Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Sep;61(3):256-264. 10.4046/trd.2006.61.3.256.
Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 after Administration of Endotoxin in Diabetic Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Clinical Research institute, Cheonan, Korea. welkim@schch.co.kr
- KMID: 1970265
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2006.61.3.256
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: An acute lung injury(ALI) is characterized by the recruitment, activation, and apoptosis of inflammatory cells, numerous products released by inflammatory cells such as reactive oxygen species, inflammatory mediators, and a variety of proteolytic enzymes. It was reported that bacterial infections in diabetics showed impaired PMN functions such as reduced PMN respiratory burst and decreased microbicidal activity in inflamed tissue. However, the effect of the proteinase - inhibitor (MMP-9 vs TIMP-1) in ALI in diabetics is unclear. This study evaluated the differences in the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 after the stimulation of endotoxin in a rat model.
METHODS
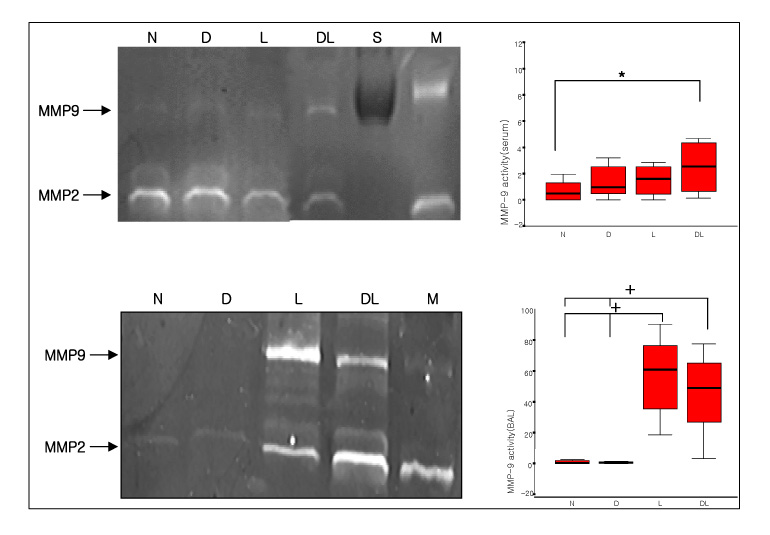
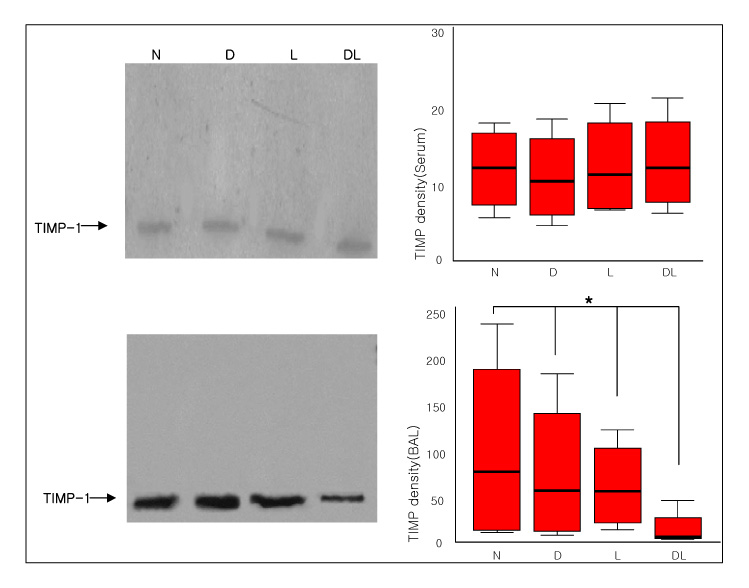
Six-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were classified into normal, DM, LPS and DM+LPS groups. The peripheral blood, BAL fluids, and lung tissues were obtained from individual rats. The MMP-9 activity was measured by gelatin zymography and the TIMP-1 level was measured by Western blotting.
