J Adv Prosthodont.
2015 Feb;7(1):21-26. 10.4047/jap.2015.7.1.21.
Cytotoxicity of temporary cements on bovine dental pulp-derived cells (bDPCs) using realtime cell analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Inonu University, Malatya, Turkey. mrlmalkoc@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Selcuk University, Konya, Turkey.
- 3Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Kirikkale University, Kirikkale, Turkey.
- 4Research Center, Faculty of Dentistry, Selcuk University, Konya, Turkey.
- 5Department of Periodontology, Faculty of Dentistry, Selcuk University, Konya, Turkey.
- KMID: 1974886
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2015.7.1.21
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the cytotoxicity of temporary luting cements on bovine dental pulp-derived cells (bDPCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Four different temporary cements were tested: Rely X Temp E (3M ESPE), Ultratemp (Ultradent), GC Fuji Temp (GC), and Rely X Temp NE (3M ESPE). The materials were prepared as discs and incubated in Dulbecco's modified eagle's culture medium (DMEM) for 72 hours according to ISO 10993-5. A real-time cell analyzer was used to determine cell vitality. After seeding 200 microL of the cell suspensions into the wells of a 96-well plate, the bDPCs were cured with bioactive components released by the test materials and observed every 15 minutes for 98 hours. One-way ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer tests were used to analyze the results of the proliferation experiments.
RESULTS
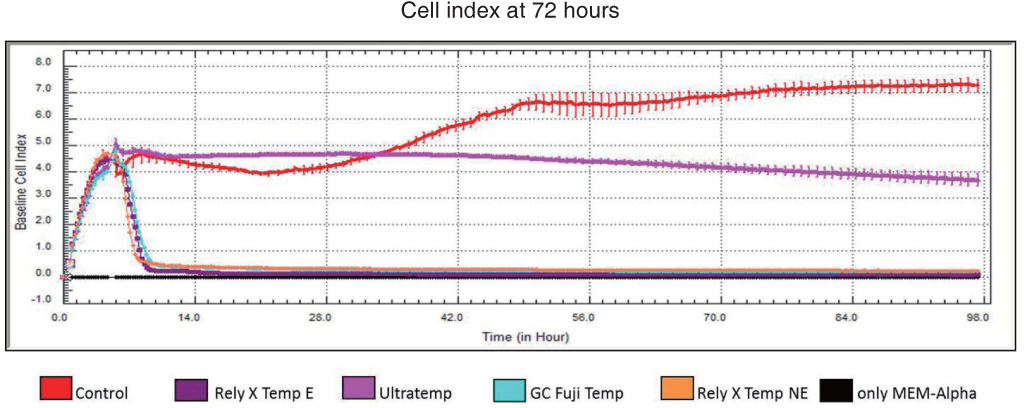
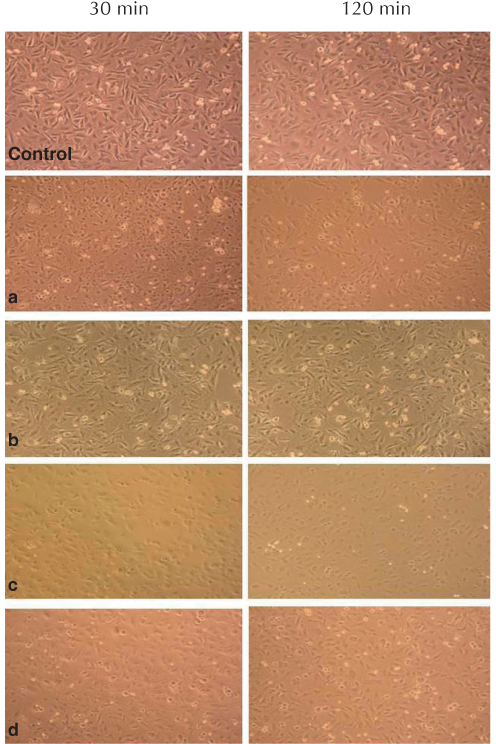
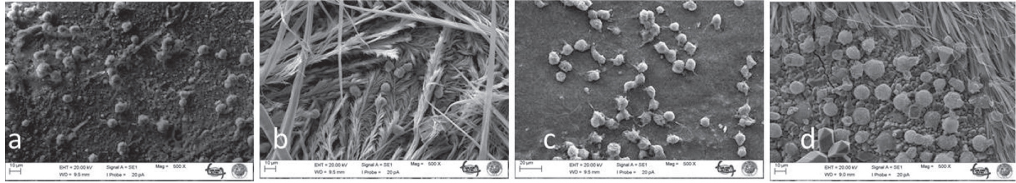
All tested temporary cements showed significant decreases in the bDPCs index. Rely X Temp E, GC Fuji Temp, and Rely X Temp NE were severely toxic at both time points (24 and 72 hours) (P<.001). When the cells were exposed to media by Ultratemp, the cell viability was similar to that of the control at 24 hours (P>.05); however, the cell viability was significantly reduced at 72 hours (P<.001). Light and scanning electron microscopy examination confirmed these results.
CONCLUSION
The cytotoxic effects of temporary cements on pulpal tissue should be evaluated when choosing cement for luting provisional restorations.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pashley EL, Tao L, Pashley DH. The sealing properties of temporary filling materials. J Prosthet Dent. 1988; 60:292–297.2. Rosenstiel SF, Land MF, Fujimoto J. Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics. In : Rosenstiel SF, editor. Luting agents and cementation procedures. St. Louis; Missouri: Mosby Elsevier;2006. p. 909–925.3. Olin PS, Rudney JD, Hill EM. Retentive strength of six temporary dental cements. Quintessence Int. 1990; 21:197–200.4. Ribeiro JC, Coelho PG, Janal MN, Silva NR, Monteiro AJ, Fernandes CA. The influence of temporary cements on dental adhesive systems for luting cementation. J Dent. 2011; 39:255–262.5. Paul SJ, Schärer P. Effect of provisional cements on the bond strength of various adhesive bonding systems on dentine. J Oral Rehabil. 1997; 24:8–14.6. Albers HF. Tooth-colored restoratives: Principles and techniques. In : Albers HF, editor. Diagnosis. London: BC Decker;2002. p. 23–24.7. Ülker HE, Hiller KA, Schweikl H, Seidenader C, Sengun A, Schmalz G. Human and bovine pulp-derived cell reactions to dental resin cements. Clin Oral Investig. 2012; 16:1571–1578.8. Kong N, Jiang T, Zhou Z, Fu J. Cytotoxicity of polymerized resin cements on human dental pulp cells in vitro. Dent Mater. 2009; 25:1371–1375.9. Malkoc S, Corekci B, Botsali HE, Yalçin M, Sengun A. Cytotoxic effects of resin-modified orthodontic band adhesives. Are they safe. Angle Orthod. 2010; 80:890–895.10. ISO 10993-5. Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 5: Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity. Geneva; Switzerland: International Standards Organization (ISO);2009.11. Urcan E, Haertel U, Styllou M, Hickel R, Scherthan H, Reichl FX. Real-time xCELLigence impedance analysis of the cytotoxicity of dental composite components on human gingival fibroblasts. Dent Mater. 2010; 26:51–58.12. Malkoç S, Öztürk F, Çörekçi B, Bozkurt BS, Hakki SS. Realtime cell analysis of the cytotoxicity of orthodontic mini-implants on human gingival fibroblasts and mouse osteoblasts. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012; 141:419–426.13. Schmalz G. Use of cell cultures for toxicity testing of dental materials-advantages and limitations. J Dent. 1994; 22:S6–S11.14. Costa MT, Lenza MA, Gosch CS, Costa I, Ribeiro-Dias F. In vitro evaluation of corrosion and cytotoxicity of orthodontic brackets. J Dent Res. 2007; 86:441–445.15. Koulaouzidou EA, Helvatjoglu-Antoniades M, Palaghias G, Karanika-Kouma A, Antoniades D. Cytotoxicity of dental adhesives in vitro. Eur J Dent. 2009; 3:3–9.16. Thonemann B, Schmalz G. Immortalization of bovine dental papilla cells with simian virus 40 large t antigen. Arch Oral Biol. 2000; 45:857–869.17. Sengün A, Yalçın M, Ülker HE, Öztürk B, Hakkı SS. Cytotoxicity evaluation of dentin bonding agents by dentin barrier test on 3-dimensional pulp cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011; 112:e83–e88.18. Galler KM, Schweikl H, Thonemann B, D›Souza RN, Schmalz G. Human pulp-derived cells immortalized with Simian Virus 40 T-antigen. Eur J Oral Sci. 2006; 114:138–146.19. Koulaouzidou EA, Papazisis KT, Economides NA, Beltes P, Kortsaris AH. Antiproliferative effect of mineral trioxide aggregate, zinc oxide-eugenol cement, and glass-ionomer cement against three fibroblastic cell lines. J Endod. 