J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2022 Jun;26(2):107-110. 10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.2.107.
Lower Leg Abscess in Klebsiella pneumoniae Invasive Syndrome Caused by Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Busan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2530492
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2022.26.2.107
Abstract
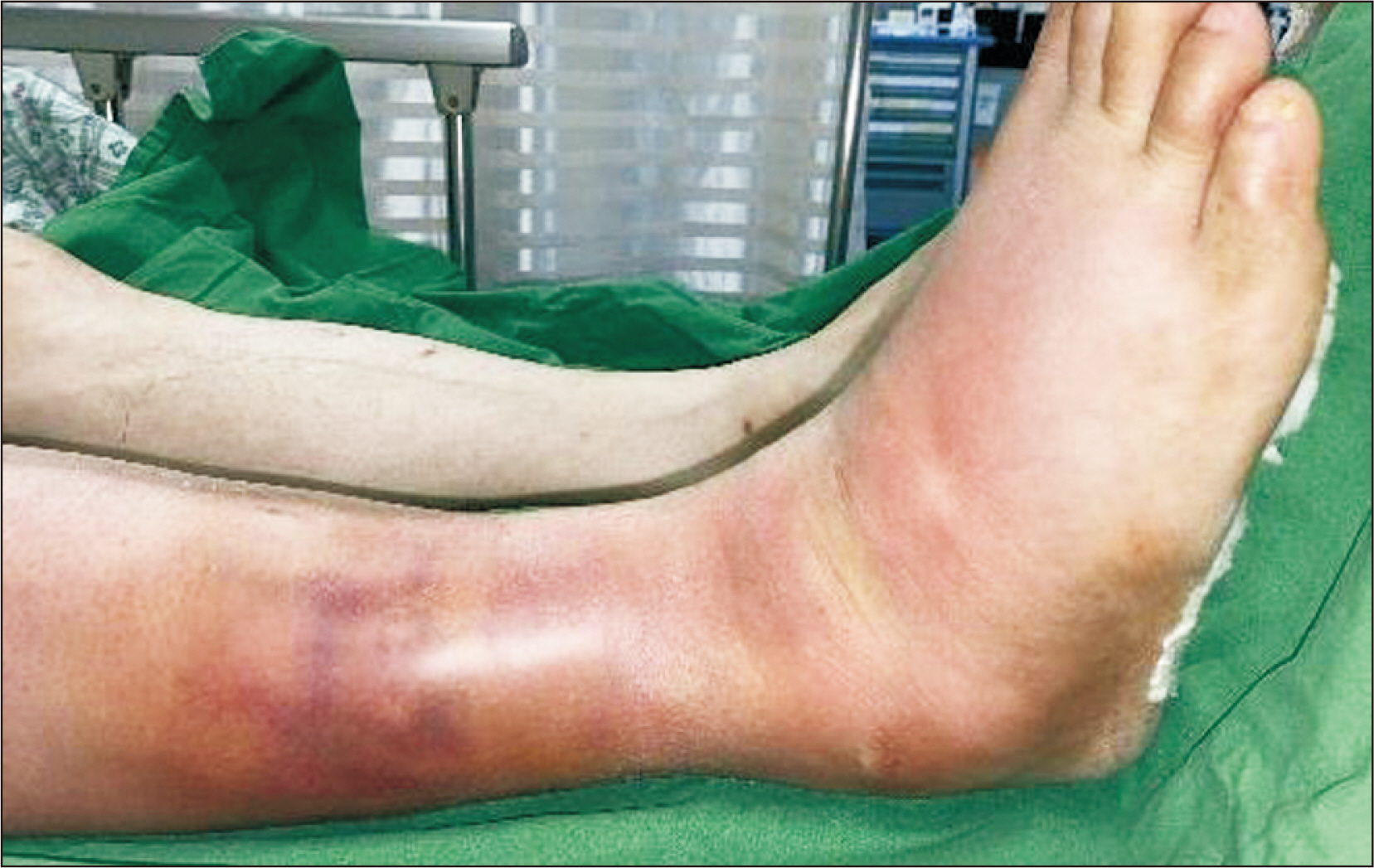
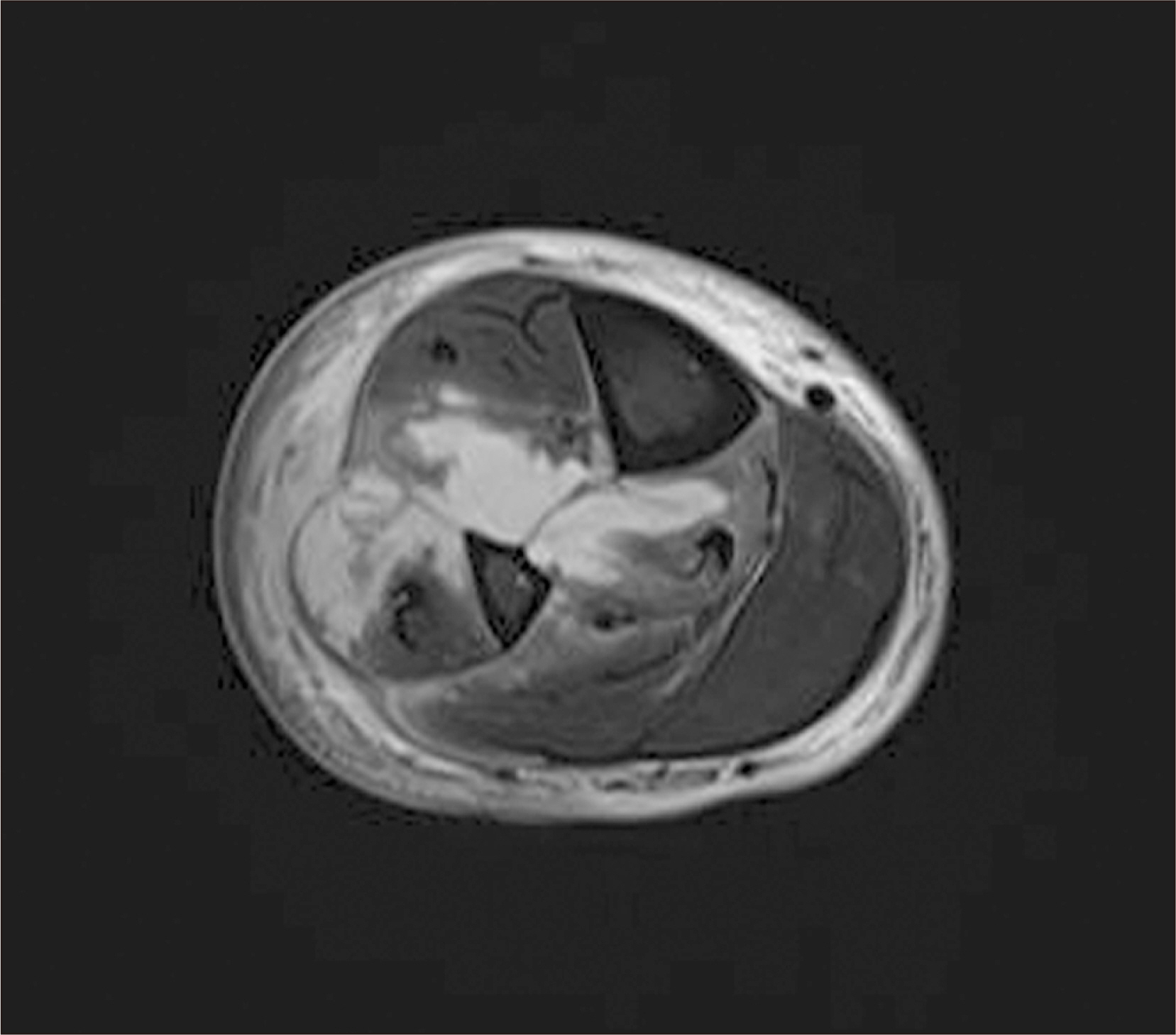
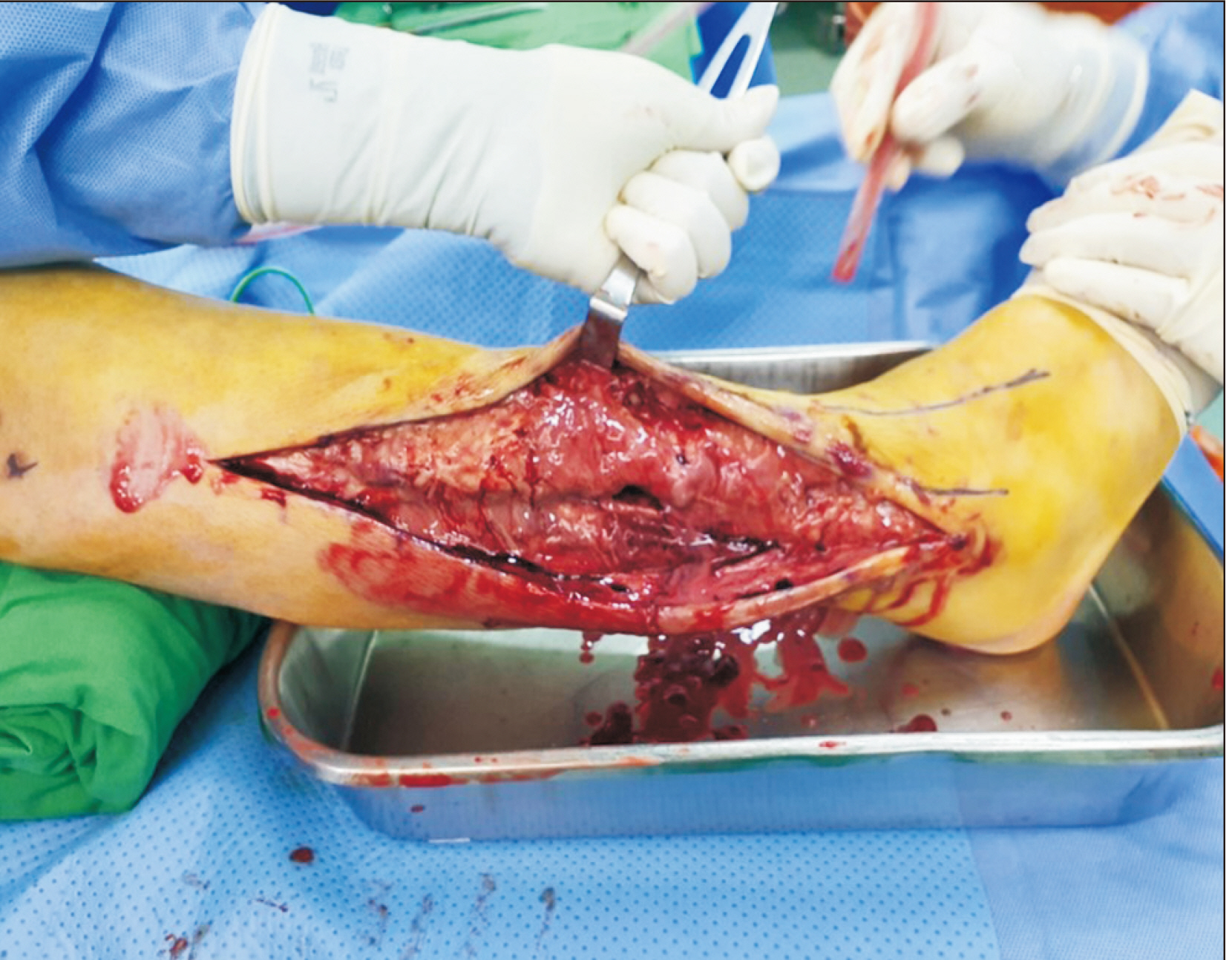
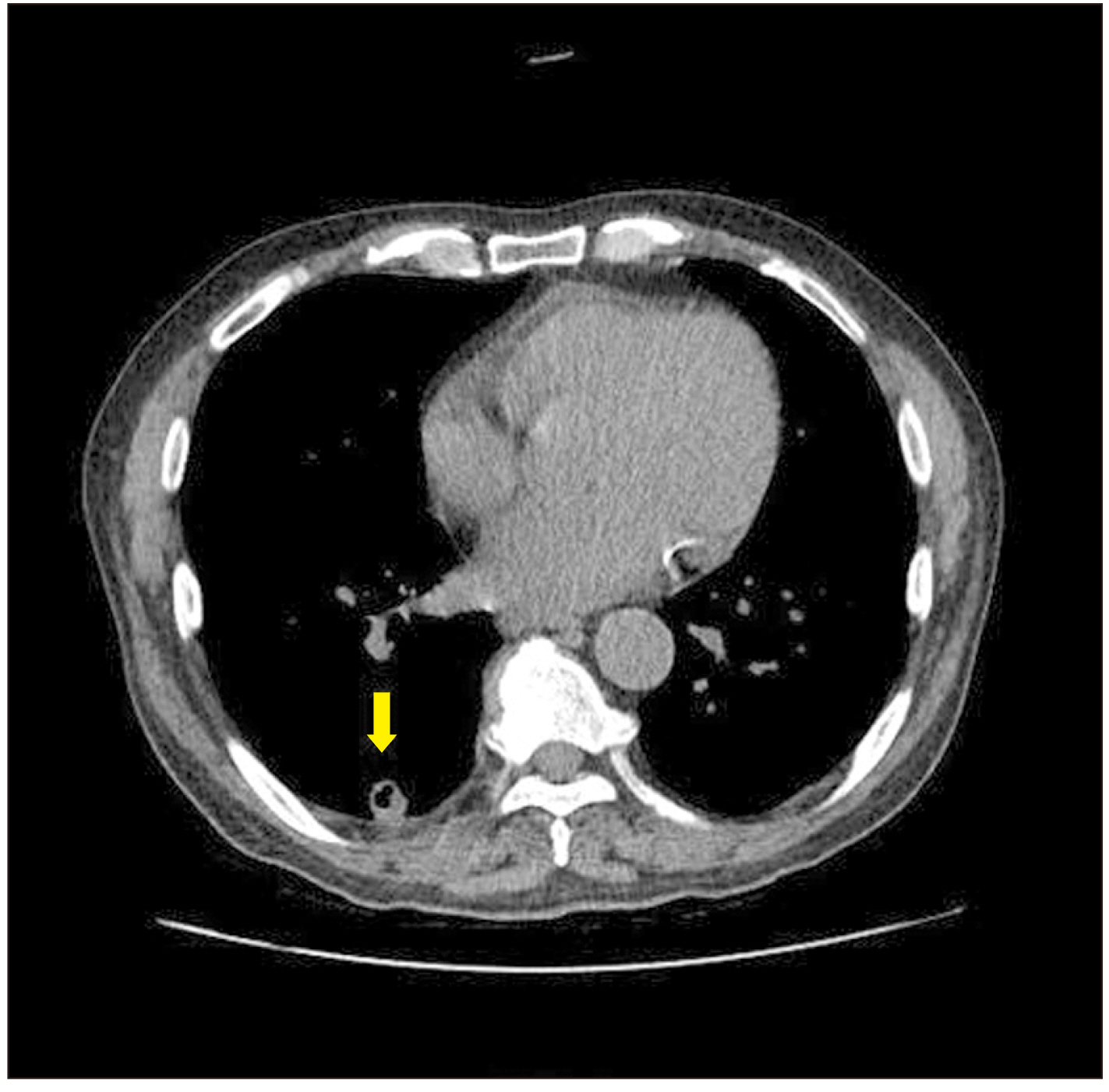
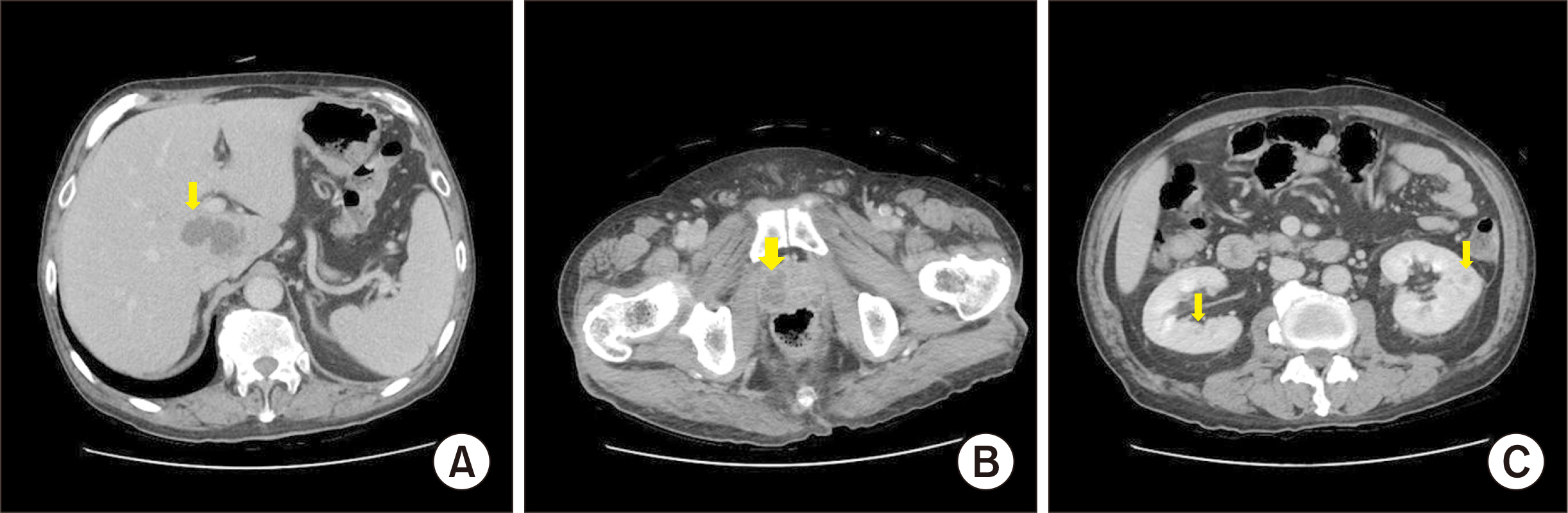
- Klebsiella pneumoniae is known to cause an invasive syndrome characterized by primary liver abscess associated with metastatic infection. The characteristics of the metastatic infection involving the musculoskeletal system in