J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Dec;42(6):711-717. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.6.711.
Bilateral Femoral Derotatioal Osteotomy in Spastic Diplegia: Outcome Assessment of Single Stage Multilevel Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pmsmed@hanafos.com
- KMID: 1947775
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.6.711
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the outcome of multilevel surgery including femoral derotational osteotomy, and analyze the effect of bilateral femoral derotational osteotomy on the gait of spastic diplegia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
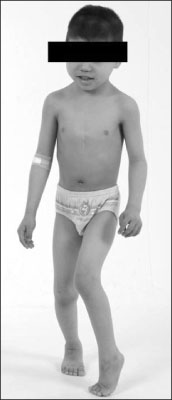
The medical records of 26 spastic diplegics, who had undergone a bilateral intertrochanteric femoral derotational osteotomy, bilateral distal hamstring lengthening, bilateral rectus femoris transfer, and bilateral heel cord lengthening, were evaluated. There were 16 boys and 10 girls with a mean age of 7.6 years. The pre- and post-operative gait analysis, functional assessment score, and physical examination were archived and analyzed.
RESULTS
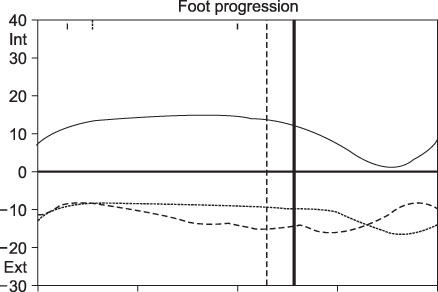
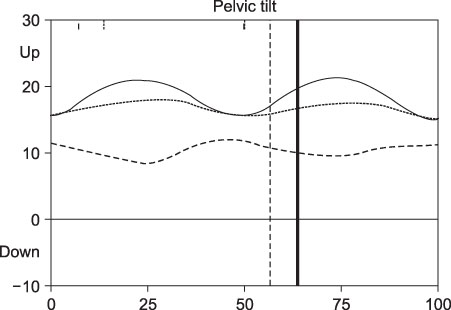
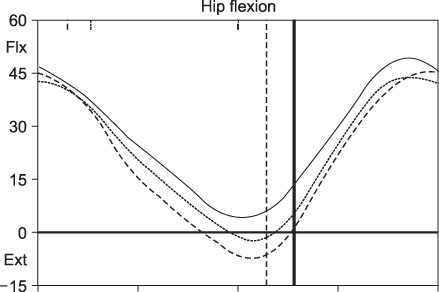
In the physical examination, the femoral anteversion, hip flexion contracture, and popliteal angle decreased significantly, while the ankle range of dorsiflexion increased significantly. In three dimensional gait analysis, the cadence remained constant while the walking speed improved significantly. In transverse plane kinematics, the mean pelvic rotation did not show any difference but foot progression angle fell into the normal range after surgery. In the sagittal plane, the maximal hip extension and H3 power generation improved significantly, while the mean anterior pelvic tilt decreased significantly. The functional assessment score improved from 7 to 9, which was significant.
CONCLUSION
The walking ability of spastic diplegia with in-toeing, stiff knee and tip toeing gait improved after single stage multilevel surgery including a femoral derotational osteotomy. Femoral derotation osteotomy without psoas lengthening improved the anterior pelvic tilt despite the distal hamstring lengthening
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung CY, Park MS, Choi IH, Cho TJ, Yoo WJ. Gait patterns according to the torsional deformities in spastic hemiplegia: a preliminary report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2004. 39:298–305.
Article2. LaGasse DJ, Staheli LT. The measurement of femoral anteversion. A comparison of the fluoroscopic and biplane roentgenographic methods of measurement. Clin Orthop. 1972. 86:13–15.3. Novacheck TF, Trost JP, Schwartz MH. Intramuscular psoas lengthening improves dynamic hip function in children with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002. 22:158–164.
Article4. Rodda JM, Graham HK. Classification of gait patterns in spastic hemiplegia and spastic diplegia: a basis for a management algorithm. Eur J Neurol. 2001. 8:Suppl 5. 98–108.
Article5. Rodda JM, Graham HK, Carson L, Galea MP, Wolfe R. Sagittal gait patterns in spastic diplegia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004. 86:251–258.
Article6. Ruwe PA, Gage JR, Ozonoff MB, DeLuca PA. Clinical determination of femoral anteversion. A comparison with established techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:820–830.
Article7. Schwartz MH, Novacheck TF, Trost J. A tool for quantifying hip flexor function during gait. Gait Posture. 2000. 12:122–127.
Article8. Schwartz MH, Viehweger E, Stout J, Novacheck TF, Gage JR. Comprehensive treatment of ambulatory children with cerebral palsy: an outcome assessment. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004. 24:45–53.9. Weiner DS, Cook AJ, Hoyt WA Jr, Oravec CE. Computed tomography in the measurement of femoral anteversion. Orthopedics. 1978. 1:299–306.
Article10. Winters TF, Gage JR, Hicks R. Gait patterns in spastic hemiplegia in children and young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:437–441.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Results of One-Stage Correction for Hip Instability in Cerebral Palsy
- Comparative Study on the Results of Femoral Osteotomy and Innominate Osteotomy in LCPD
- Energy Expenditure during Gait in Adults with Cerebral Palsy
- Effect of Treadmill Training With Eyes Open and Closed on Knee Proprioception, Functional Balance and Mobility in Children With Spastic Diplegia
- Hyperactive Stretch Reflexes as a Prognostic Factor of Ambulation in the Children with Spastic Diplegia