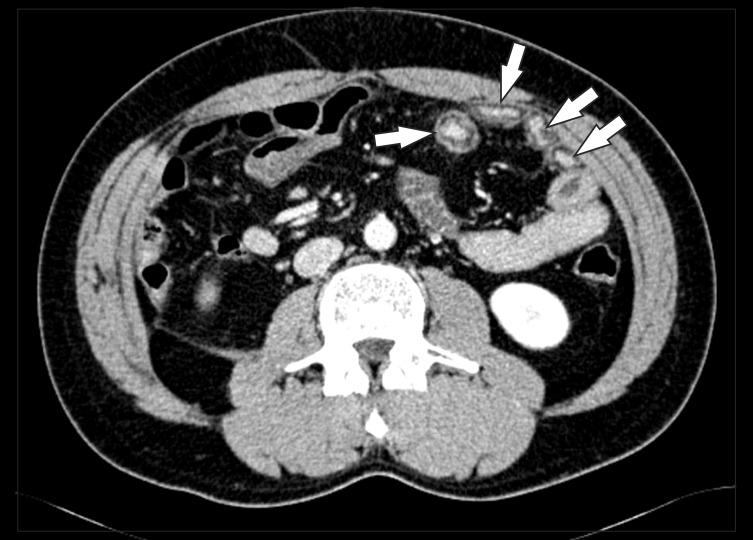
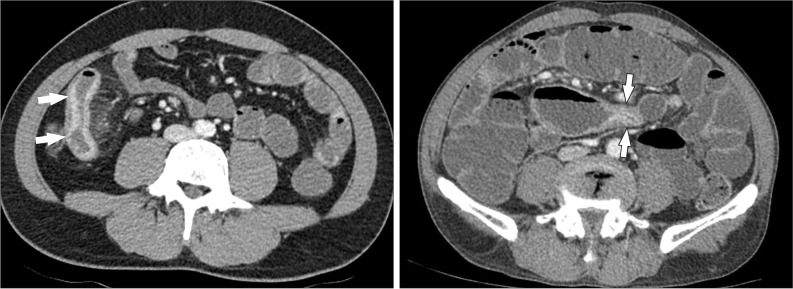
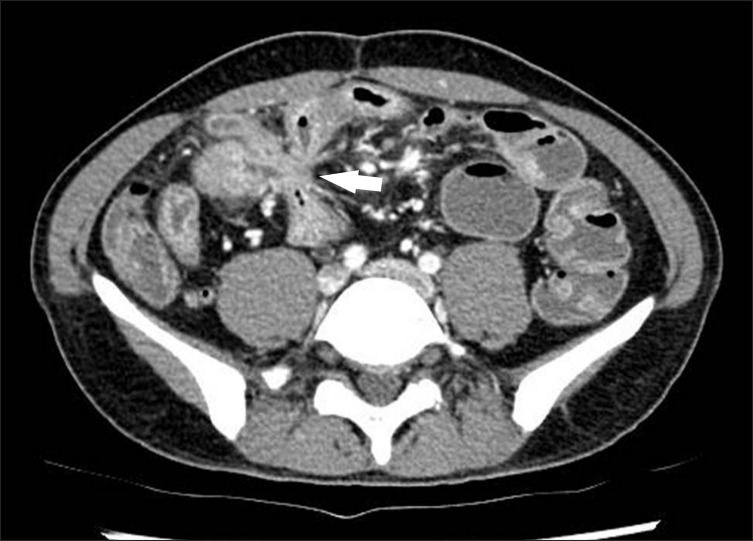
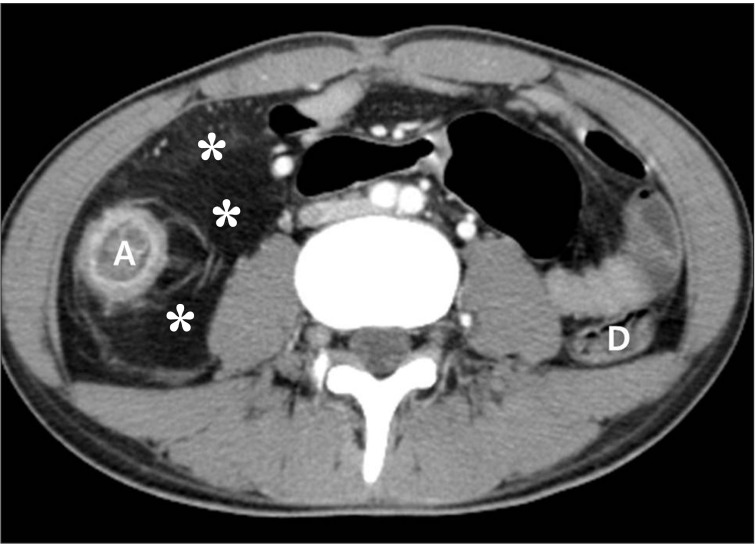
Intest Res.