RESULTS
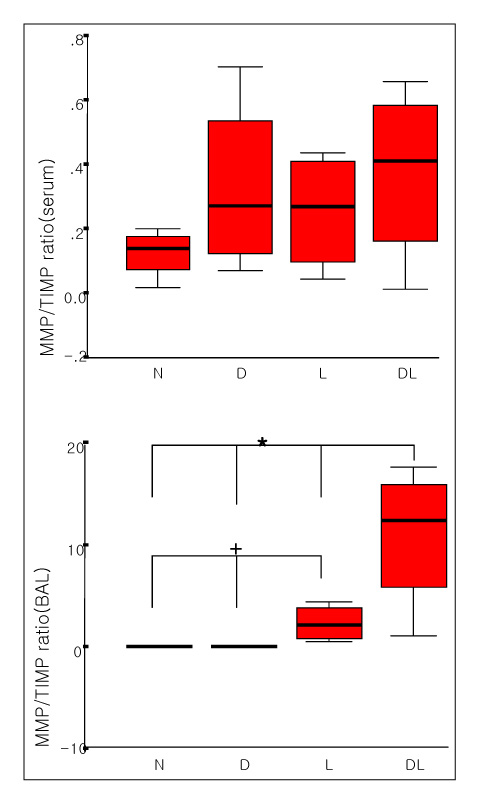
The total BAL cells of the DM-LPS groups were significantly lower than the LPS groups (p < 0.01). The MMP-9 activities in the serum were higher in the DM+LPS groups than in the other groups. The MMP-9 activities in the BAL fluids were significantly higher in the DM+LPS group than in the normal and diabetic rats (p < 0.05). TIMP-1 expressions in the BAL fluids were significantly lower in the DM+LPS group than other groups (p < 0.05). The ratio between MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the BAL fluids was significantly higher in the DM+LPS groups (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
In ALI in diabetics the higher MMP-9 activity and lower TIMP-1 level are believed to prolonged and intensify the course of inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Bacterial Infections
Blotting, Western
Gelatin
Humans
Inflammation
Lung
Male
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9*
Models, Animal
Peptide Hydrolases
Rats*
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Reactive Oxygen Species
Respiratory Burst
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1*
Gelatin
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9
Peptide Hydrolases
Reactive Oxygen Species
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hanley ME, Repine JE. Pathogenesis aspects of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 15:260–270.2. Holter JF, Weiland JE, Patcht ER, Gadek JE, Davis WB. Protein permeability in the adult respiratory distress syndrome: loss of size selectivity of the alveolar epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1986. 78:1513–1522.3. Simon RH, DeHart PD, Todd RF 3rd. Neutrophil-induced injury of rat pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986. 78:1375–1386.4. Smedly LA, Tonnesen MG, Sandhaus RA, Haslett C, Guthrie LA, Johnston RB Jr, et al. Neutrophil-mediated injury to endothelial cells: enhancement by endotoxin and essential role of neutrophil elastase. J Clin Invest. 1986. 77:1233–1243.5. Katzenstein AL, Bloor CM, Liebow AA. Diffuse alveoar damage: the role of oxygen, shock and related factors. Am J Pathol. 1976. 85:209–228.6. Palmgren MS, deShazo RD, Carter RM, Zimny ML, Shah SV. Mechanisms of neutrophil damage to human alveolar extracelluar matrix: the role of serine and metalloproteinases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992. 89:905–915.7. Shapiro SD, Senior RM. Matrix metalloproteinases: matrix degradation and more. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. 20:1100–1102.8. Matute-Bello G, Liles WC, Radella F 2nd, Steinberg KP, Ruzinski JT, Jonas M, et al. Neutrophil apoptosis in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156:1969–1977.9. van den Steen PE, Proost P, Wuyts A, van Damme J, Opdenakker G. Neutrophil gelatinase B potentiates interleukin-8 tenfold by aminoterminal processing, whereas it degrades CTAP-III, PF-4, and GRO-alpha and leaves RANTES and MCP-2 intact. Blood. 2000. 96:2673–2681.10. Gibbs DF, Shanley TP, Warner RL, Murphy HS, Varani J, Johnson KJ. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in models of macrophage-dependent acute lung injury: evidence for alveolar macrophage as source of proteinases. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. 20:1145–1154.11. Atkinson JJ, Senior RM. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. 28:12–24.12. Stetler-Stevenson WG. Dynamics of matrix turnover during pathologic remodeling of the extracellular matrix. Am J Pathol. 1996. 148:1345–1350.13. Lanchou J, Corbel M, Tanguy M, Germain N, Boichot E, Theret N, et al. Imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases(MMP-9 and MMP-2) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases(TIMP-1 and TIMP-2) in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients. Crit Care Med. 2003. 31:536–542.14. Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR, Karchmer AW. