 was closely related to the degree of venous wall degeneration. Activated MMP-2 and MMP-9 were observed in both groups and expressed more in the proximal GSV of the patients. In the Western blotting, the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 were significantly higher than other MMPs and TIMP-2 in the patients with varicose veins.
CONCLUSION
MMP-9 is much more expressed in the wall of degenerative veins. This matrix-degrading enzyme may play an important role in the degeneration of venous wall followed by its remodeling.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Blotting, Western
Endothelial Cells
Extracellular Matrix
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Light
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Metalloproteases
Muscles
Saphenous Vein
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2
Varicose Veins
Veins
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Metalloproteases
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rose SS. Goldman MP, Weiss RA, Bergan JJ, editors. Anatomic observation on causes of varicose veins. Varicose Veins and Telangiectasias: Diagnosis and Treatment. 1999. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Quality Medical Publishing;12–41.2. Elsharawy MA, Naim MM, Abdelmaguid EM, Al-Mulhim AA. Role of saphenous vein wall in the pathogenesis of primary varicose veins. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007. 6:219–224.3. Golledge J, Quigley FG. Pathogenesis of varicose veins. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2003. 25:319–324.4. Raffetto JD, Khalil RA. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. 75:346–359.5. Parra JR, Cambria RA, Hower CD, Dassow MS, Freischlag JA, Seabrook GR, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 is increased in the saphenofemoral junction of patients with varices in the leg. J Vasc Surg. 1998. 28:669–675.6. Badier-Commander C, Verbeuren T, Lebard C, Michel JB, Jacob MP. Increased TIMP/MMP ratio in varicose veins: a possible explanation for extracellular matrix accumulation. J Pathol. 2000. 192:105–112.7. Gillespie DL, Patel A, Fileta B, Chang A, Barnes S, Flagg A, et al. Varicose veins possess greater quantities of MMP-1 than normal veins and demonstrate regional variation in MMP-1 and MMP-13. J Surg Res. 2002. 106:233–238.8. Kosugi I, Urayama H, Kasashima F, Ohtake H, Watanabe Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator in varicose veins. Ann Vasc Surg. 2003. 17:234–238.9. Woodside KJ, Hu M, Burke A, Murakami M, Pounds LL, Killewich LA, et al. Morphologic characteristics of varicose veins: possible role of metalloproteinases. J Vasc Surg. 2003. 38:162–169.10. Kowalewski R, Sobolewski K, Wolanska M, Gacko M. Matrix metalloproteinases in the vein wall. Int Angiol. 2004. 23:164–169.11. Huh S, Choi HH, Kim HK. The expression of matrix metalloproteinase according to hydrostatic pressure in varicose veins. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 77:344–352.12. Mozes G, Carmichael SW, Gloviczki P. Gloviczki P, Yao JST, editors. Developement and anatomy of the venous system. Handbook of Venous Disorders: Guidelines of the American Venous Forum. 2001. 2nd ed. New York: Arnold;11–24.13. Milroy CM, Scott DJ, Beard JD, Horrocks M, Bradfield JW. Histological appearances of the long saphenous vein. J Pathol. 1989. 159:311–316.14. Leu HJ, Vogt M, Pfrunder H. Morphological alterations of non-varicose and varicose veins (A morphological contribution to the discussion on pathogenesis of varicose veins). Basic Res Cardiol. 1979. 74:435–444.15. Somers P, Knaapen M. The histopathology of varicose vein disease. Angiology. 2006. 57:546–555.16. Maurel E, Azema C, Deloly J, Bouissou H. Collagen of the normal and the varicose human saphenous vein: a biochemical study. Clin Chim Acta. 1990. 193:27–37.17. Venturi M, Bonavina L, Annoni F, Colombo L, Butera C, Peracchia A, et al. Biochemical assay of collagen and elastin in the normal and varicose vein wall. J Surg Res. 1996. 60:245–248.18. Sansilvestri-Morel P, Rupin A, Badier-Commander C, Kern P, Fabiani JN, Verbeuren TJ, et al. Imbalance in the synthesis of collagen type I and collagen type III in smooth muscle cells derived from human varicose veins. J Vasc Res. 2001. 38:560–568.19. Naoum JJ, Hunter GC, Woodside KJ, Chen C. Current advances in the pathogenesis of varicose veins. J Surg Res. 2007. 141:311–316.20. Sansilvestri-Morel P, Fioretti F, Rupin A, Senni K, Fabiani JN, Godeau G, et al. Comparison of extracellular matrix in skin and saphenous veins from patients with varicose veins: does the skin reflect venous matrix changes? Clin Sci (Lond). 2007. 112:229–239.21. Newby AC. Matrix metalloproteinases regulate migration, proliferation, and death of vascular smooth muscle cells by degrading matrix and non-matrix substrates. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. 69:614–624.22. Berceli SA, Jiang Z, Klingman NV, Schultz GS, Ozaki CK. Early differential MMP-2 and -9 dynamics during flow-induced arterial and vein graft adaptations. J Surg Res. 2006. 134:327–334.23. Rotmans JI, Velema E, Verhagen HJ, Blankensteijn JD, de Kleijn DP, Stroes ES, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition reduces intimal hyperplasia in a porcine arteriovenousgraft model. J Vasc Surg. 2004. 39:432–439.24. Pascarella L, Schmid-Schönbein GW, Bergan J. An animal model of venous hypertension: the role of inflammation in venous valve failure. J Vasc Surg. 2005. 41:303–311.25. Lehoux S, Lemarié CA, Esposito B, Lijnen HR, Tedgui A. Pressure-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to early hypertensive remodeling. Circulation. 2004. 109:1041–1047.26. Nomura S, Yoshimura K, Akiyama N, Mikamo A, Furutani A, Aoki H, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors reduce matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in human varicose veins. Eur Surg Res. 2005. 37:370–378.27. Jacob MP, Cazaubon M, Scemama A, Prié D, Blanchet F, Guillin MC, et al. Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 as a marker of blood stasis in varicose veins. Circulation. 2002. 106:535–538.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expressions of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase in Great Saphenous Veins of Patients with Varicose Veins
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -13 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-4 in Varicose Veins
- The Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase according to Hydrostatic Pressure in Varicose Veins
- The Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression in Early Arterialized Saphenous Vein Grafts
- Clinical Significance of Tissue Levels of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases in Gastric Cancer