2015 Jan;13(1):27-38. 10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.27.
Computed Tomography Enterography and Magnetic Resonance Enterography in the Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. shkim7071@gmail.com
- KMID: 1807374
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2015.13.1.27
Abstract
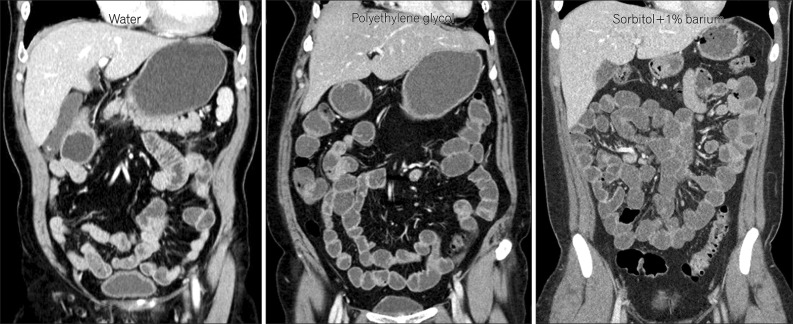
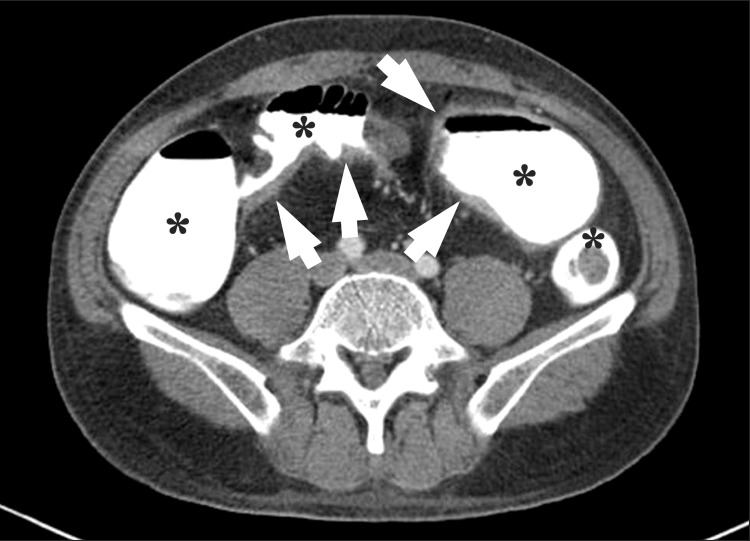
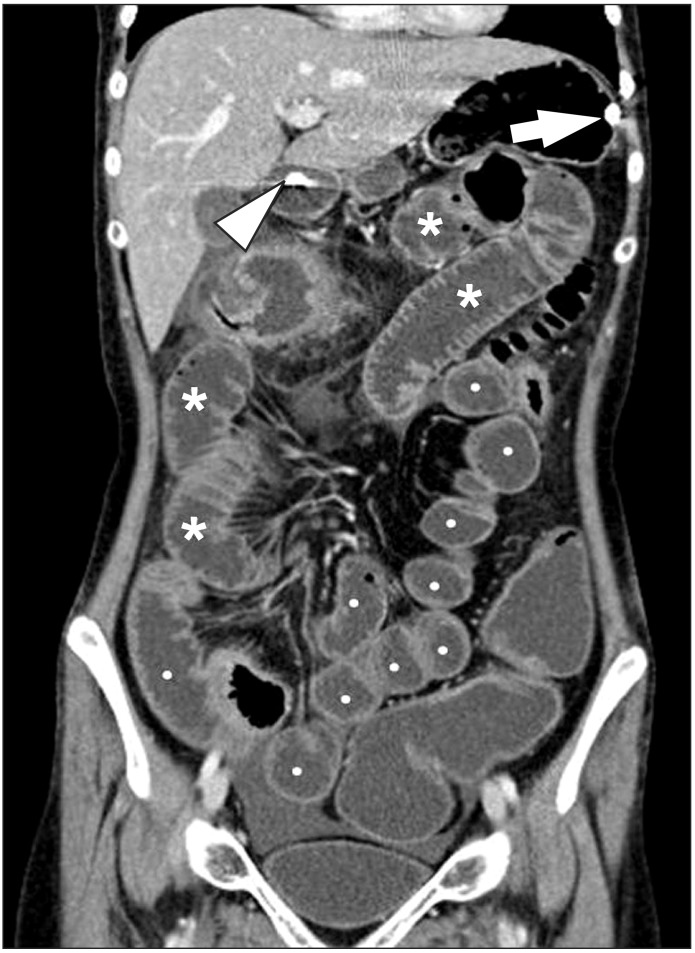
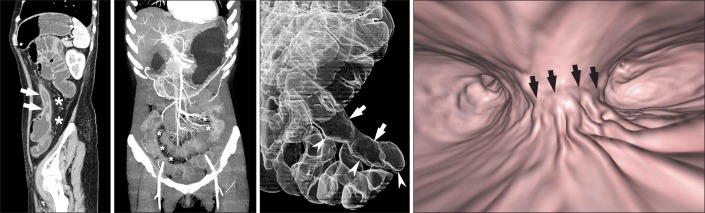
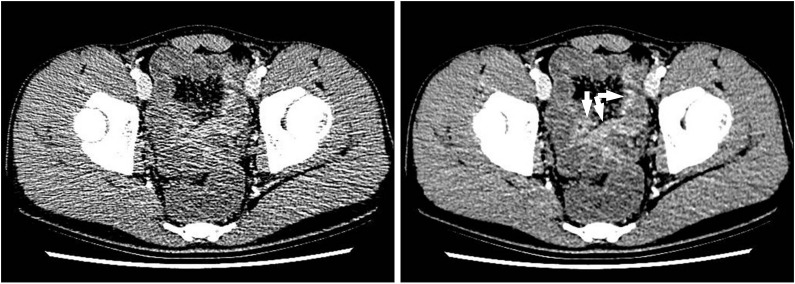
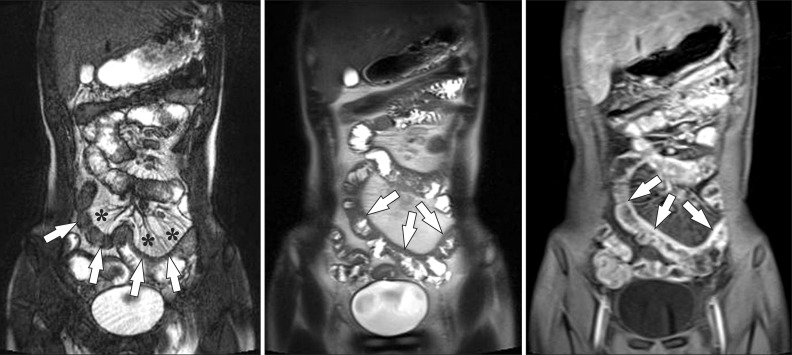
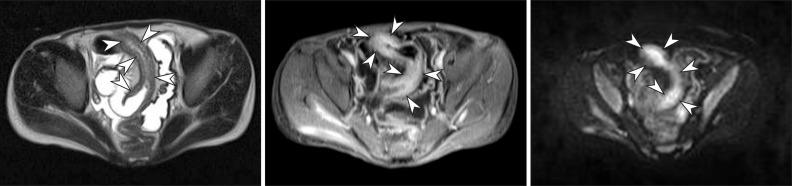
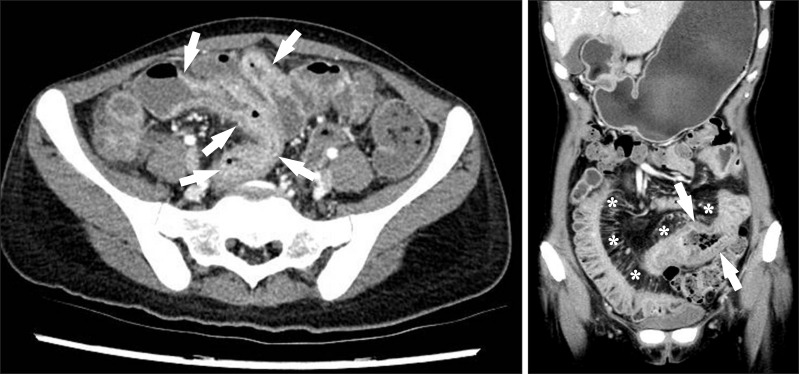
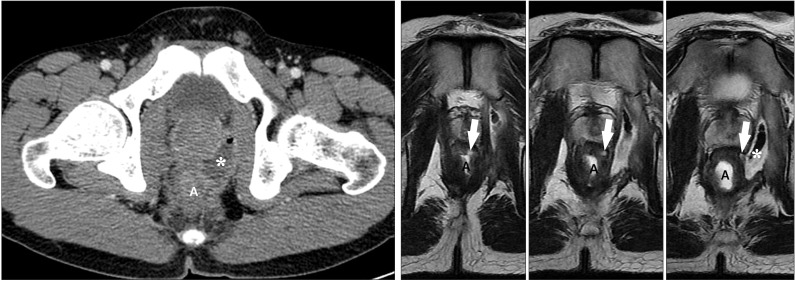
- Imaging of the small bowel is complicated by its length and its overlapping loops. Recently, however, the development of crosssectional imaging techniques, such as computed tomography enterography (CTE) and magnetic resonance enterography (MRE) has shifted fundamental paradigms in the diagnosis and management of patients with suspected or known Crohn's disease (CD). CTE and MRE are noninvasive imaging tests that involve the use of intraluminal oral and intravenous contrast agents to evaluate the small bowel. Here, we review recent advances in each cross-sectional imaging modality, their advantages and disadvantages, and their diagnostic performances in the evaluation of small bowel lesions in CD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Crohn’s disease at radiological imaging: focus on techniques and intestinal tract
