J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2011 Dec;46(6):528-532.
Spondylodiscitis with Epidural Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. wkmin@knu.ac.kr
Abstract
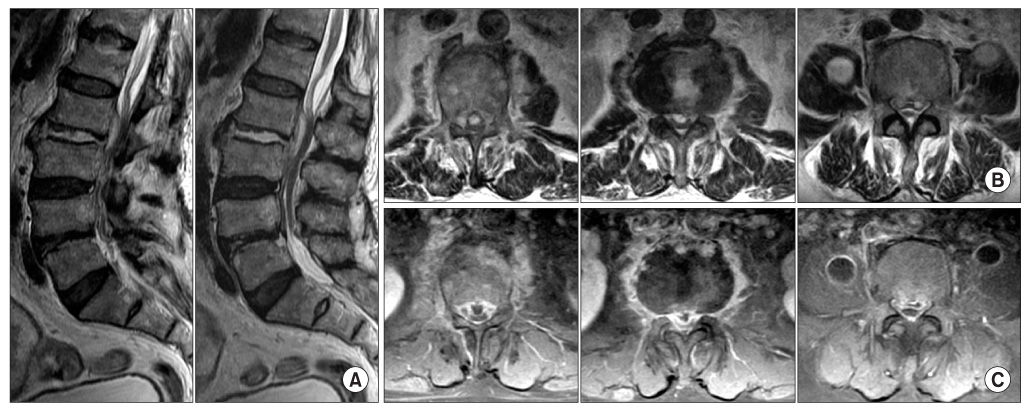
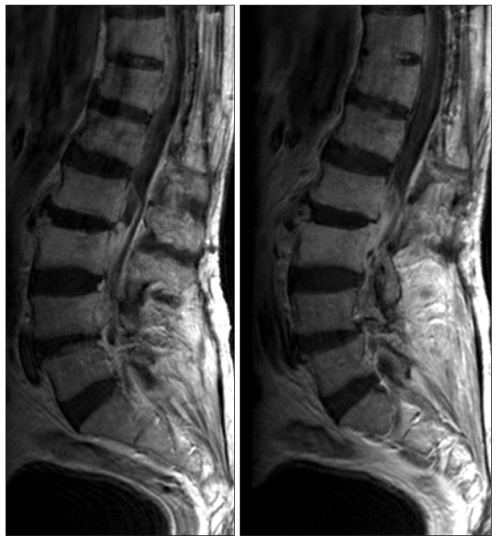
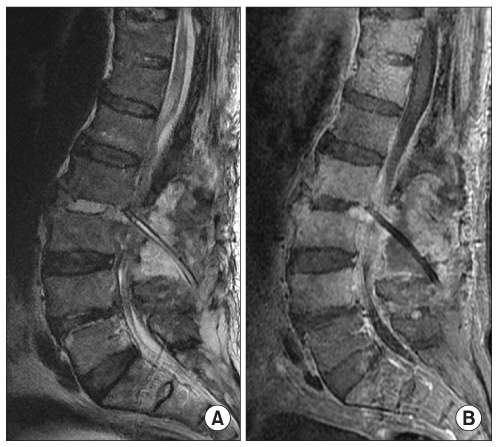
- Spondylodiscitis is very rare complication caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Among those, few cases of spondylodiscitis concomitant with epidural abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae have been reported. We present a case of lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis with epidural abscess caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae that successfully treated with administration of cefotaxime, surgical drainage and intermittent closed continuous saline irrigation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chevalier X, Marty M, Larget-Piet B. Klebsiella pneumoniae septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint. J Rheumatol. 1992. 19:1817–1819.2. Torda AJ, Gottlieb T, Bradbury R. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: analysis of 20 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1995. 20:320–328.
Article3. Vorbeck F, Morscher M, Ba-Ssalamah A, Imhof H. Infectious spondylitis in adults. Radiologe. 1996. 36:795–804.
Article4. Kouroussis C, Georgoulias V, Souglakos J, Simvoulakis E, Karabekios S, Samonis G. Spontaneous spondylodiscitis caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infection. 1999. 27:368–369.
Article5. Porras JA, Bayona C, Gutiérrez MC, Vidal F. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to Klebsiella pneumoniae. An Med Interna. 1994. 11:154–155.6. Apple JS, Halvorsen RA, Chapman TM, Martinez S. Klebsiella pneumoniae arthritis of the hip in a diabetic patient. South Med J. 1984. 77:229–231.
Article7. DelCurling O Jr, Gower DJ, McWhorter JM. Changing concepts in spinal epidural abscess: a report of 29 cases. Neurosurgery. 1990. 27:185–192.8. Yacoub WN, Sohn HJ, Chan S, Petrosyan M, Vermaire HM, Kelso RL, et al. Psoas abscess rarely requires surgical intervention. Am J Surg. 2008. 196:223–227.
Article9. Ohara N, Tominaga O, Uchiyama M, Nakano H, Muto T. Primary iliopsoas abscess successfully treated by ultrasonographically guided percutaneous drainage. J Orthop Sci. 1998. 3:221–224.
Article10. Tofuku K, Koga H, Yone K, Komiya S. Continuous irrigation in pyogenic spondylitis accompanied by iliopsoas abscess. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. 32:E382–E387.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- Spontaneous Cervical Spondylodiscitis and Epidural Abscess Caused by Klebsiella Pneumonia-single Stage Operation with Decompressive Corpectomy and Autologous Bone Fusion
- Lower Leg Abscess in Klebsiella pneumoniae Invasive Syndrome Caused by Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Case Report
- Hematogenous Brain Abscess Resulting from Prostatic Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Ventriculitis Associated with Liver Abscess Caused by Klebsiella Pneumoniae