J Adv Prosthodont.
2011 Jun;3(2):57-62. 10.4047/jap.2011.3.2.57.
The effect of ceramic thickness and number of firings on the color of a zirconium oxide based all ceramic system fabricated using CAD/CAM technology
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Goa Dental College and Hospital, Bambolim, Goa, India. vinaybachhav@gmail.com
- KMID: 1975077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2011.3.2.57
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Ceramics have a long history in fixed prosthodontics for achieving optimal esthetics and various materials have been used to improve ceramic core strength. However, there is a lack of information on how color is affected by fabrication procedure. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of various dentin ceramic thicknesses and repeated firings on the color of zirconium oxide all-ceramic system (Lava(TM)) fabricated using CAD/CAM technology.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty disc-shaped cores, 12 mm in diameter with a 1 mm thickness were fabricated from zirconium oxide based all ceramic systems (Lava(TM), 3M ESPE, St Paul, MN, USA) and divided into three groups (n = 10) according to veneering with dentin ceramic thicknesses: as 0.5, 1, or 1.5 mm. Repeated firings (3, 5, 7, or 9) were performed, and the color of the specimens was compared with the color after the initial firing. Color differences among ceramic specimens were measured using a spectrophotometer (VITA Easyshade, VITA Zahnfabrik, Bad Sackingen, Germany) and data were expressed in CIELAB system coordinates. A repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test were used to analyze the data (n = 10, alpha=.05).
RESULTS
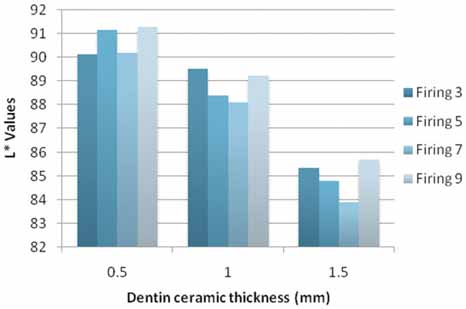
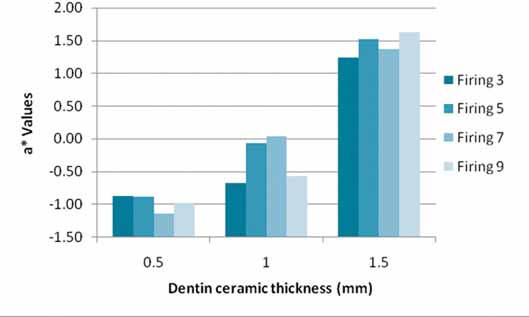
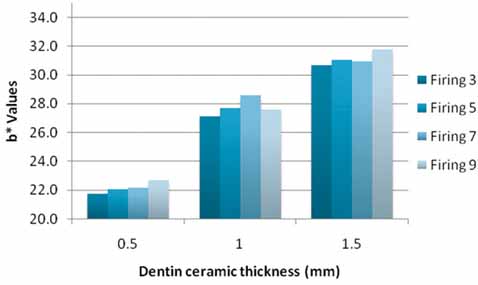
L*a*b* values of the ceramic systems were affected by the number of firings (3, 5, 7, or 9 firings) (P<.001) and ceramic thickness (0.5, 1, or 1.5 mm) (P<.001). Significant interactions were present in L*a*b* values between the number of firings and ceramic thickness (P<.001). An increase in number of firings resulted in significant increase in L* values for both 0.5 mm and 1.5 mm thicknesses (P<.01, P=.013); however it decreased for 1 mm thickness (P<.01). The a* values increased for 1 mm and 1.5 mm thicknesses (P<.01), while it decreased for 0.5 mm specimens. The b* values increased significantly for all thicknesses (P<.01, P=.022). As the dentin ceramic thickness increased, significant reductions in L* values (P<.01) were recorded. There were significant increases in both a* and b* values (P<.01) as the dentin ceramic thickness increased.
CONCLUSION
The number of firings and dentin ceramic thickness have a definite effect on the final color of all ceramic system tested. The mean DeltaE value increased as the dentin ceramic thicknesses increased for zirconium-oxide based all ceramic specimens tested. However, the mean DeltaE values were less than 3.7DeltaE units which is rated as a match in the oral environment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The effects of repetitive firing processes on the optical, thermal, and phase formation changes of zirconia
Alper Ozdogan, Hatice Ozdemir
J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(1):9-14. doi: 10.4047/jap.2020.12.1.9.
