Intest Res.
2015 Jan;13(1):85-89. 10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.85.
Perianal Abscess and Proctitis by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ys810.jung@samsung.com
- KMID: 1807381
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.85
Abstract
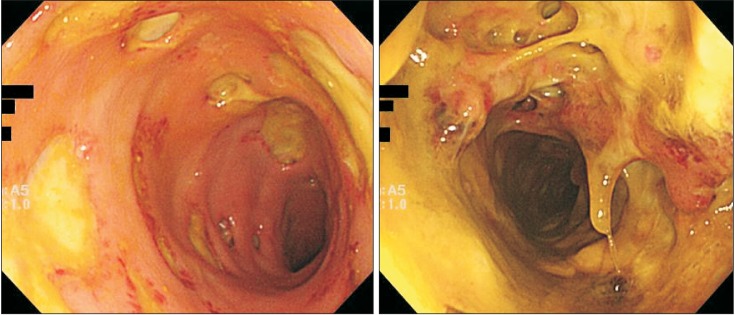
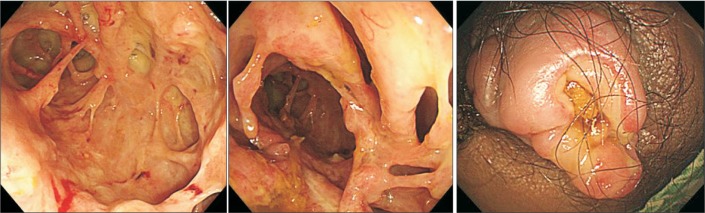
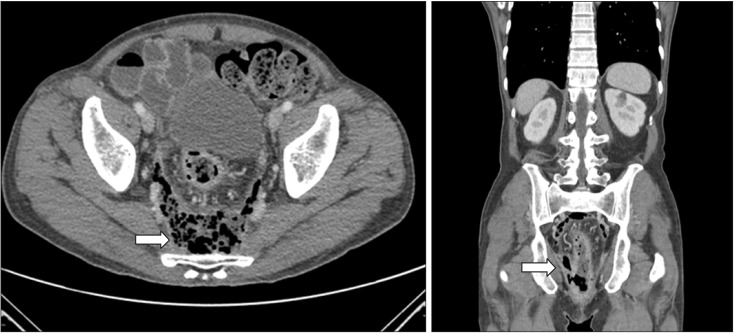
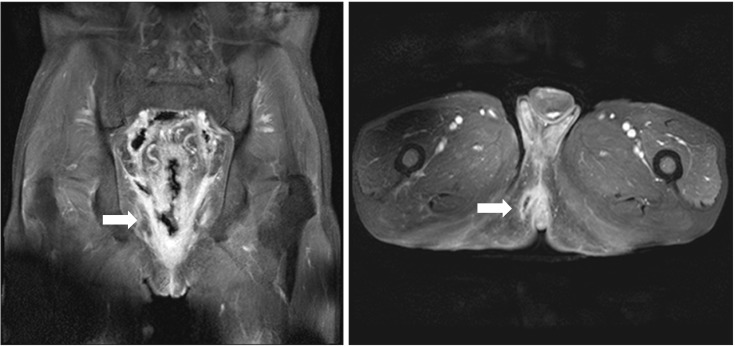
- Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) can at times cause invasive infections, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus and a history of alcohol abuse. A 61-year-old man with diabetes mellitus and a history of alcohol abuse presented with abdominal and anal pain for two weeks. After admission, he underwent sigmoidoscopy, which revealed multiple ulcerations with yellowish exudate in the rectum and sigmoid colon. The patient was treated with ciprofloxacin and metronidazole. After one week, follow up sigmoidoscopy was performed owing to sustained fever and diarrhea. The lesions were aggravated and seemed webbed in appearance because of damage to the rectal mucosa. Abdominal computed tomography and rectal magnetic resonance imaging were performed, and showed a perianal and perirectal abscess. The patient underwent laparoscopic sigmoid colostomy and perirectal abscess incision and drainage. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing K. pneumoniae was identified in pus culture. The antibiotics were switched to ertapenem. He improved after surgery and was discharged. K. pneumoniae can cause rapid invasive infection in patients with diabetes and a history of alcohol abuse. We report the first rare case of proctitis and perianal abscess caused by invasive K. pneumoniae infection.