2005; 31:44–46.20. Torabinejad M, Hong CU, Pitt Ford TR, Kettering JD. Cytotoxicity of four root end filling materials. J Endod. 1995; 21:489–492.21. Kwon JS, Illeperuma RP, Kim J, Kim KM, Kim KN. Cytotoxicity evaluation of zinc oxide-eugenol and non-eugenol cements using different fibroblast cell lines. Acta Odontol Scand. 2014; 72:64–70.22. Schmalz G, Rotgans J. An in vitro study on the toxicity of an odour-free and flavourless zinc oxide and eugenol cement. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 1979; 86:85–88.23. Hensten-Pettersen A, Helgeland K. Evaluation of biologic effects of dental materials using four different cell culture techniques. Scand J Dent Res. 1977; 85:291–296.24. Sela J, Ulmansky M. Reaction of normal and inflamed dental pulp to Calxyl and zinc oxide and eugenol in rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1970; 30:425–430.25. Ülker HE, Ülker M, Gümüş HÖ, Yalçın M, Şengün A. Cytotoxicity testing of temporary luting cements with twoand three-dimensional cultures of bovine dental pulp-derived cells. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:910459.26. Kurata S, Morishita K, Kawase T, Umemoto K. Cytotoxic efeffects of acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, their corresponding saturated carboxylic acids, HEMA, and hydroquinone on fibroblasts derived from human pulp. Dent Mater J. 2012; 31:219–225.27. Sunzel B, Söderberg TA, Johansson A, Hallmans G, Gref R. The protective effect of zinc on rosin and resin acid toxicity in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and human gingival fibroblasts in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997; 37:20–28.28. Hume WR. Influence of dentine on the pulpward release of eugenol or acids from restorative materials. J Oral Rehabil. 1994; 21:469–473.29. Hanks CT, Wataha JC, Parsell RR, Strawn SE, Fat JC. Permeability of biological and synthetic molecules through dentine. J Oral Rehabil. 1994; 21:475–487.30. Schmalz G, Hoffmann M, Weis K, Schweikl H. Influence of albumin and collagen on the cell mortality evoked by zinc oxide-eugenol in vitro. J Endod. 2000; 26:284–287.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A study on biocompatability of resin cements for all-ceramic crown
- Advances in Research on Stem Cell-Based Pulp Regeneration
- Characterization of Human Dental Pulp Cells from Supernumerary Teeth by Using Flow Cytometry Analysis
- Can different agents reduce the damage caused by bleaching gel to pulp tissue? A systematic review of basic research
- Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Current in vivo Approaches to Study Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Pulp Injury and Regeneration