Reference
-
1. Piconi C, Maccauro G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999. 20:1–25.2. Meyenberg KH, Lüthy H, Schärer P. Zirconia posts: a new all-ceramic concept for nonvital abutment teeth. J Esthet Dent. 1995. 7:73–80.3. Derand T, Molin M, Kvam K. Bond strength of composite luting cement to zirconia ceramic surfaces. Dent Mater. 2005. 21:1158–1162.4. Wohlwend A, Studer S, Schärer P. The zirconium oxide abutment: an all-ceramic abutment for the esthetic improvement of implant superstructures. Quintessence Dent Technol. 1997. 1:63–74.5. Keith O, Kusy RP, Whitley JQ. Zirconia brackets: an evaluation of morphology and coefficients of friction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994. 106:605–614.6. Christel P, Meunier A, Heller M, Torre JP, Peille CN. Mechanical properties and short-term in-vivo evaluation of yttrium-oxide-partially-stabilized zirconia. J Biomed Mater Res. 1989. 23:45–61.7. Luthardt RG, Sandkuhl O, Reitz B. Zirconia-TZP and alumina-advanced technologies for the manufacturing of single crowns. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 1999. 7:113–119.8. Seghi RR, Johnston WM, O'Brien WJ. Spectrophotometric analysis of color differences between porcelain systems. J Prosthet Dent. 1986. 56:35–40.9. Judd DB, Wyszecki G. Color in business, science and industry. 1975. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons;105–122.10. Heffernan MJ, Aquilino SA, Diaz-Arnold AM, Haselton DR, Stanford CM, Vargas MA. Relative translucency of six all-ceramic systems. Part II: core and veneer materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 88:10–15.11. Isgrò G, Pallav P, van der Zel JM, Feilzer AJ. The influence of the veneering porcelain and different surface treatments on the biaxial flexural strength of a heat-pressed ceramic. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 90:465–473.12. Dozić A, Kleverlaan CJ, Meegdes M, van der Zel J, Feilzer AJ. The influence of porcelain layer thickness on the final shade of ceramic restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 90:563–570.13. Mclean JW. New dental ceramics and esthetics. J Esthet Dent. 1995. 7:141–149.14. Wee AG, Monaghan P, Johnston WM. Variation in color between intended matched shade and fabricated shade of dental porcelain. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 87:657–666.15. Kingery WD, Bowen HK, Uhlmann DR. Introduction to ceramics. 1976. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons;646–689.16. Heffernan MJ, Aquilino SA, Diaz-Arnold AM, Haselton DR, Stanford CM, Vargas MA. Relative translucency of six all-ceramic systems. Part I: core materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 88:4–9.17. Kelly JR, Nishimura I, Campbell SD. Ceramics in dentistry: historical roots and current perspectives. J Prosthet Dent. 1996. 75:18–32.18. Seghi RR, Sorensen JA. Relative flexural strength of six new ceramic materials. Int J Prosthodont. 1995. 8:239–246.19. Wagner WC, Chu TM. Biaxial flexural strength and indentation fracture toughness of three new dental core ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 1996. 76:140–144.20. Giordano RA. Dental ceramic restorative systems. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1996. 17:779–782. 784–786.21. CIE (Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage). CIE Publication No. 15. Colorimetry-technical report. 2004. 3rd ed. Vienna: Bureau Central de la CIE.22. Seghi RR, Hewlett ER, Kim J. Visual and instrumental colorimetric assessments of small color differences on translucent dental porcelain. J Dent Res. 1989. 68:1760–1764.23. Johnston WM, Kao EC. Assessment of appearance match by visual observation and clinical colorimetry. J Dent Res. 1989. 68:819–822.24. Ruyter IE, Nilner K, Moller B. Color stability of dental composite resin materials for crown and bridge veneers. Dent Mater. 1987. 3:246–251.25. O'Brien WJ, Kay KS, Boenke KM, Groh CL. Sources of color variation on firing porcelain. Dent Mater. 1991. 7:170–173.26. Hammad IA, Stein RS. A qualitative study for the bond and color of ceramometals. Part II. J Prosthet Dent. 1991. 65:169–179.27. Jacobs SH, Goodacre CJ, Moore BK, Dykema RW. Effect of porcelain thickness and type of metal-ceramic alloy on color. J Prosthet Dent. 1987. 57:138–145.28. Barghi N, Lorenzana RE. Optimum thickness of opaque and body porcelain. J Prosthet Dent. 1982. 48:429–431.29. Shokry TE, Shen C, Elhosary MM, Elkhodary AM. Effect of core and veneer thicknesses on the color parameters of two all-ceramic systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2006. 95:124–129.30. Jorgenson MW, Goodkind RJ. Spectrophotometric study of five porcelain shades relative to the dimensions of color, porcelain thickness, and repeated firings. J Prosthet Dent. 1979. 42:96–105.31. Douglas RD, Przybylska M. Predicting porcelain thickness required for dental shade matches. J Prosthet Dent. 1999. 82:143–149.32. Antonson SA, Anusavice KJ. Contrast ratio of veneering and core ceramics as a function of thickness. Int J Prosthodont. 2001. 14:316–320.33. Lee YK, Cha HS, Ahn JS. Layered color of all-ceramic core and veneer ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2007. 97:279–286.34. Barghi N, Goldberg . Porcelain shade stability after repeated firing. J Prosthet Dent. 1977. 37:173–175.35. Barghi N, Richardson JT. A study of various factors influencing shade of bonded porcelain. J Prosthet Dent. 1978. 39:282–284.36. Uludag B, Usumez A, Sahin V, Eser K, Ercoban E. The effect of ceramic thickness and number of firings on the color of ceramic systems: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2007. 97:25–31.37. Ozturk O, Uludag B, Usumez A, Sahin V, Celik G. The effect of ceramic thickness and number of firings on the color of two all-ceramic systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2008. 100:99–106.38. Knispel G. Factors affecting the process of color matching restorative materials to natural teeth. Quintessence Int. 1991. 22:525–531.39. Crispin BJ, Seghi RR, Globe H. Effect of different metal ceramic alloys on the color of opaque and dentin porcelain. J Prosthet Dent. 1991. 65:351–356.40. Mulla FA, Weiner S. Effects of temperature on color stability of porcelain stains. J Prosthet Dent. 1991. 65:507–512.41. Lund PS, Piotrowski TJ. Color changes of porcelain surface colorants resulting from firing. Int J Prosthodont. 1992. 5:22–27.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of repeated firings on the color of zirconia-based all-ceramic system
- The effect of repeated firings on the color change and surface roughness of dental ceramics
- Comparative fracture strength analysis of Lava and Digident CAD/CAM zirconia ceramic crowns
- Marginal fit of the digident CAD/CAM zirconia ceramic crowns
- A comparison of the fidelity of various zirconia-based all-ceramic crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM systems