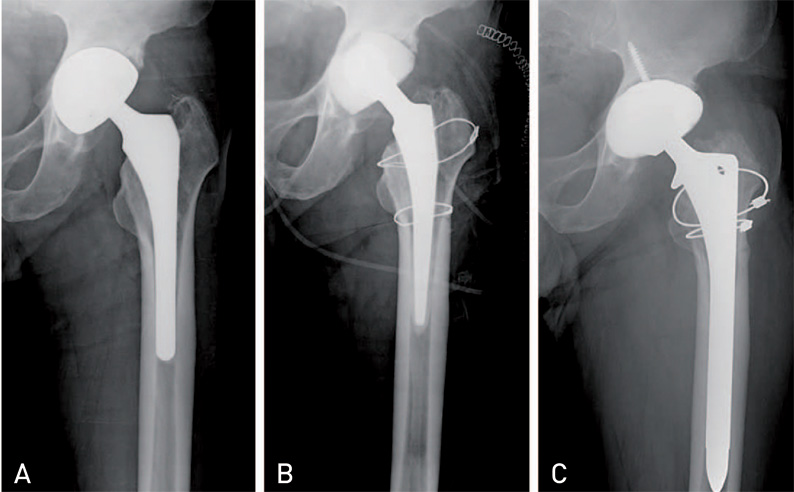
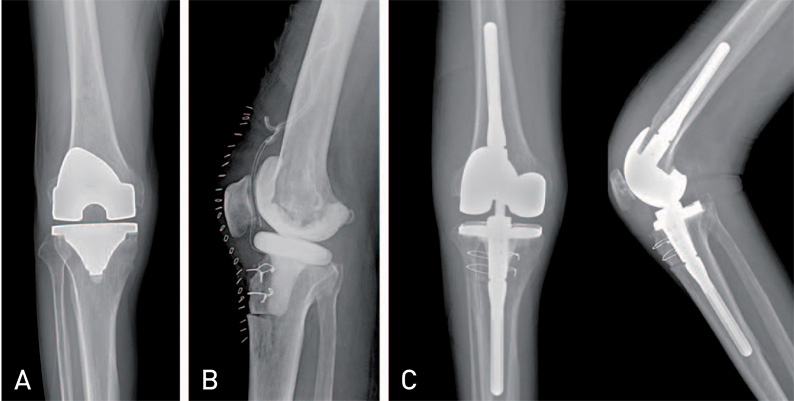
Hip Pelvis.
2014 Dec;26(4):235-242. 10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.235.
Clinical Characteristics of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection for Chronic Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. kangjoon@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1907699
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.235
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Deep infection after hip and knee arthroplasty is a serious complication and is difficult to treat due to its toxicity. The aims of our study were to find out the differences of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) infection after hip and knee arthroplasty focusing on clinical course and laboratory findings.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed 61 staphylococcal infection cases after hip and knee arthroplasty (MSSA in 25 patients, MRSA in 36 patients). Vital signs, laboratory tests, microbiology and clinical courses were analyzed. The average follow-up period was 3.8 years (range, 2 to 10.1 years).
RESULTS
At initial visit, MRSA group showed significant higher erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein (CRP) and neutrophil percentage. The average duration for the normalization of CRP was longer in MRSA group (MRSA: 36.7+/-25.1 days, MSSA: 24.7+/-13.6 days; P=0.008). The mean interval between staging operation was longer in MRSA group (MRSA: mean 8.7 weeks [range, 6.4 to 21.4 weeks], MSSA: mean 6.8 weeks [range, 6 to 13.1 weeks]; P=0.012). MRSA group (13.9%) revealed higher recurrence rate than MSSA group (4%). Two patients (5.6%) from MRSA group expired by sepsis. One limb amputation (2.7%) was carried out in MRSA group.
CONCLUSION
MRSA infection after arthroplasty showed more toxic serologic parameter and poorer prognosis. Aggressive treatment should be considered for MRSA infection following arthroplasty.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amputation
Arthroplasty
Blood Sedimentation
C-Reactive Protein
Drug Resistance, Microbial
Extremities
Follow-Up Studies
Hip*
Humans
Knee*
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus*
Neutrophils
Prognosis
Recurrence
Retrospective Studies
Sepsis
Staphylococcal Infections
Staphylococcus aureus
Vancomycin
Vital Signs
C-Reactive Protein
Vancomycin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, Pattison G, Whitehouse S, Bannister GC. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:688–691.
Article2. Kurtz SM, Lau E, Schmier J, Ong KL, Zhao K, Parvizi J. Infection burden for hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23:984–991.
Article3. Peersman G, Laskin R, Davis J, Peterson M. Infection in total knee replacement: a retrospective review of 6489 total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 392:15–23.4. Fehring TK, Odum S, Griffin WL, Mason JB, Nadaud M. Early failures in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 392:315–318.
Article5. Bjerke-Kroll BT, Christ AB, McLawhorn AS, Sculco PK, Jules-Elysée KM, Sculco TP. Periprosthetic joint infections treated with two-stage revision over 14 years: an evolving microbiology profile. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:877–882.
Article6. Ridgeway S, Wilson J, Charlet A, Kafatos G, Pearson A, Coello R. Infection of the surgical site after arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:844–850.
Article7. Cosgrove SE, Sakoulas G, Perencevich EN, Schwaber MJ, Karchmer AW, Carmeli Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a metaanalysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:53–59.
