Korean J Urol.
2007 Apr;48(4):408-415. 10.4111/kju.2007.48.4.408.
Predictive Variables of the Progression to Androgen Independent Prostate Cancer after Combined Androgen Blockade
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. jsrim@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Seoul National University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 8Department of Urology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1997108
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2007.48.4.408
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Despite of the effectiveness of androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer, it progress to androgen independent prostate cancer (AIPC) after various periods of time. The objective of this study was to analyze the clinical and pathological variables that predict progression to AIPC after combined androgen blockade (CAB).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 343 patients who were treated with CAB for prostate cancer. Binary logistic regression test was used to analyze the independent predictors for the progression to AIPC. The time to AIPC, according to variables, was assessed by the Kaplan-Meier method and the variables were compared using the Log-Rank test.
RESULTS
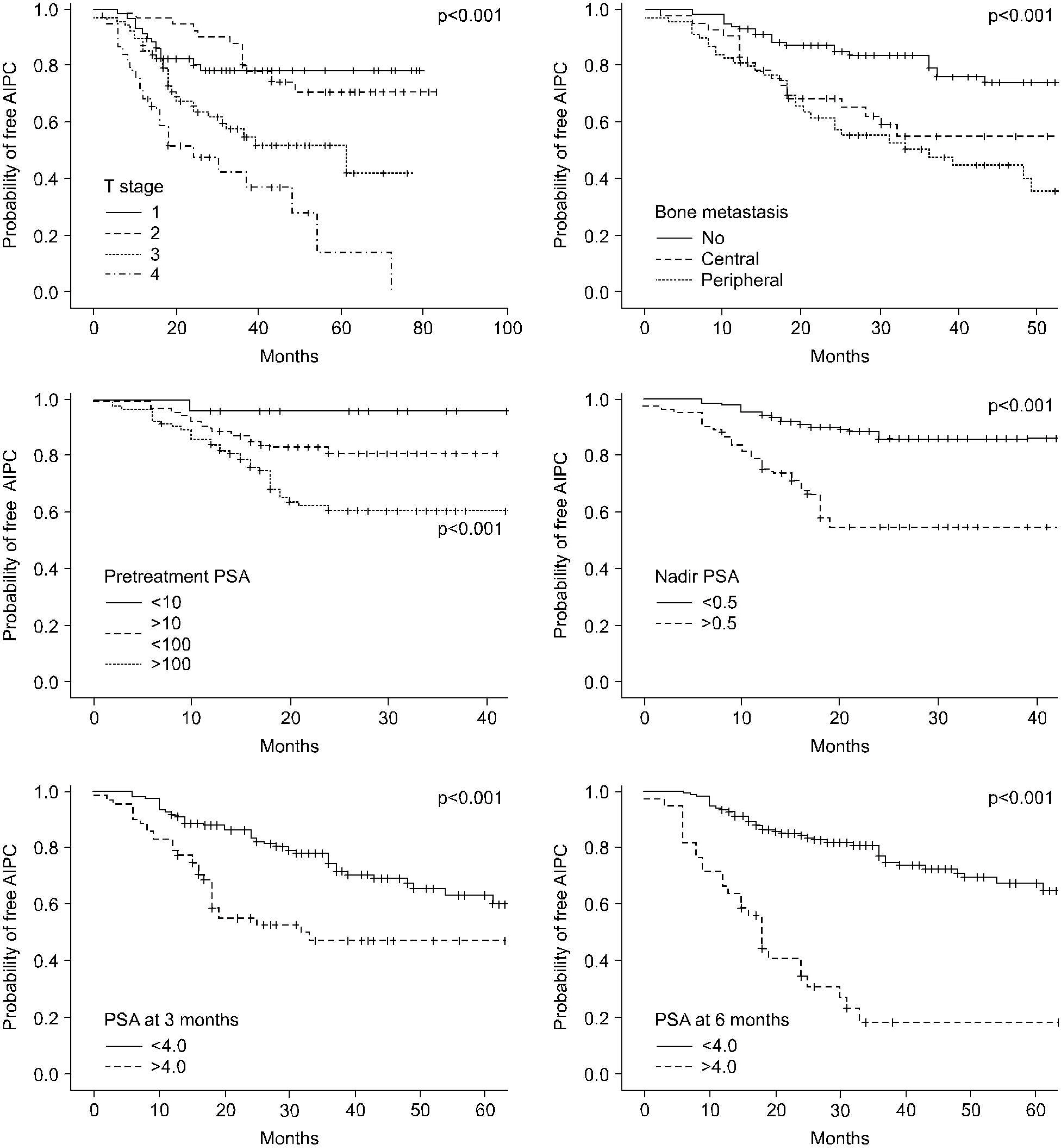
The mean follow-up was 42.1 months (range: 12-120). Seventy seven patients (33.3%) experienced progression to AIPC at a median of 20.2 months (range: 6-72). On univariate analysis, the percentage of positive prostate biopsies, the Gleason score, the T stage, the extent of bone metastasis, lymph node metastasis, the pretreatment PSA level, the nadir PSA and the PSA level at 3 and 6 months all had a significant relationship with the progression to AIPC. The receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for the nadir PSA showed that the optimal cut-off point to predict progression to AIPC was 0.5ng/ml with an area under curve of 0.769. A multivariate analysis demonstrated that the Gleason score (>7), the nadir PSA (>0.5ng/ml), and the PSA level at 6 months (>4.0ng/ml) were significantly correlated with the progression to AIPC.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggested that Gleason score, the nadir PSA and the PSA level at 6 months were independent variables to predict progression to AIPC after CAB. The PSA level at 6 months may be the most accurate variable to predict progression to AIPC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Experience with Limited Lymph Node Dissection for Prostate Cancer in Korea: Single Center Comparison of 247 Open and 354 Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy Series
Daeheon Choi, Doejung Kim, Yoon Soo Kyung, Ju Hyun Lim, Sang Hoon Song, Dalsan You, In Gab Jeong, Choung-Soo Kim
Korean J Urol. 2012;53(11):755-760. doi: 10.4111/kju.2012.53.11.755.