this invasive syndrome are not well understood. The authors present a case report of a patient who developed abscesses of the lower extremities along with abscesses of multiple organs, such as the liver and eye, caused by K. pneumonia. The patient was diagnosed early, and the infection was successfully controlled after several surgical treatments.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Siu LK, Yeh KM, Lin JC, Fung CP, Chang FY. 2012; Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: a new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 12:881–7. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70205-0. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70205-0. PMID: 23099082.
Article2. Zheng S, Florescu S, Mendoza M. 2020; Klebsiella pneumoniae invasive syndrome in a diabetic patient with gallbladder abscess. Clin Case Rep. 8:1940–2. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.3038. DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.3038. PMID: 33088524. PMCID: PMC7562885.
Article3. Park BC, Lim HR, Shin MH. 2019; Endogenous endophthalmitis by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae invasive syndrome. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 60:1334–8. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.12.1334. DOI: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.12.1334.
Article4. Wang JH, Liu YC, Lee SS, Yen MY, Chen YS, Wang JH, et al. 1998; Primary liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis. 26:1434–8. doi: 10.1086/516369. DOI: 10.1086/516369. PMID: 9636876.
Article5. Shon AS, Bajwa RP, Russo TA. 2013; Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: a new and dangerous breed. Virulence. 4:107–18. doi: 10.4161/viru.22718. DOI: 10.4161/viru.22718. PMID: 23302790. PMCID: PMC3654609.
Article6. Tu YC, Lu MC, Chiang MK, Huang SP, Peng HL, Chang HY, et al. 2009; Genetic requirements for Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced liver abscess in an oral infection model. Infect Immun. 77:2657–71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01523-08. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01523-08. PMID: 19433545. PMCID: PMC2708586.
Article7. Hu BS, Lau YJ, Shi ZY, Lin YH. 1999; Necrotizing fasciitis associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 29:1360–1. doi: 10.1086/313471. DOI: 10.1086/313471. PMID: 10525011.
Article8. Chen SC, Wu WY, Yeh CH, Lai KC, Cheng KS, Jeng LB, et al. 2007; Comparison of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscesses. Am J Med Sci. 334:97–105. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31812f59c7. DOI: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31812f59c7. PMID: 17700198.
Article9. Kim GS, Lee JH, Choi SA, Lim SR. 2005; A case of Klebsiella pneuomoniae liver abscess complicated with brain abscess and endophthalmitis. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 23:578–80.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ventriculitis Associated with Invasive
Klebsiella Pneumoniae Syndrome: A Case Report - A Case of Bilateral Lower Leg Cellulitis Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Spondylodiscitis with Epidural Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- Ventriculitis Associated with Liver Abscess Caused by Klebsiella Pneumoniae
- Ventriculitis Associated with Invasive