J Lipid Atheroscler.
2015 Jun;4(1):17-25. 10.12997/jla.2015.4.1.17.
Consumption of Added Sugars and Lipid Profiles in Korean Population from a Cohort Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Epidemiology and Health Promotion, Institute for Health Promotion, Graduate School of Public Health, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. jsunha@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2005731
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2015.4.1.17
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the study was to examine the relationship between added sugar consumption and dyslipidemia.
METHODS
Final study subjects consisted of 18,713 participants after the exclusion of participants with dyslipidemia or under lipid lowering medications at baseline. Added sugar levels were categorized into tertiles [men: Low <8.0 g, Middle: 8.0-21.9 g, High > or =22.0 g; women: Low <6.0 g, Middle 6.0-14.9 g, High > or =15.0 g]. Dyslipidemia was analyzed based on two of the most recent guidelines identified from the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP ATP III) and the 2009 Korean Society of Lipidology and Atherosclerosis (KSLA). We used Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazard models to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) of dyslipidemia.
RESULTS
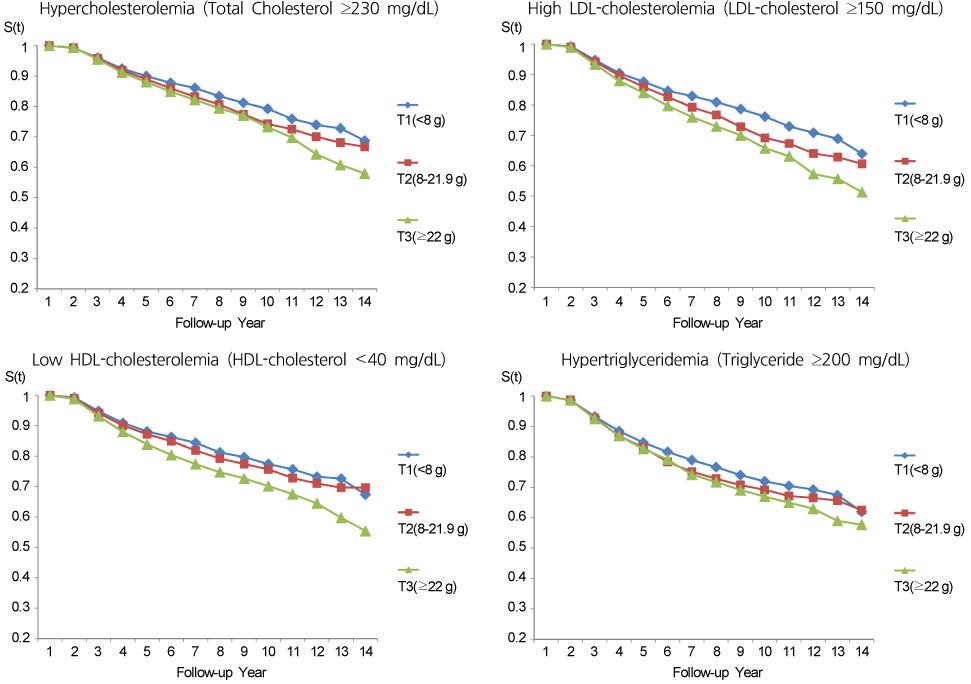
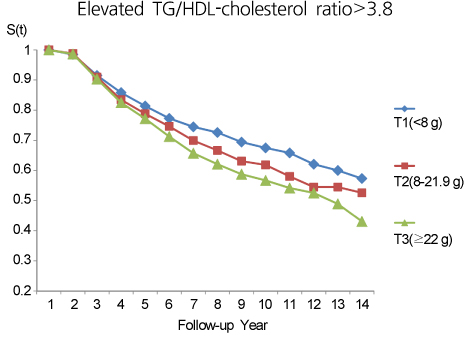
High added sugar was associated with hypercholesteremia (HR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.06-1.40), high LDL cholesterolemia (1.29; 1.13-1.48), and low HDL cholesterolemia (1.26; 1.10-1.44) based on the KSLA Standard in men. In women, the high added sugar was only related to the risk for hypercholesteremia (1.26; 1.07-1.49) based on the KSLA Standard. A similar trend was shown in both men and women with application of NCEP-ATP III standard.
CONCLUSION
In this study, an increase in added sugar consumption was associated with an increased risk of dyslipidemia in men. Additional studies assessing the association between cardiovascular and other diseases should be conducted in the future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Dietary guidelines for Americans. Washington, D.C.: United States Department of Agriculture;2000.2. The Korean Nutrition Society. Korean dietary reference intakes for Korean. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society;2010.3. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2003; 916:i–viii. 1–149.4. Collino M. High dietary fructose intake: sweet or bitter life? World J Diabetes. 2011; 2:77–81.
Article5. Welsh JA, Sharma A, Abramson JL, Vaccarino V, Gillespie C, Vos MB. Caloric sweetener consumption and dyslipidemia among US adults. JAMA. 2010; 303:1490–1497.
Article6. Tappy L, Lê KA, Tran C, Paquot N. Fructose and metabolic diseases: new findings, new questions. Nutrition. 2010; 26:1044–1049.
Article7. Welsh JA, Sharma AJ, Grellinger L, Vos MB. Consumption of added sugars is decreasing in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011; 94:726–734.
Article8. Hanak V, Munoz J, Teague J, Stanley A Jr, Bittner V. Accuracy of the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio for prediction of the low-density lipoprotein phenotype B. Am J Cardiol. 2004; 94:219–222.
Article9. da Luz PL, Favarato D, Faria-Neto JR Jr, Lemos P, Chagas AC. High ratio of triglycerides to HDL-cholesterol predicts extensive coronary disease. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008; 63:427–432.10. Kim JS, Kang HT, Shim JY, Lee HR. The association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in the general Korean population: based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2007-2009. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 97:132–138.
Article11. Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR). Ministry of Health and Welfare statistical year book 2013. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2013.12. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Total sugar intake survey 2012 [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2012. cited 2014 Jul 16. Available from: http://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do?mid=675&seq=17881&cmd=v.13. Park JM, Yoo EG, Kim DH. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2002; 45:646–653.14. Kim SH, Ahn BC, Joung H, Park MJ. Lipid profiles and prevalence of dyslipidemia in Korean adolescents. Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 27:208–216.
Article15. Moon SJ, Lee KY, Kim SY. Application of convenient method for the study of nutritional status of middleaged Korean women. Yonsei Nonchong. 1980; 17:203–218.16. Korean Dietetic Association. Diabetes management [Internet]. Seoul: Korean Dietetic Association;2010. cited 2013 Jun 10. Available from: http://www.dietitian.or.kr/sub5_14_08.asp.17. Lim H, Kim SY, Wang Y, Lee SJ, Oh K, Sohn CY, et al. Preservation of a traditional Korean dietary pattern and emergence of a fruit and dairy dietary pattern among adults in South Korea: secular transitions in dietary patterns of a prospective study from 1998 to 2010. Nutr Res. 2014; 34:760–770.
Article18. Korean Society of Lipidology and Atherosclerosis. Hyperlipidemia teatment guideline. Seoul: Korean Society of Lipidology and Atherosclerosis;2009.19. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002; 106:3143–3421.20. Wang H, Steffen LM, Zhou X, Harnack L, Luepker RV. Consistency between increasing trends in added-sugar intake and body mass index among adults: the Minnesota Heart Survey, 1980-1982 to 2007-2009. Am J Public Health. 2013; 103:501–507.
Article21. Park KS. Insulin resistance and insulin resistance syndrome. Hanyang Med Rev. 2009; 29:130–133.22. Yoo HJ. Visceral obesity. J Korean Med Assoc. 2007; 50:725–728.
Article23. Reaven GM. Role of insulin resistance in human disease (syndrome X): an expanded definition. Annu Rev Med. 1993; 44:121–131.
Article24. Kong EH. Obesity and hyperlipidemia. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2005; 55–59.25. Ginsberg HN, Zhang YL, Hernandez-Ono A. Metabolic syndrome: focus on dyslipidemia. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006; 14:Suppl 1. 41S–49S.
Article26. Rashid S, Barrett PH, Uffelman KD, Watanabe T, Adeli K, Lewis GF. Lipolytically modified triglyceride-enriched HDLs are rapidly cleared from the circulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002; 22:483–487.
Article27. Goldberg IJ. Clinical review 124: diabetic dyslipidemia: causes and consequences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:965–971.28. Kang HT, Yoon JH, Kim JY, Ahn SK, Linton JA, Koh SB, et al. The association between the ratio of triglyceride to HDL-C and insulin resistance according to waist circumference in a rural Korean population. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012; 22:1054–1060.
Article29. Johnson RK, Appel LJ, Brands M, Howard BV, Lefevre M, Lustig RH, et al. Dietary sugars intake and cardiovascular health: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2009; 120:1011–1020.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metabolism and Health Impacts of Dietary Sugars
- Ultra-processed foods and total sugars intake in Korea: evidence from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
- The Specific Food Consumption Pattern and Blood Lipid Profiles of Korean Adults
- Effects of natural mono- and di-saccharide as alternative sweeteners on inflammatory bowel disease: a narrative review
- Status and needs of nutrition education for children's sugars intake reduction in elementary school