Giuseppe Cicero, Silvio Mazziotti
Intest Res. 2021;19(4):365-378. doi: 10.5217/ir.2020.00097.Magnetic resonance enterography for the evaluation of the deep small intestine in Crohn's disease
Kazuo Ohtsuka, Kento Takenaka, Yoshio Kitazume, Toshimitsu Fujii, Katsuyoshi Matsuoka, Maiko Kimura, Takashi Nagaishi, Mamoru Watanabe
Intest Res. 2016;14(2):120-126. doi: 10.5217/ir.2016.14.2.120.
Reference
-
1. Raptopoulos V, Schwartz RK, McNicholas MM, Movson J, Pearlman J, Joffe N. Multiplanar helical CT enterography in patients with Crohn's disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 169:1545–1550. PMID: 9393162.
Article2. Paulsen SR, Huprich JE, Fletcher JG, et al. CT enterography as a diagnostic tool in evaluating small bowel disorders: review of clinical experience with over 700 cases. Radiographics. 2006; 26:641–657. PMID: 16702444.
Article3. Maglinte DD, Sandrasegaran K, Lappas JC. CT enteroclysis: techniques and applications. Radiol Clin North Am. 2007; 45:289–301. PMID: 17502218.4. Wold PB, Fletcher JG, Johnson CD, Sandborn WJ. Assessment of small bowel Crohn disease: noninvasive peroral CT enterography compared with other imaging methods and endoscopy--feasibility study. Radiology. 2003; 229:275–281. PMID: 12944602.
Article5. Negaard A, Sandvik L, Berstad AE, et al. MRI of the small bowel with oral contrast or nasojejunal intubation in Crohn's disease: randomized comparison of patient acceptance. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008; 43:44–51. PMID: 18158695.
Article6. Hara AK, Leighton JA, Heigh RI, et al. Crohn disease of the small bowel: preliminary comparison among CT enterography, capsule endoscopy, small-bowel follow-through, and ileoscopy. Radiology. 2006; 238:128–134. PMID: 16373764.
Article7. Huprich JE, Fletcher JG, Alexander JA, Fidler JL, Burton SS, Mc-Cullough CH. Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: evaluation with 64-section multiphase CT enterography--initial experience. Radiology. 2008; 246:562–571. PMID: 18227546.
Article8. Hakim FA, Alexander JA, Huprich JE, Grover M, Enders FT. CT-enterography may identify small bowel tumors not detected by capsule endoscopy: eight years experience at Mayo Clinic Rochester. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:2914–2919. PMID: 21735085.9. Hammer MR, Podberesky DJ, Dillman JR. Multidetector computed tomographic and magnetic resonance enterography in children: state of the art. Radiol Clin North Am. 2013; 51:615–636. PMID: 23830789.