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1906–1912.15. Lippmann ML, Goldberg SK, Walkenstein MD, Herring W, Gordon M. Bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia: a community hospital experience. Chest. 1995. 108:1608–1613.16. Chen KY, Hsueh PR, Liaw YS, Yang PC, Luh KT. A 10-year experience with bacteriology of acute thoracic empyema. Chest. 2000. 117:1685–1689.17. Bashar M, Alcabes P, Rom WN, Condos R. Increased incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in diabetic patients on the Bellevue chest service, 1987 to 1997. Chest. 2001. 120:1514–1519.18. Goldman MD. Lung dysfunction in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:1915–1918.19. Becher G, Winsel K, Beck E, Neubauer G, Stresemann E. Breath condensate as a method of noninvasive assessment of inflammation mediators from the lower airways. Pneumologie. 1997. 51:Suppl 2. 456–459.20. Enomoto T, Usuki J, Azuma A, Nakagawa T, Kudoh S. Diabetes mellitus may increase risk for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2003. 123:2007–2011.21. Marhoffer W, Stein M, Maeser E, Federlin K. Impairment of polymorphonuclear leukocyte function and metabolic control of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1992. 15:256–260.22. Shah SV, Wallin JD, Eilen SD. Chemiluminescence and superoxide anion production by leukocytes from diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983. 57:402–409.23. Anderson B, Goldsmith GH, Spagnuolo PJ. Neutrophil adhesive dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: the role of cellular and plasma factors. J Lab Clin Med. 1988. 111:275–285.24. Delamaire M, Maugendre D, Moreno M, le Goff MC, Allannic H, Genetet B. Impaired leukocyte functions in diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 1997. 14:29–34.25. Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Bandyopadhyay A, Chaudhuri A. Insulin suppresses plasma concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:3310–3314.26. Death AK, Fisher EJ, McGrath KC, Yue DK. High glucose alters matrix metalloproteinase expression in two key vascular cells: potential impact on atherosclerosis in diabetes. Atherosclerosis. 2003. 168:263–269.27. Lee YC, Lee HB, Rhee YK, Song CH. The involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in airway inflammation of patients with acute asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001. 31:1623–1630.28. Hayashi T, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Fleming MV, Fishback N, Koss MN, Liotta LA, et al. Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitor in lungs of patients with diffuse alveolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1996. 149:1241–1256.29. Ricou B, Nicod L, Lacraz S, Welgus HG, Suter PM, Dayer JM. Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996. 154:346–352.30. Finlay GA, O'Driscoll LR, Russell KJ, D'Arcy EM, Masterson JB, FitzGerald MX, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases expression and production by alveolar macrophages in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156:240–247.31. Gunther A, Walmrath D, Grimminger F, Seeger W. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 22:247–258.32. Pecsvarady Z, Fisher TC, Darwin CH, Fabok A, Maqueda TS, Saad MF, et al. Decreased polymorphonuclear leukocyte deformability in NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1994. 17:57–63.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Hantaan Virus on Fibronectin and Matrix Metalloproteinase-3
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- Significance of Increased Expression of the Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Human Colorectal Carcinomas
- Expression of MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP-2 mRNA in Breast Carcinomas
- Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 Expression by an Adenosine A1 Agonist in Trabecular Meshwork Cells