J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Aug;54(2):148-150. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.148.
Intracranial Calcification Caused by a Brain Abscess : A Rare Cause of Intracranial Calcification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. chosunns@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 1814256
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.148
Abstract
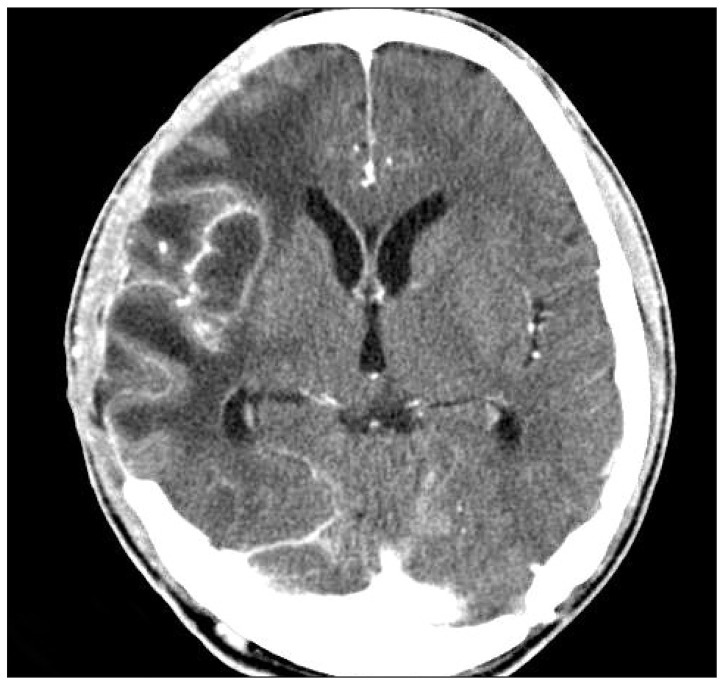
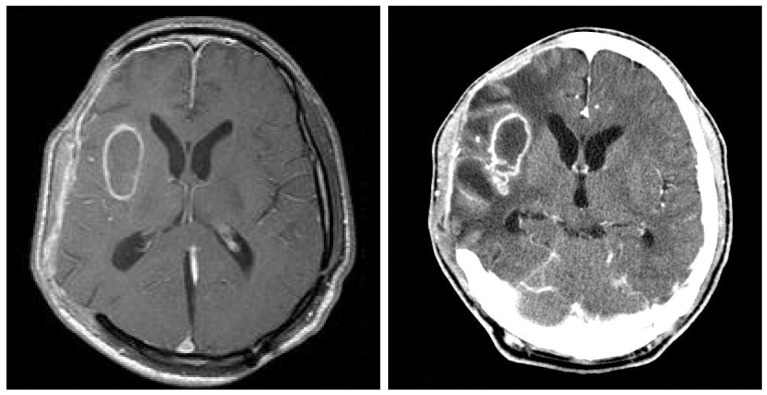
- Intracranial calcifications are relatively common computed tomographic findings in the field of neurosurgery, and cysticercosis, tuberculosis, HIV, and cryptococcus are acquired intracranial infections typically associated with calcifications. However, intracranial calcification caused by a bacterial brain abscess is rare. Here, we present a rare case of intracranial calcification caused by a bacterial brain abscess, from which staphylococcus hominis was isolated. To the best of our knowledge, no previous report has been published on intracranial calcification caused by bacterial brain abscess after decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. In this article, the pathophysiological mechanism of this uncommon entity is discussed and relevant literature reviewed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alkan A, Parlak M, Baysal T, Sigirci A, Kutlu R, Altinok T. En-plaque tuberculomas of tentorium in a pregnant woman : follow-up with MRI (2003:2b). Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:1190–1193. PMID: 12772710.
Article2. Cambria S, Salpietro F, Cambria M. Calcified brain abscesses. Case report. J Neurosurg Sci. 1984; 28:103–105. PMID: 6527142.3. Deepak S, Jayakumar B, Shanavas . Extensive intracranial calcification. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005; 53:948. PMID: 16515234.4. Falcone S, Post MJ. Encephalitis, cerebritis, and brain abscess : pathophysiology and imaging findings. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2000; 10:333–353. PMID: 10775955.5. Gortvai P, De Louvois J, Hurley R. The bacteriology and chemotherapy of acute pyogenic brain abscess. Br J Neurosurg. 1987; 1:189–203. PMID: 3267286.
Article6. Kieffer SA, Gold LH. Intracranial physiologic calcifications. Semin Roentgenol. 1974; 9:151–162. PMID: 4824739.
Article7. Kloos WE. Taxonomy and systematics of staphylococci indigenous to humans. In : Crossley B, Archer GL, editors. The staphylococci in human disease. New York: Churchill Livingstone;1997.8. Ludwig B, Nix W, Lanksch W. Computed tomography of the "armored brain". Neuroradiology. 1983; 25:39–43. PMID: 6856080.
Article9. Nitta H, Tachibana O, Hayashi Y, Oki H. Unusually large calcified brain abscess : CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990; 14:485–486. PMID: 2335625.10. Osborn AG. Pyogenic parenchymal infections. In : Osborn AG, editor. Diagnostic Neuroradiology. St. Louis: Mosby;1994. p. 668–692.11. Rizvi T, Garg A, Singh M, Sharma MC. Large intracranial mass with a calcified rim - is it a brain abscess? Pediatr Neurosurg. 2005; 41:112–114. PMID: 15942285.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Hypoparathyroidism Combined with Extensive Intracranial Calcification: A Case Report
- Fahr's Disease With Intracerebral Hemorrhage at the Uncommon Location: A Case Report
- Predisposing Factors and Clinical Impact of Linear Intracrania l Calcification Following External Ventricular Drainage
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated with Marked Intracranial Calcification
- A Case of Idiopathic Hypoparathyroidism with Extensive Intracranial Calcification