Imaging Sci Dent.
2014 Sep;44(3):243-247. 10.5624/isd.2014.44.3.243.
Chronic osteitic rhinosinusitis as a manifestation of cystic fibrosis: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic and Biomedical Sciences, The University of Texas School of Dentistry at Houston, Houston, TX, USA. aniket.b.jadhav@uth.tmc.edu
- 2Department of Diagnostic Sciences, Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, The University of Connecticut School of Dental Medicine, Farmington, CT, USA.
- KMID: 1974489
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.3.243
Abstract
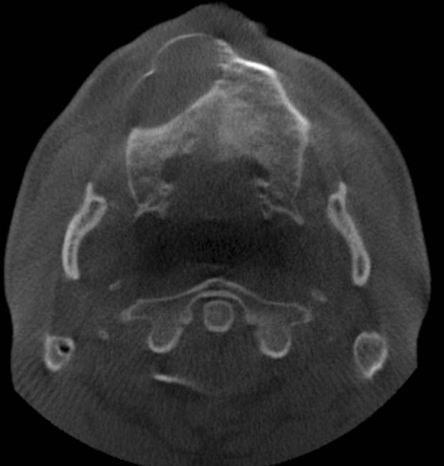
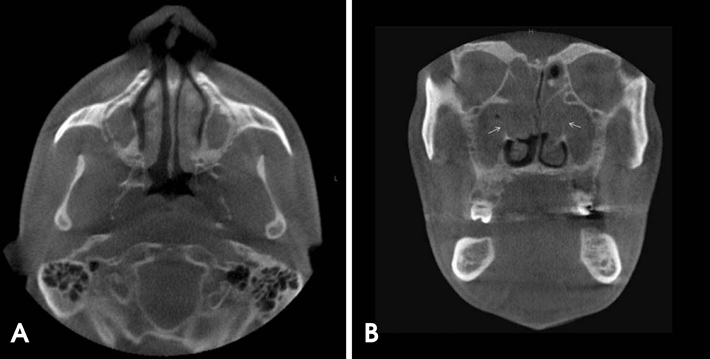
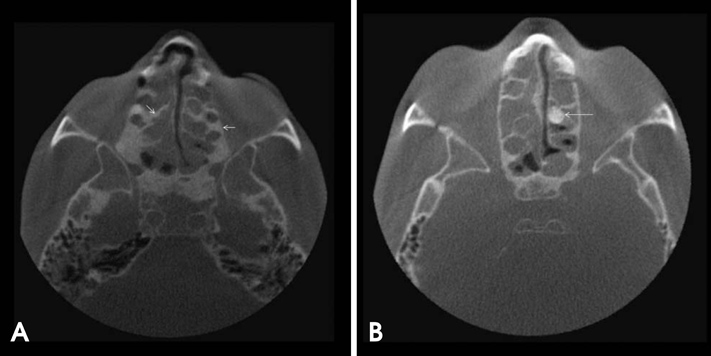
- A 28-year-old male patient with a history of cystic fibrosis (CF) was referred to the University of Connecticut School of Dental Medicine for an evaluation of a cystic lesion in the right maxilla using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). CF is an autosomal recessive disease characterized by an abnormal production of viscous mucus, affecting the mucociliary clearance. The CBCT scan revealed a large cystic lesion in the right maxilla extending from the right maxillary second molar to the midline in the region of the right central incisor with a significant buccal expansion. Further evaluation revealed complete opacification of the paranasal sinuses with medial bulging of the lateral maxillary sinus walls. The maxillary and sphenoid sinuses also appeared hypoplastic. The peculiar finding seen in this case was the presence of marked sclerosis and an increase in the thickness of the adjacent bony framework. This report aimed to describe the common sinonasal findings associated with CF and its underlying pathophysiology.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boucher RC, Knowles MR, Yankaskas JR. Cystic fibrosis. In : Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Martin T, King T, Schraufnagel DM, Murray JE, editors. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2010. p. 985–1022.2. Matsui H, Grubb BR, Tarran R, Randell SH, Gatzy JT, Davis CW, et al. Evidence for periciliary liquid layer depletion, not abnormal ion composition, in the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis airways disease. Cell. 1998; 95:1005–1015.
Article3. Boyle MP. Adult cystic fibrosis. JAMA. 2007; 298:1787–1793.
Article4. Lobo J, Rojas-Balcazar JM, Noone PG. Recent advances in cystic fibrosis. Clin Chest Med. 2012; 33:307–328.
Article5. Nishioka GJ, Cook PR, McKinsey JP, Rodriguez FJ. Paranasal sinus computed tomography scan findings in patients with cystic fibrosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 114:394–399.
Article6. Eggesbø HB, Dølvik S, Stiris M, Søvik S, Storrøsten OT, Kolmannskog F. Complementary role of MR imaging of ethmomaxillary sinus disease depicted at CT in cystic fibrosis. Acta Radiol. 2001; 42:144–150.
Article7. Scarfe WC, Farman AG. What is cone-beam CT and how does it work? Dent Clin North Am. 2008; 52:707–730.
Article8. Chang EH. New insights into the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis sinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014; 4:132–137.
Article9. Berkhout MC, Rijntjes E, El Bouazzaoui LH, Fokkens WJ, Brimicombe RW, Heijerman HG. Importance of bacteriology in upper airways of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2013; 12:525–529.
Article10. Gysin C, Alothman GA, Papsin BC. Sinonasal disease in cystic fibrosis: Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and management. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000; 30:481–489.
Article11. King VV. Upper respiratory disease, sinusitis, and polyposis. Clin Rev Allergy. 1991; 9:143–157.
Article12. Eggesbø HB, Søvik S, Dølvik S, Eiklid K, Kolmannskog F. CT characterization of developmental variations of the paranasal sinuses in cystic fibrosis. Acta Radiol. 2001; 42:482–493.
Article13. Eggesbø HB, Søvik S, Dølvik S, Kolmannskog F. CT characterization of inflammatory paranasal sinus disease in cystic fibrosis. Acta Radiol. 2002; 43:21–28.
Article14. April MM, Zinreich SJ, Baroody FM, Naclerio RM. Coronal CT scan abnormalities in children with chronic sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1993; 103:985–990.
Article15. Gentile VG, Isaacson G. Patterns of sinusitis in cystic fibrosis. Laryngoscope. 1996; 106:1005–1009.
Article16. Kennedy DW, Senior BA, Gannon FH, Montone KT, Hwang P, Lanza DC. Histology and histomorphometry of ethmoid bone in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1998; 108:502–507.
Article17. Chiu AG. Osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2005; 38:1237–1242.
Article18. Cho SH, Min HJ, Han HX, Paik SS, Kim KR. CT analysis and histopathology of bone remodeling in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 135:404–408.
Article19. Loebinger MR, Bilton D, Wilson R. Upper airway 2: bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis and sinusitis. Thorax. 2009; 64:1096–1101.20. Kocak M, Smith TL, Smith MM. Bone involvement in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 10:49–52.
Article21. Georgalas C, Videler W, Freling N, Fokkens W. Global osteitis scoring scale and chronic rhinosinusitis: a marker of revision surgery. Clin Otolaryngol. 2010; 35:455–461.
Article