J Clin Neurol.
2007 Dec;3(4):175-180. 10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.175.
Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Zonisamide Monotherapy in Epilepsy Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. sppark@mail.knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1808549
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.175
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Zonisamide (ZNS) is a useful antiepileptic drug with a broad therapeutic spectrum. However, there is limited information on the long-term use of ZNS as a monotherapy. This study investigated the long-term effects of ZNS as a monotherapy for the treatment of epilepsy.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed the records of epilepsy patients treated with ZNS monotherapy at our clinic. We identified outcomes for patients treated with ZNS monotherapy for a minimum of 6 months. Efficacy was quantified as the percentage change in seizure frequency, and safety was assessed by the frequency and types of adverse events.
RESULTS
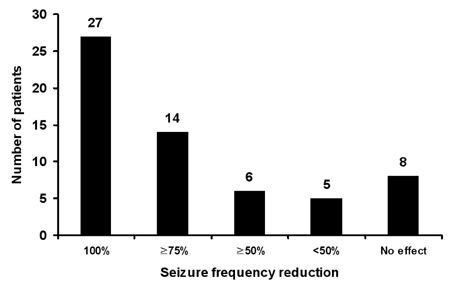
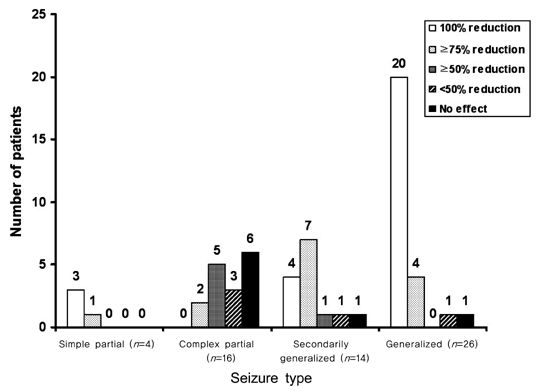
Sixty patients who received ZNS for a minimum of 6 months were included. The mean duration of treatment was 19.8 months (range, 6-37 months), and the mean ZNS dosage was 255 mg/day (range, 100-500 mg/day). Twenty-seven patients (45%) were seizure-free, and an additional 20 patients (33%) had above 50% seizure frequency reduction at the last follow-up visit. Partial seizures with or without secondary generalization and generalized seizures were well controlled by ZNS, whereas complex partial seizures were not. Forty-eight patients (80%) reported mild-to-moderate adverse events, including memory loss (35%), attention deficit (27%), and weight loss (20%).
CONCLUSIONS
Long-term ZNS monotherapy is effective at treating a broad spectrum of seizure disorders, except complex partial seizures. However, a specific adverse event, such as cognitive impairment, is common and long-lasting.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Cognitive Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs
Sung-Pa Park, Soon-Hak Kwon
J Clin Neurol. 2008;4(3):99-106. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.3.99.Zonisamide Changes Unilateral Cortical Excitability in Focal Epilepsy Patients
Eun Yeon Joo, Hye-Jung Kim, Yang-Hee Lim, Ki-Hwan Ji, Seung Bong Hong
J Clin Neurol. 2010;6(4):189-195. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2010.6.4.189.
Reference
-
1. Masuda Y, Ishizaki M, Shimizu M. Zonisamide: pharmacology and clinical efficacy in epilepsy. CNS Drug Rev. 1998. 4:341–360.
Article2. Leppik IE. Zonisamide. Epilepsia. 1999. 40:Suppl 5. S23–S29.
Article3. Oommen KJ, Mathews S. Zonisamide: a new antiepileptic drug. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1999. 22:192–200.4. Leppik IE, Willmore LJ, Homan RW, Fromm G, Oommen KJ, Penry JK, et al. Efficacy and safety of zonisamide: results of a multicenter study. Epilepsy Res. 1993. 14:165–173.
Article5. Tosches WA, Tisdell J. Long-term efficacy and safety of monotherapy and adjunctive therapy with zonisamide. Epilepsy Behav. 2006. 8:522–526.
Article6. Ohtahara S, Yamatogi Y. Erratum to "Safety of zonisamide therapy: prospective follow-up survey". Seizure. 2007. 16:87–93.
Article7. Wilfong AA. Zonisamide monotherapy for epilepsy in children and young adults. Pediatr Neurol. 2005. 32:77–80.
Article8. Kothare SV, Kaleyias J, Mostofi N, Valencia I, Melvin JJ, Hobdell E, et al. Efficacy and safety of zonisamide monotherapy in a cohort of children with epilepsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2006. 34:351–354.
Article9. Brodie MJ. Zonisamide as adjunctive therapy for refractory partial seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2006. 68:Suppl 2. S11–S16.
Article10. Leppik IE. Practical prescribing and long-term efficacy and safety of zonisamide. Epilepsy Res. 2006. 68:Suppl 2. S17–S24.
Article11. Newmark ME, Dubinsky S. Zonisamide monotherapy in a multi-group clinic. Seizure. 2004. 13:223–225.
Article12. Fukushima K, Seino M. A long-term follow-up of zonisamide monotherapy. Epilepsia. 2006. 47:1860–1864.
Article13. Lee KS, Ahn JH, Kim BS, Kang MS, Chung SW, Kim YI, et al. The effect of zonisamide in epileptic patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1991. 9:220–227.14. Lee SY. The antiepileptic effect of zonisamide (P-132). New Med J. 1991. 34:79–84.15. Chang HI, Yoon DJ, Oh DJ, Song JY, Lim OG, Lee KK, et al. A clinical study on the antiepileptic effect of zonisamide. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1992. 31:778–784.16. Kim KJ, Chae SA, Ko TS, Kim DW, Hwang YS. The effect of zonisamide in children with refractory epilepsies. Korean J Pediatr. 1993. 36:1139–1145.17. Cho KH, Kim YS, Sin KC, Son JH, Kim BC, Kim MK, et al. The antiepileptic effect and safety of zonisamide in patients with intractable seizure. New Med J. 1994. 37:89–95.18. Korean Zonisamide Study Group (KZSG). Double-blind, randomized, comparative clinical trial of zonisamide and carbamazepine as initial monotherapy in newly diagnosed epilepsy. J Korean Epilep Soc. 1999. 3:50–57.19. Mattson RH, Cramer JA, Collins JF. Prognosis for total control of complex partial and secondarily generalized tonic clonic seizures. Department of Veterans Affairs Epilepsy Cooperative Studies No. 118 and No. 264 Group. Neurology. 1996. 47:68–76.
Article20. Kothare SV, Valencia I, Khurana DS, Hardison H, Melvin JJ, Legido A. Efficacy and tolerability of zonisamide in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2004. 6:267–270.21. Lin KM, Poland RE, Lesser IM. Ethnicity and psychopharmacology. Cult Med Psychiatry. 1986. 10:151–165.
Article22. Piazzini A, Canevini MP, Maggiori G, Canger R. The perception of memory failure in patients with epilepsy. Eur J Neurol. 2001. 8:613–620.
Article23. Sapolsky RM. Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000. 57:925–935.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of zonisamide in children with refractory epilepsies
- A Case of Renal stones during treatment with Zonisamide
- Safety and Efficacy of Topiramate Monotherapy in Children with Recent-onset Seizures
- The Effect of Zonisamide in Epileptic Patients
- A meta-analysis: efficacy and safety of anti-epileptic drugs prescribed in Korea as monotherapy and adjunctive treatment for patients with focal epilepsy