Cancer Res Treat.
2008 Dec;40(4):211-213.
TTP-HUS Associated with Sunitinib
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hoy.lim@samsung.com
Abstract
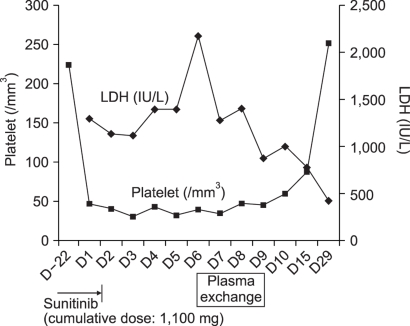
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome (TTP-HUS) is a rare condition that is severe and may be fatal. Adverse reactions to drugs increasingly are reported as probable causes of TTP-HUS. Many chemotherapeutic agents have also been implicated in causing TTP-HUS. We reported a woman with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who presented with TTP- HUS associated with sunitinib. She had gross hematuria and generalized edema. The hemoglobin concentration was 8.9 g/dl and the platelet count was 46,000/mm3. Her reticulocyte count was increased to 4.1% and the peripheral blood smear revealed red blood cell fragmentation and spherocytes. The patient completely recovered after discontinuing the use of sunitinib and undergoing plasmapheresis. Because of the increasing use of sunitinib in the treatment of cancer patients, oncologists should be aware of the possibility of TTP-HUS related to sunitinib, as early recognition and prompt therapeutic intervention can be beneficial.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Medina PJ, Sipols JM, George JN. Drug-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Curr Opin Hematol. 2001; 8:286–293. PMID: 11604563.
Article2. Zakarija A, Bennett C. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2005; 31:681–690. PMID: 16388419.
Article3. Zupancic M, Shah PC, Shah-Khan F. Gemcitabine-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Lancet Oncol. 2007; 8:634–641. PMID: 17613425.
Article4. Chow LQ, Eckhardt SG. Sunitinib: from rational design to clinical efficacy. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:884–896. PMID: 17327610.
Article5. Rock EP, Goodman V, Jiang JX, Mahjoob K, Verbois SL, Morse D, et al. Food and Drug Administration drug approval summary: Sunitinib malate for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor and advanced renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist. 2007; 12:107–113. PMID: 17227905.
Article6. Rini BI, Tamaskar I, Shaheen P, Salas R, Garcia J, Wood L, et al. Hypothyroidism in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007; 99:81–83. PMID: 17202116.
Article7. Chu TF, Rupnick MA, Kerkela R, Dallabrida SM, Zurakowski D, Nguyen L, et al. Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Lancet. 2007; 370:2011–2019. PMID: 18083403.
Article8. Kapiteijn E, Brand A, Kroep J, Gelderblom H. Sunitinib induced hypertension, thrombotic microangiopathy and reversible posterior leukencephalopathy syndrome. Ann Oncol. 2007; 18:1745–1747. PMID: 17890216.
Article9. Frangie C, Lefaucheur C, Medioni J, Jacquot C, Hill GS, Nochy D. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy caused by anti-VEGF-antibody treatment for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2007; 8:177–178. PMID: 17267332.10. Eremina V, Jefferson JA, Kowalewska J, Hochster H, Haas M, Weisstuch J, et al. VEGF inhibition and renal thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:1129–1136. PMID: 18337603.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sunitinib-Associated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- ADAMTS13 Activity in Childhood Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome(HUS)
- Therapeutic Plasma Exchanges in Patients with Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura/Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in three pregnancies
- Plasma Exchange for Patients with Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura-Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (TTP-HUS) in Pusan National University Hospital (2003~2011)