Article10. Lee SS, Kim AY, Yang SK, et al. Crohn disease of the small bowel: comparison of CT enterography, MR enterography, and small-bowel follow-through as diagnostic techniques. Radiology. 2009; 251:751–761. PMID: 19276325.
Article11. Hara AK, Swartz PG. CT enterography of Crohn's disease. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:289–295. PMID: 18649092.
Article12. Bodily KD, Fletcher JG, Solem CA, et al. Crohn Disease: mural attenuation and thickness at contrast-enhanced CT Enterography--correlation with endoscopic and histologic findings of inflammation. Radiology. 2006; 238:505–516. PMID: 16436815.
Article13. Vogel J, da Luz Moreira A, Baker M, et al. CT enterography for Crohn disease: accurate preoperative diagnostic imaging. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007; 50:1761–1769. PMID: 17701255.14. Siddiki HA, Fidler JL, Fletcher JG, et al. Prospective comparison of state-of-the-art MR enterography and CT enterography in small-bowel Crohn's disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:113–121. PMID: 19542402.
Article15. Fletcher JG. CT enterography technique: theme and variations. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 34:283–288. PMID: 18551337.
Article16. Minordi LM, Vecchioli A, Mirk P, Bonomo L. CT enterography with polyethylene glycol solution vs CT enteroclysis in small bowel disease. Br J Radiol. 2011; 84:112–119. PMID: 20959377.
Article17. Berther R, Patak MA, Eckhardt B, Erturk SM, Zollikofer CL. Comparison of neutral oral contrast versus positive oral contrast medium in abdominal multidetector CT. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:1902–1909. PMID: 18414870.
Article18. Megibow AJ, Babb JS, Hecht EM, et al. Evaluation of bowel distention and bowel wall appearance by using neutral oral contrast agent for multi-detector row CT. Radiology. 2006; 238:87–95. PMID: 16293806.19. Maglinte DD, Sandrasegaran K, Lappas JC, Chiorean M. CT Enteroclysis. Radiology. 2007; 245:661–671. PMID: 18024448.
Article20. Vandenbroucke F, Mortele KJ, Tatli S, et al. Noninvasive multidetector computed tomography enterography in patients with small-bowel Crohn's disease: is a 40-second delay better than 70 seconds? Acta Radiol. 2007; 48:1052–1060. PMID: 17963078.
Article21. Kambadakone AR, Prakash P, Hahn PF, Sahani DV. Low-dose CT examinations in Crohn's disease: impact on image quality, diagnostic performance, and radiation dose. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:78–88. PMID: 20566800.
Article22. Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, Kujak JL, Lawder HJ, Pavlicek W. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:764–771. PMID: 19696291.
Article23. Ghetti C, Ortenzia O, Serreli G. CT iterative reconstruction in image space: a phantom study. Phys Med. 2012; 28:161–165. PMID: 21497530.24. Lee SJ, Park SH, Kim AY, et al. A prospective comparison of standard-dose CT enterography and 50% reduced-dose CT enterography with and without noise reduction for evaluating Crohn disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:50–57. PMID: 21701010.
Article25. Craig O, O'Neill S, O'Neill F, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography using lower doses of radiation for patients with Crohn's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:886–892. PMID: 22469992.
Article26. Kaza RK, Platt JF, Al-Hawary MM, Wasnik A, Liu PS, Pandya A. CT enterography at 80 kVp with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction versus at 120 kVp with standard reconstruction: image quality, diagnostic adequacy, and dose reduction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:1084–1092. PMID: 22528897.
Article27. Gee MS, Harisinghani MG. MRI in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 33:527–534. PMID: 21512607.
Article28. Ippolito D, Invernizzi F, Galimberti S, Panelli MR, Sironi S. MR enterography with polyethylene glycol as oral contrast medium in the follow-up of patients with Crohn disease: comparison with CT enterography. Abdom Imaging. 2010; 35:563–570. PMID: 19582502.29. Jensen MD, Kjeldsen J, Rafaelsen SR, Nathan T. Diagnostic accuracies of MR enterography and CT enterography in symptomatic Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:1449–1457. PMID: 21905974.
Article30. Gee MS, Nimkin K, Hsu M, et al. Prospective evaluation of MR enterography as the primary imaging modality for pediatric Crohn disease assessment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:224–231. PMID: 21701034.