MeSH Terms
-
Abscess*
Alcoholism
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Ciprofloxacin
Colon, Sigmoid
Colostomy
Diabetes Mellitus
Diarrhea
Drainage
Exudates and Transudates
Fever
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Klebsiella pneumoniae*
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Metronidazole
Middle Aged
Mucous Membrane
Pneumonia
Proctitis*
Rectum
Sigmoidoscopy
Suppuration
Ulcer
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Ciprofloxacin
Metronidazole
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liu CK, Liu CP, Leung CH, Sun FJ. Clinical and microbiological analysis of adult perianal abscess. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011; 44:204–208. PMID: 21524615.
Article2. Ryan KJ, Ray CG. Sherris medical microbiology: an introduction to infectious diseases. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical;2003.3. Chung DR, Lee SS, Lee HR, et al. Emerging invasive liver abscess caused by K1 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae in Korea. J Infect. 2007; 54:578–583. PMID: 17175028.
Article4. Chung DR, Lee H, Park MH, et al. Fecal carriage of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains closely related to liver abscess isolates in Koreans living in Korea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012; 31:481–486. PMID: 21739348.
Article5. Fang CT, Lai SY, Yi WC, Hsueh PR, Liu KL, Chang SC. Klebsiella pneumoniae genotype K1: an emerging pathogen that causes septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:284–293. PMID: 17599305.6. Ko WC, Paterson DL, Sagnimeni AJ, et al. Community-acquired Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: global differences in clinical patterns. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002; 8:160–166. PMID: 11897067.
Article7. Tsay RW, Siu LK, Fung CP, Chang FY. Characteristics of bacteremia between community-acquired and nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infection: risk factor for mortality and the impact of capsular serotypes as a herald for community-acquired infection. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162:1021–1027. PMID: 11996612.
Article8. Lee KH, Hui KP, Tan WC, Lim TK. Klebsiella bacteraemia: a report of 101 cases from National University Hospital, Singapore. J Hosp Infect. 1994; 27:299–305. PMID: 7963472.
Article9. Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44(Suppl 2):S27–S72. PMID: 17278083.
Article10. Gaynes R, Edwards JR. Overview of nosocomial infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41:848–854. PMID: 16107985.
Article11. Czaja CA, Scholes D, Hooton TM, Stamm WE. Population-based epidemiologic analysis of acute pyelonephritis. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:273–280. PMID: 17599303.
Article12. Fuxench-Lopez Z, Ramirez-Ronda CH. Pharyngeal flora in ambulatory alcoholic patients: prevalence of gram-negative bacilli. Arch Intern Med. 1978; 138:1815–1816. PMID: 363086.
Article13. Joshi N, Caputo GM, Weitekamp MR, Karchmer AW. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1906–1912. PMID: 10601511.
Article14. Szabo G. Consequences of alcohol consumption on host defence. Alcohol Alcohol. 1999; 34:830–841. PMID: 10659718.
Article15. Park GY, Kim SW, Kim HI, et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae as the most frequent pathogen of endogenous endophthalmitis. Korean J Med. 2012; 82:200–207.
Article16. Cheng DL, Liu YC, Yen MY, Liu CY, Wang RS. Septic metastatic lesions of pyogenic liver abscess. Their association with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia in diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1991; 151:1557–1559. PMID: 1872659.
Article17. Jung TS, Kim GW, Koh JI, et al. Endogenous Klebsiella endophthalmitis concurrent with prostate and perianal abscesses. Korean J Urol. 2008; 49:1055–1057.
Article18. Lee YS, Kim SY, Kim YJ, Lee EJ. A Case of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy associated with perianal abscess by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2005; 13:94–98.19. Eun CS, Han DS, Kim JP, et al. Comparative value of colonic tissue culture and stool culture for diagnosis of acute infectious colitis. Intest Res. 2004; 2:83–88.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- Spondylodiscitis with Epidural Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- A Case of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Associated with Perianal Abscess by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- A Case of Liver Abscess Metastasizing to Prostate Resulting in Prostatic Abscess
- Hematogenous Brain Abscess Resulting from Prostatic Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae