Endocrinol Metab.
2013 Sep;28(3):236-240. 10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.236.
Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndrome Type III with Primary Hypoparathyroidism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ho3632@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1973830
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.236
Abstract
- Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome is defined as multiple endocrine gland insufficiencies accompanied by autoimmune diseases of the endocrine and nonendocrine system. After Schmidt introduced a case of nontuberculosis adrenal gland dysfunction with thyroiditis in 1926, Neufeld defined polyglandular autoimmune syndrome by I, II, and III subtypes in 1980 by their presentation of occurrence age, heredity methods, relationship with human leukocyte antigen, and accompanying diseases. We report a case of a 32-year-old female with polyglandular autoimmune syndrome III accompanied by type 1 diabetes mellitus that was treated with insulin (36 units per day) for 11 years. She had insulin deficiency and Hashimoto thyroiditis as an autoimmune disorder. In addition, she had several features similar to Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy including short stature, truncal obesity, round face, short neck, low intelligence (full IQ 84), and decreased memory. Although Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy is morphological evidence of pseudohypoparathyroidism or pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism, she had primary hypoparathyroidism on laboratory results. Here, we report a case of polyglandular autoimmune syndrome III with type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, and primary hypoparathyroidism, accompanied by clinical features similar to Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy.
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Glands
Adult
Autoimmune Diseases
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1
Endocrine Glands
Female
Fibrous Dysplasia, Polyostotic
Hashimoto Disease
Heredity
Humans
Hypoparathyroidism
Insulin
Intelligence
Leukocytes
Memory
Neck
Obesity
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
Thyroid Gland
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis, Autoimmune
Fibrous Dysplasia, Polyostotic
Insulin
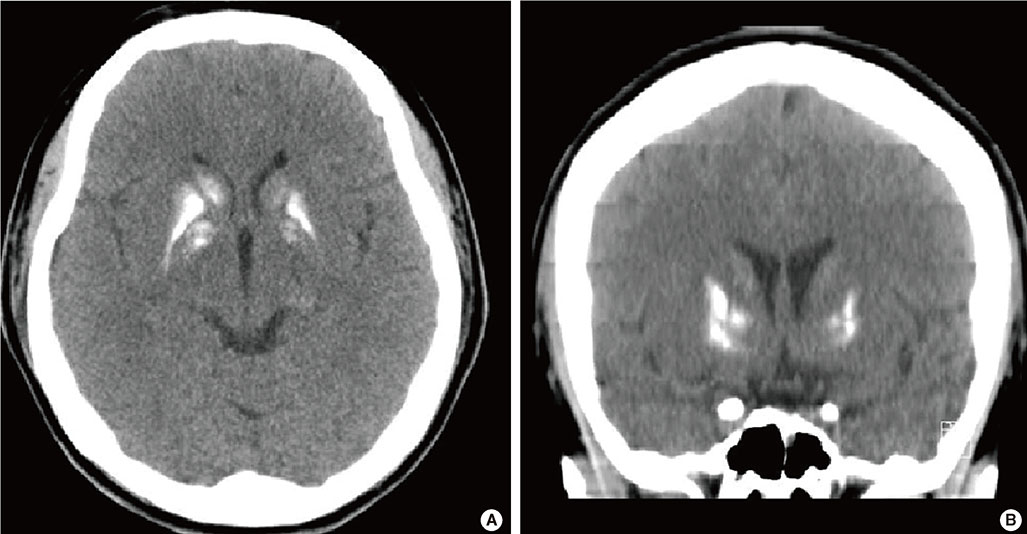
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Brief Review of Articles in '
Endocrinology and Metabolism ' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):251-256. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.251.