Article31. Expert Panel on Gastrointestinal Imaging. American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria®: Crohn disease. 2011. 1–17. Available from: http://www.acr.org/~/media/ACR/Documents/AppCriteria/Diagnostic/CrohnDisease.pdf.32. Fidler JL, Guimaraes L, Einstein DM. MR imaging of the small bowel. Radiographics. 2009; 29:1811–1825. PMID: 19959523.
Article33. Oto A, Zhu F, Kulkarni K, Karczmar GS, Turner JR, Rubin D. Evaluation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for detection of bowel inflammation in patients with Crohn's disease. Acad Radiol. 2009; 16:597–603. PMID: 19282206.
Article34. Oto A, Kayhan A, Williams JT, et al. Active Crohn's disease in the small bowel: evaluation by diffusion weighted imaging and quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 33:615–624. PMID: 21563245.35. Yacoub JH, Oto A. New magnetic resonance imaging modalities for Crohn disease. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2014; 22:35–50. PMID: 24238131.
Article36. Ye BD, Yang SK, Shin SJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of Crohn's disease. Intest Res. 2012; 10:26–66.
Article37. Schwartz DA, Loftus EV Jr, Tremaine WJ, et al. The natural history of fistulizing Crohn's disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 2002; 122:875–880. PMID: 11910338.
Article38. Maconi G, Sampietro GM, Parente F, et al. Contrast radiology, computed tomography and ultrasonography in detecting internal fistulas and intra-abdominal abscesses in Crohn's disease: a prospective comparative study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:1545–1555. PMID: 12873576.
Article39. Prassopoulos P, Papanikolaou N, Grammatikakis J, Rousomoustakaki M, Maris T, Gourtsoyiannis N. MR enteroclysis imaging of Crohn disease. Radiographics. 2001; 21(Special Issue):S161–S172. PMID: 11598255.40. Maglinte DD, Gourtsoyiannis N, Rex D, Howard TJ, Kelvin FM. Classification of small bowel Crohn's subtypes based on multimodality imaging. Radiol Clin North Am. 2003; 41:285–303. PMID: 12659339.
Article41. Koh DM, Miao Y, Chinn RJ, et al. MR imaging evaluation of the activity of Crohn's disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 177:1325–1332. PMID: 11717076.
Article42. Solem CA, Loftus EV Jr, Fletcher JG, et al. Small-bowel imaging in Crohn's disease: a prospective, blinded, 4-way comparison trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:255–266. PMID: 18513722.
Article43. Masselli G, Casciani E, Polettini E, Gualdi G. Comparison of MR enteroclysis with MR enterography and conventional enteroclysis in patients with Crohn's disease. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:438–447. PMID: 17899102.
Article44. Gölder SK, Schreyer AG, Endlicher E, et al. Comparison of capsule endoscopy and magnetic resonance (MR) enteroclysis in suspected small bowel disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006; 21:97–104. PMID: 15846497.45. Fiorino G, Bonifacio C, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. Prospective comparison of computed tomography enterography and magnetic resonance enterography for assessment of disease activity and complications in ileocolonic Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:1073–1080. PMID: 21484958.
Article46. Jensen MD, Ormstrup T, Vagn-Hansen C, Ostergaard L, Rafaelsen SR. Interobserver and intermodality agreement for detection of small bowel Crohn's disease with MR enterography and CT enterography. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:1081–1088. PMID: 21484959.
Article47. Towbin AJ, Sullivan J, Denson LA, Wallihan DB, Podberesky DJ. CT and MR enterography in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease. Radiographics. 2013; 33:1843–1860. PMID: 24224581.
Article48. Koelbel G, Schmiedl U, Majer MC, et al. Diagnosis of fistulae and sinus tracts in patients with Crohn disease: value of MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152:999–1003. PMID: 2705359.
Article49. Essary B, Kim J, Anupindi S, Katz JA, Nimkin K. Pelvic MRI in children with Crohn disease and suspected perianal involvement. Pediatr Radiol. 2007; 37:201–208. PMID: 17180366.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Computed Tomography Enterography/Magnetic Resonance Enterography: Is It in Prime Time?
- Preparation, Technique, and Imaging of Computed Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Enterography
- A Look into the Small Bowel in Crohn's Disease
- Pediatric Magnetic Resonance Enterography: Focused on Crohn's Disease
- Magnetic resonance enterography for the evaluation of the deep small intestine in Crohn's disease