Article8. Goyal N, Miller A, Tripathi M, Parvizi J. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): colonisation and pre-operative screening. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95-B:4–9.9. Hawkshead JJ 3rd, Patel NB, Steele RW, Heinrich SD. Comparative severity of pediatric osteomyelitis attributable to methicillin-resistant versus methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009; 29:85–90.
Article10. Ju KL, Zurakowski D, Kocher MS. Differentiating between methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis in children: an evidence-based clinical prediction algorithm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:1693–1701.
Article11. Saavedra-Lozano J, Mejías A, Ahmad N, et al. Changing trends in acute osteomyelitis in children: impact of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28:569–575.12. Salgado CD, Dash S, Cantey JR, Marculescu CE. Higher risk of failure of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 461:48–53.
Article13. Parvizi J, Pawasarat IM, Azzam KA, Joshi A, Hansen EN, Bozic KJ. Periprosthetic joint infection: the economic impact of methicillin-resistant infections. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25:6 Suppl. 103–107.14. Tsukayama DT, Estrada R, Gustilo RB. Infection after total hip arthroplasty. A study of the treatment of one hundred and six infections. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:512–523.
Article15. Workgroup Convened by the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. New definition for periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:1136–1138.16. Estes CS, Beauchamp CP, Clarke HD, Spangehl MJ. A two-stage retention d?bridement protocol for acute periprosthetic joint infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:2029–2038.
Article17. Van Kleunen JP, Knox D, Garino JP, Lee GC. Irrigation and débridement and prosthesis retention for treating acute periprosthetic infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:2024–2028.
Article18. Koo KH, Yang JW, Cho SH, et al. Impregnation of vancomycin, gentamicin, and cefotaxime in a cement spacer for two-stage cementless reconstruction in infected total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16:882–892.
Article19. Meehan J, Jamali AA, Nguyen H. Prophylactic antibiotics in hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:2480–2490.
Article20. Della Valle CJ, Bogner E, Desai P, et al. Analysis of frozen sections of intraoperative specimens obtained at the time of reoperation after hip or knee resection arthroplasty for the treatment of infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:684–689.
Article21. Pepe MS. The statistical evaluation of medical tests for classification and prediction. 1st ed. Oxford, USA: Oxford University Press;2004.22. Bocchini CE, Hulten KG, Mason EO Jr, Gonzalez BE, Hammerman WA, Kaplan SL. Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes are associated with enhanced inflammatory response and local disease in acute hematogenous Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis in children. Pediatrics. 2006; 117:433–440.
Article23. Lo WT, Tang CS, Chen SJ, Huang CF, Tseng MH, Wang CC. Panton-Valentine leukocidin is associated with exacerbated skin manifestations and inflammatory response in children with community-associated staphylococcal scarlet fever. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49:e69–e75.
Article24. Jung WJ, Kang YA, Park MS, et al. Prediction of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in patients with non-nosocomial pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:370.25. Berbari E, Mabry T, Tsaras G, et al. Inflammatory blood laboratory levels as markers of prosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:2102–2109.
Article26. Spangehl MJ, Masri BA, O'Connell JX, Duncan CP. Prospective analysis of preoperative and intraoperative investigations for the diagnosis of infection at the sites of two hundred and two revision total hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:672–683.
Article27. Insall JN, Thompson FM, Brause BD. Two-stage reimplantation for the salvage of infected total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65:1087–1098.
Article28. Petty W, Bryan RS, Coventry MB, Peterson LF. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975; 6:1005–1014.
Article29. Whittaker JP, Warren RE, Jones RS, Gregson PA. Is prolonged systemic antibiotic treatment essential in two-stage revision hip replacement for chronic Gram-positive infection? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91:44–51.
Article30. Aggarwal VK, Rasouli MR, Parvizi J. Periprosthetic joint infection: Current concept. Indian J Orthop. 2013; 47:10–17.
Article31. Dubée V, Zeller V, Lhotellier L, et al. Continuous high-dose vancomycin combination therapy for methicillin-resistant staphylococcal prosthetic hip infection: a prospective cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013; 19:E98–E105.
Article32. Liu C, Kakis A, Nichols A, Ries MD, Vail TP, Bozic KJ. Targeted use of vancomycin as perioperative prophylaxis reduces periprosthetic joint infection in revision TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472:227–231.
Article33. Nickinson RS, Board TN, Gambhir AK, Porter ML, Kay PR. The microbiology of the infected knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2010; 34:505–510.
Article34. Kuzyk PR, Dhotar HS, Sternheim A, Gross AE, Safir O, Backstein D. Two-stage revision arthroplasty for management of chronic periprosthetic hip and knee infection: techniques, controversies, and outcomes. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22:153–164.
Article35. Hoad-Reddick DA, Evans CR, Norman P, Stockley I. Is there a role for extended antibiotic therapy in a two-stage revision of the infected knee arthroplasty? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:171–174.
Article36. Deirmengian C, Hallab N, Tarabishy A, et al. Synovial fluid biomarkers for periprosthetic infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:2017–2023.
Article37. Jacovides CL, Parvizi J, Adeli B, Jung KA. Molecular markers for diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:6 Suppl. 99–103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Nosocomial Infections
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Molecular Epidemiologic Methods Used in the Analysis of Methicillin-Resistant staphylococcus aureus
- A statistical analysis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection in Neonates