Reference
-
1. Neufeld M, Maclaren N, Blizzard R. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Pediatr Ann. 1980; 9:154–162.2. Papadopoulos KI, Hallengren B. Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type II in patients with idiopathic Addison's disease. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1990; 122:472–478.3. Park YS. Loss of function of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene and development of poyendocrinopathy. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 2003; 18:439–449.4. Song CU, Shong MH, Kim YK, Ro HK, Yoon SI, Kim SS, Seong KY, Kim SY. A case of polyglandular autoimmune syndrome presenting Graves' disease, pernicious anemia and insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1993; 8:211–216.5. Jeong ET, Park JH, Kim DH, Jeong BO, Ko KS, Rhee BD. A case of polygrandular autoimmune syndrome. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1995; 10:418–423.6. Kim CH, Kim HK, Park JY, Song YK, Kim KS, Yoo KS. A case of polyglandular autoimmune syndrome. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1997; 12:672–676.7. Kim JS, Lee MD, Kim HS, Chung CH. A case of polygrandular automune type II syndrome associated empty sella. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1998; 13:295–300.8. Lee YS, Lee JM, Park HO, Park SK, Yoon SR, Kim SY, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK. A case of type II autoimmune polyglandular syndrome: acute adrenal crisis presented as the first manifestation of Addison's disease in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis and hypgonadism. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1998; 13:115–120.9. Levine MA, Germain-Lee E, Jan de Beur S. Genetic basis for resistance to parathyroid hormone. Horm Res. 2003; 60:Suppl 3. 87–95.10. Lemay M, McNeely WF, Raisz LG. Dyschondroplasia with soft tissue calcification and ossification, and normal parathyroid function (pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism). Am J Med. 1956; 21:649–656.11. Hayward BE, Moran V, Strain L, Bonthron DT. Bidirectional imprinting of a single gene: GNAS1 encodes maternally, paternally, and biallelically derived proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:15475–15480.12. Adams RD, Victor M. Principles of neurology. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Information Services Co.;1989.13. Nagamine K, Peterson P, Scott HS, Kudoh J, Minoshima S, Heino M, Krohn KJ, Lalioti MD, Mullis PE, Antonarakis SE, Kawasaki K, Asakawa S, Ito F, Shimizu N. Positional cloning of the APECED gene. Nat Genet. 1997; 17:393–398.14. Finnish-German APECED Consortium. An autoimmune disease, APECED, caused by mutations in a novel gene featuring two PHD-type zinc-finger domains. Nat Genet. 1997; 17:399–403.15. Kim JK, Byun YJ, Park CS. A case of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism with Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1991; 9:349–356.16. Ahn H, Kim KS, Kim IH, Song HJ, Cheon HW, Lee JW, Oh CH. A case of cutaneous ossification occurring in pseudohypoparathyroidism. Ann Dermatol. 1999; 11:263–266.17. Kim SR, Doh YJ, Kim HK, Moon SS, Lee JY, Jeon JH, Kim SW, Kim BW, Lee IK, Kim JG. A case of pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with normal stature. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009; 24:138–143.18. Weinstein LS, Yu S, Warner DR, Liu J. Endocrine manifestations of stimulatory G protein alpha-subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr Rev. 2001; 22:675–705.19. Levine MA, Jap TS, Mauseth RS, Downs RW, Spiegel AM. Activity of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein is reduced in erythrocytes from patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism: biochemical, endocrine, and genetic analysis of Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy in six kindreds. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986; 62:497–502.20. Ogata E, Yamamoto M, Matsumoto T, Fujita T, Fukase M, Kinoshita Y, Furukawa Y, Sohn HE, Nakajima H, Yasuda T. Standard procedure and the diagnostic criteria for the Ellsworth-Howard test using human PTH-(1-34). Nihon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi. 1984; 60:971–984.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Polygrandular Automune type II syndrome associated empty sella
- A Case of Alopecia Areata Associated with Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome Type III
- A Case of Idiopathic Hypoparathyroidism Associated with Graves' Disease
- A Case of Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndrome
- A Case of Alopecia Universalis Associated with Autoimmune Poly Glandular Syndrome type II