Reference
-
1.Ministry of Health and Welfare Republic of Korea. 2002 Annual Report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry. 2002. 11–4.2.Korea National Statistical Office. Annual report on the cause of death statistics (based on vital registration).3.Derweesh IH., Kupelian PA., Zippe C., Levin HS., Brainard J., Magi-Galluzzi C, et al. Continuing trends in pathological stage migration in radical prostatectomy specimens. Urol Oncol. 2004. 22:300–6.
Article4.Denis LJ., Keuppens F., Smith PH., Whelan P., deMoura JL., Newling D, et al. Maximal androgen blockade: final analysis of EORTC phase III trial 30853. EORTC Genito-Urinary Tract Cancer Cooperative Group and the EORTC Data Center. Eur Urol. 1998. 33:144–51.5.Kawakami J., Cowan JE., Elkin EP., Latini DM., DuChane J., Carroll PR, et al. Androgen-deprivation therapy as primary treatment for localized prostate cancer: data from Cancer of the Prostate Strategic Urologic Research Endeavor (CaPSURE). Cancer. 2006. 106:1708–14.6.Dijkman GA., Janknegt RA., De Reijke TM., Debruyne FM. Long-term efficacy and safety of nilutamide plus castration in advanced prostate cancer, and die significance of early prostate specific antigen normalization. J Urol. 1997. 158:160–3.7.Denis LJ., Camelro de Moura JL., Bono A., Sylvester R., Whelan P., Newling D, et al. Goserelin acetate and flutamide versus bilateral orchiectomy: phase III EORTC trial (30853). EORTC GU Group and EORTC Data Center. Urology. 1993. 42:119–29.8.Kim KH., Seo YJ., Lee KS. The factors affecting prognosis in patients with metastatic prostate cancer after hormonal therapy. Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:24–8.9.Benaim EA., Pace CM., Lam PM., Roehrbom CG. Nadir prostate-specific antigen as a predictor of progression to androgen-independent prostate cancer. Urology. 2002. 59:73–8.
Article10.Kwak C., Jeong SJ., Park MS., Lee E., Lee SE. Prognostic significance of the nadir prostate specific antigen level after hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. J Urol. 2002. 168:995–1000.11.Park BJ., Lee YG., Alin HK. Prognostic significance of pro-state-specific antigen level two months after maximal androgen blockade in metastatic prostate cancer. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:855–60.12.Morote J., Trilla E., Esquena S., Abascal JM., Reventos J. Nadir prostate-specific antigen best predicts the progression to androgen-independent prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2004. 108:877–81.
Article13.Cooper EH., Armitage TG., Robinson MR., Newling DW., Richards BR., Smith PH, et al. Prostate specific antigen and the prediction of prognosis in metastatic prostatic cancer. Cancer. 1990. 66((5 Suppl):):1025–8.14.Miller JI., Ahmann FR., Drach GW., Emerson SS., Botaccini MR. The clinical usefulness of serum prostate specific antigen after hormonal therapy of metastatic prostate cancer. J Urol. 1992. 147:956–61.
Article15.Daver A., Soret JY., Coblentz Y., Allain YM., Cellier P., Chau-veau P. The usefulness of prostate-specific antigen and prostatic acid phosphatase in clinical practice. Am J Clin Oncol. 1988. ll(Suppl 2):S53–60.
Article16.Lee SY., Kim YS., Hong SJ. Clinical response of combined androgen blockade in metastatic prostate cancers. Korean J Urol. 2000. 41:361–6.17.Oosterlinck W., Mattelaer J., Casselman J., Van Velthoven R., Derde MP., Kaufman L. PSA evolution: a prognostic factor during treatment of advanced prostatic carcinoma with total androgen blockade. Data from a Belgian multicentric study of 546 patients. Acta Urol Belg. 1997. 65:63–71.18.Benaim EA., Pace CM., Roehrbom CG. Gleason score predicts androgen independent progression after androgen deprivation therapy. Eur Urol. 2002. 42:12–7.
Article19.Janoff DM., Peterson C., Mongoue-Tchokote S., Peters L., Beer TM., Wersinger EM, et al. Clinical outcomes of androgen deprivation as the sole therapy for localized and locally advanced prostate cancer BJU Int. 2005. 96:503–7.20.Morote J., Esquena S., Abascal JL., Trilla E., Cecchini L., Raventos CX, et al. Usefulness of prostate-specific antigen nadir as predictor of androgen-independent progression of metastatic prostate cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 2005. 20:209–16.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunohistochemical Assay of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer
- Change of Bone Mineral Density after 1,25(OH)2VitD Therapy In Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer Patients Treated with Total Androgen Blockade: The Prospective Study
- Long-Lasting Antiandrogen Withdrawal Syndrome in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Three Cases With Complete Response
- The Therapeutic Effect of Monotherapy and Combined Therapy for Androgen Blockade in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Predictive Factor for the Early Progression of Androgen Independent Prostate Cancer in Intermittent Androgen Deprivation Therapy